por Nightcore Adrenaline 4 anos atrás
265
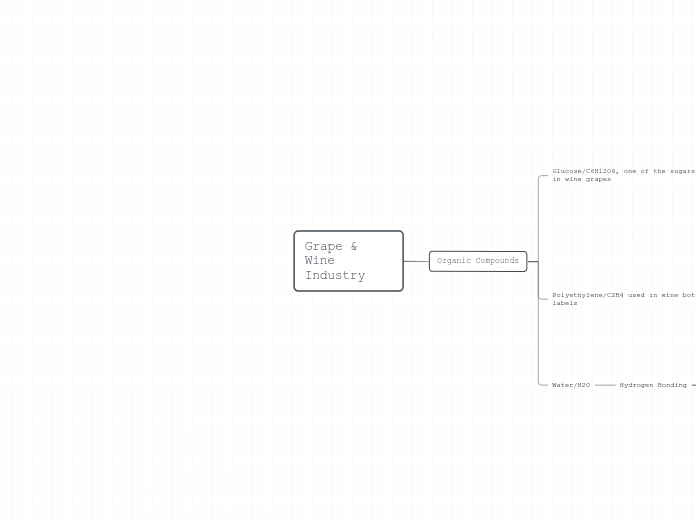
Grape & Wine Industry
por Nightcore Adrenaline 4 anos atrás
265

Mais informações
Strongest intermolecular force
Only in a bond between hydrogen, and fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. Creating an extremely strong dipole because of extremely high electronegativity.
Bonds with non-polar end of emulsifiers
Weaker intermolecular forces therefore lower boiling and melting point
Weak intermolecular forces because nonpolar molecules only have London forces (weakest intermolecular force) therefore liquid at room temp.
Soluble w/ other nonpolar molecules, therefore not soluble in water
Bonds with polar end of emulsifiers
Stronger intermolecular forces therefore higher boiling and melting point
Stronger intermolecular forces between the solute and solvent molecule, the greater the solubility
Strong intermolecular forces because of dipole force therefore solid at room temp.
Soluble w/ other polar molecules, therefore soluble in water