History 3rd Year
1916 Rising
Impact
Rise of Sinn Féin
German Plot
English accuse leades of sinn Féin of starting a plot with Germany
This turnded people against britain and vote for Sinn Féin.
They start arresting the leaders of Sinn Féin.
Women were allowed to vote.
Devalara and Collins joined Sinn Féin.
Griffith later stepped down and Develara became president.
Arthur Giffith was the man who founded Sinn Féin.
Sinn Féin 1st wanted home rule by peacful means but this soon changed.
Everyone thought Sinn Féin was responsible for the rising
Prime minsister Asquith ordered maxwell to stop.
The Public were not happy with British killing men.
Martial law and Curfew was too long and turned people against british.
Dublin citty had massive damages.
3.500 people arrested.
90 of those people were sentenced to death
15 that sighned proculamation.
Sent to a prison called Frongoch in Wales.
It was a former prisoner of war camp.
1,800 people sent to prison in England.
Put in prison without trial..
Genral Maxwell
He arrests a lot of innocent people
This turns public opinion.
Ordered the arrest of more than 3,400 men and 79 women.
These were suspected to be involved in the rising.
During the rising
Battle of Mount Street.
Succesful for Irish.
The Helga
Instead they started lobbing shels over to the GPO.
A British gunboat which could not go under the bridge.
General Lowe
He was the one Pierse had to surrender to.
In charge of troops in Dublin
Problems
Trinity collegee was barriciated.
They failed to take Dublin castle.
They never took over railway stations
Main Buildings
7- Boland's mill.
6- College of surgeons.
5- Jacobs Factory
4-South Dublin Union.
3-Mendicity Institutiom
2-Four Courts
1-GPO
Start of the 1916 rising.
Plan goes ahead
Less than 5,000 men in the rising.
Mac Donagh wrote a letter saying it was going ahead anyway.
Macneill calls it off.
Because...
10,000 men were lost for the rising.
The castle document
The Aud didnt deliver the guns.
The Aud
It was then purposely sank and the German captain was imprisoned.
It was too risky to stay.
Supposed to land in Fenit.
20,000 rifles.
Roger Casement
Hanged in England
He got guns off germany
Orginised the Aud.
Worked as a diplimat.
Born in Dublin
Arms never reached the Volenteers
The Military Councical of the IRB.
The people involved were Padraig Pearse, Eamonn Ceannt, Joseph Plunkett and Séan mac Diarmada.
They planned the 1916 rising.
Its main task was to plan and carry out the rebellion.
A group within the IRB (Irish Republican Brotherhood.)
Background
Dublin slums
Their was a high rate of diseases.
Tuberculosis (TB) It spread through tenants very quickly.
Infant mortality rate was very low.
Died after 1st year.
1/3 of dublins population lived in slums.
The Lockout
James Connelly formed Irish Citizens Army (ICA).
workers were brought in to work from England.
These were called BlackLeg Labourers.
William Murphy got angry and said anyone who was part of a union could not work.
20,000 workers went on strike.
ITGWU-Irish Transport and General Workers Union
James Larkin was leaader
Holocaust
Life as a Jew
World war 2
Impacts
Short Term Impacts
War crime trials
Refugees
Destruction
Economic revival
Death
Long Term Impacts
United nations
Toward european unity
End of european supermacy
Growth of superpowers
Fate of Japan
Fate of Germany
Course of the war
The turning point in the war for the allies:
War of the Pacific
Atomic Bombs
Hiroshima
Nagisaki
Okiwawa
Iwojima
Leyte Gulf
Guada canal
Battle of Mid-way
Battle of Coral sea
Pearl Harbour
Dresden 1945
Battle of the bulge
The Battle of the Atlantic (The war at sea)
The alllies defeated the U-Boat threat by:
Use of ultra, code-breaking operation, which provided information to direct convoys away from the paths of wolfpacks.
Use of air reconnaissance, radar, sonar and depth charges.
Increased shipbuilding
Germany used submarines (U boats) to sink aillied shipping. Fleets of U boats called wolfpacks left the french and norwegian coasts and raided the allied conveys crossing the sea.
In the words of american president Roosevelt America became the "Arsenal of democracy".
America supplied Britain with supplies of food, military goods and industrial products to britain.
D-Day Landings
Omaha, Utah, Gold, Juno and Sword were the beaches
They invaded on 5 beaches.
They dropped Para-troopers
Eisenhower was the commander
America joined the war
Soon after hittler declared war on america.
Japan attacked pearl harbour
Battle of Kurst
Germans loose
Largest tank battle in the war
Operation Citadel
Battle of Stalingrad (Major turning point in Operation Barborossa)
The german army suffered greatly due to the russians attacking them in a pincer movement from both sides.
Stalin insisted the city must not be lost.
The german army led by Von Paulus fought vicious street battles.
Their advance was stop due to the battle.
Hittlers armies advanced toward stalingrad, this was a key place for hittler as it had the oil fields of caucasus.
Operation Barbarossa (Invasion of Soveit Russia)
The soveit army soon began to retreat.
He targeted these attacks towards large soveit cities such as Leningrad, Moscow and Kiev.
He used blitzkrieg tactics in a three- pronged attack
The attack on russia was called operation barbarossa.
Hittler wanted to create lebensraum in eastern europe for the third reich.
Soveit russia was hittlers biggest enemy
The Great Patriotic War
The russians counter attacked in December.
The germans captured kiev but failed to capture the other two cities.
Hittlers early progress was paused due to russian winter
The low temperatures reached up to -40 degrees.
The rainy season made it very hard for the germans to fight back.
Many soldiers froze to death.
