F-18 Bone Scintigraphy
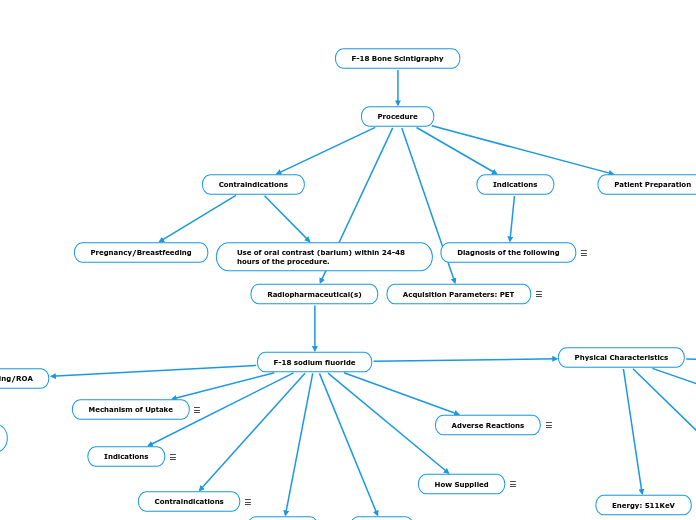
Procedure
Acquisition Parameters: PET
Camera Type: PET or PET/CT; Standard
Energy Peak: 511 KeV; Standard
Injection to Imaging time: 90-120 minutes; Standard
Attenuation correction: PET: cesium or germanium sources; PET/CT: CT acquisition.
Patient Position: Supine; Standard
Arm position: indication specific; Standard
Acquisition mode: 2-D or 3-D; Standard
Bed positions: Adequate to cover whole body or specific area of interest; Standard
Time/Bed positions: 2-D (2-5 minutes) 3-D (2-3 minutes)
View: Top of the head to the toes.
Radiopharmaceutical(s)
F-18 sodium fluoride
Dosing/ROA
Pediatric Dose:0.06 mCi/kg (minimum of 0.5mCi administered) I.V.
Adult Dose: 5mCi (5-10 mCi) I.V.
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F) in a shielded container; excursions permitted to 15–30°C (59–86°F).
Use the solution within 12 hours of the EOS reference time.
How Supplied
Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection is supplied in a multiple-dose Type I glass vial with elastomeric stopper and aluminum crimp seal containing between 370 and 7,400
MBq/mL (10–200 mCi/mL) of no carrier-added sodium fluoride F18, at the EOS reference time, in aqueous 0.9% sodium chloride solution. The total volume and total
radioactivity per vial are variable. Each vial is enclosed in a shielded container of appropriate thickness.
Adverse Reactions
No adverse reactions have been reported for Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection based on a review of the published literature, publicly available reference sources, and adverse drug reaction reporting systems.
Warnings
Allergic Reactions: As with any injectable drug product,
allergic reactions and anaphylaxis may occur. Emergency
resuscitation equipment and personnel should be immediately
available.
Cancer Risk: Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection may increase the risk of cancer. Use the smallest dose necessary for imaging and ensure safe handling to protect the patient and health care worker.
Pregnancy
Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection is a radioactive diagnostic agent for positron emission tomography (PET) indicated for imaging of bone to define areas of altered osteogenic activity
Mechanism of Uptake
Fluoride F18 ion normally accumulates in the skeleton in an even fashion, with greater
deposition in the axial skeleton (e.g. vertebrae and pelvis) than in the appendicular
skeleton and greater deposition in the bones around joints than in the shafts of long
bones.
Physical Characteristics
Half-life of 109.7 minutes
F18 decays by positron (β+) emission
Cyclotron Produced
Energy: 511KeV
Patient Preparation
- Patient may eat and take medications as necessary before the procedure.
- Obtain focused history and focus on the following:
A.Clinical indication for the study, including current symptoms.
B.History of fractures, trauma, and associated bone abnormalities.
C. History of current or previous therapeutic protocols that may affect the bone scan.
D.History of surgical procedures that may affect the bone scan.
E.Review of current medications that may affect the distribution of the tracer.
F. Confirmation of pregnancy status and/or lactation.
Indications
Diagnosis of the following
- Neoplastic disease
- Occult fracture
- Stress reaction/stress fracture
- Avascular necrosis
- Arthritis
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
- Bone infarcts
- Bone graft viability
- Paget's disease
- Unexplained bone pain
Contraindications
Use of oral contrast (barium) within 24-48 hours of the procedure.
Pregnancy/Breastfeeding