Lorrries tanks and aeroplains seized up and tough weather conditions made it hard for soldiers to fight.
As the russians reatreated they used a scorched earth policy.
Such as food and crops.
This meaned they burned many things around them as they retreated.
He also prepared for the war by moving heavy industry east of the ural mountains.
They produced T-34 and Katyusha rocket launchers.
Stalin Called Russians to fight the great patriotic war against germany.
The desert war in north africa.
Battle of El Alamein
This was one major turning point in the war.
Battle of El Alamien the british army led by montgomery defeated rommel.
Hittler wanted tocapture the suaz canal.
Hittler sent Erwin Rommel and his troops to help the italians.
However mussolinios army based in libya was defeated by the british troops based in eygpt.
Mussolini's italian army joined the war by invading southern france in effort to help the germans
The Blitz
America helped britain under the leadership of President Roosevelt.
Britain survived the battle of britain and the blitz.
some people evacuted to the countryside.
Cities such as london, coventry, liverpool and glasgow were attacked regularly during the night.
German planes continued to bomb british cities during the blitz.
Battle of Britain
this was hittlers first defeat.
Hittler then posponed ivasion of britain as he realized they were loosing
British used radar to detect on coming german planes.
British spitfires and hurricanes matched the german messershmitts and heinkels.
Next they switched their attack to airfields and radar stations.Germans attacked britain daily.
Luftwaffe attacked shipping in the english channel
Operation Sealion and Battle of Britain.
He started the battle of britain between the british royal airforce and the german Luftwaffe.
Hittler prepared invasion of britain called operation sealion.
Chruchill replaced chamberlain as prime minister
Invasion of France
France was divided into vichy france and and German teritory.
Hittler got in by making a diversion at the top of Belguim then went through the bottom of belguim.
He defeated many troops and pushed them back to Dunkirk
Hittler also used Blitzkrieg tactics in France.
Weser Crossing
Paratroopers were also droped
These were troops who jumped out of a plane with parachutes.
Germans landed on ports along Norway and Denmark.
Hittler invaded here to ensure the German iron ore supply.
April 1940
Invasion of Denmark and Norway
Phoney war.
Nothing happens until may.
Blitzkrieg
Fast atacks to cause shock.
Lightning war
Invasion of Poland
Hittler used this as an excuse and invaded poland.
The German SS dressed in polish army uniforms and attacked a german radio station
5 Steps towards war
5- Phoney war
4- Poland
3-1938- the sudetenland
2- March- Austria- Anschluss (unity.)
1- 1936- march the rhineland
The Drift War
The Causes of World war 2
The Munich Conference 1938
6 Months later hittler took the rest of Czechslovakia.
They agreed that Czech must hand over Sudenland to Germany.
The Czech government was excluded.
Leaders from a couple of countries met with hittler.
Hittler wanted to claim back the german speaking area of Czechslovakia (The Sudenland).
The Gerrmans did not like the terms of the treaty.
Japanese Aggresion
this brought america into world war 2
Japan Bombed pearl harbour
America imposed economic sanctions
This brought japan into conflict with america.
LEague of nations also failed to stop japan.
Japan expanded into china.
American Isolation
America were by themselves as they were not in the league of nations.
Nazi-Soviet Pact
This ment stallion could prepare for a future war
they also agreed to split Poland
They agreed toa 10 year non- agression pact
Nazis and communists were bitter enimies
Policy of Appeasment
Hittler began to demand more.
However hittler saw this as their weakness.
Britain and france believed if they gave into hittlers demands it would prevent war.
Weakness of the league of Nations
The eleague had many weaknesses
Had to rely on economic sanctions
No army
Decision had to be unanimous so it was difficult to make decisions.
America did not join
The league wanted to achieve peace
Hittlers Actions
He united Germany and Austria in 1938.
He sent an army into Rhineland
He began to re- enforce the a army this broke the treaty of versailles.
Hittlers Aims
Lebensraum- living space for extra Germans
Abolition of treaty of Versailles
To expand and form a Greater Germany
The Troubles in Northern Ireland
Impacts of the troubles
The impact of anglo- irish relations.
the four agreements helped improve these relations.
the impact of the troubles on the north-south relations
Good Friday agreement.
Downing street declaration
Sunningdale agreement
change in government policy in 1970s
Huge tension inbetween north and south.
Economic consequences of the troubles
dependance on state welfare bonuses (Dole).
Significant rise in unemployment.
Greater poverty in northern ireland compared to the rest of britain.
High unemployment among youth.
Belfast city centre loosing business
Foreign firms did not want to set up factories
Businesses wrecked by bombing.
politacal consequences of the troubles
Irish government have greater say in irish affairs.
Unionists forced to share power with nationalists.
Destruction during troubles
Bridges and border crossings destroyed.
Destruction in belfast and other major towns.
16,000 bombings.
Deaths during troubles
Most Deaths in Belfast.
Over 3.5k people died.
Attemps at peace.
4- 1998 Good Friday Agreement
Voilence Continues it was partcially sucessful.
They agreed on Sharing power, PSNI (Police service of northern ireland.) replace RUC, will be united ireland if it is voted, Paramilitaries must give up their weapons.
John Hume (SDLP) and David Trimble (Ulster Unionist)
3- Downing street declaration
It happened in 1993
Allowed the people of NI and Ireland to determine their own future and solve problems by mutual consent. (Vote)
2- Hillsbrough Agreement
They would consult at an Inter-governmental conference.
they agreed that the north and south would agree on security matters.
PM Margret Thatcher and Taoiseach Garret Fitzgerald.
1- Sunningdale agreement.
Opposition to agreement- Ian Paisley and the unionists are not happy and shut northern ireland down.
Unionists party (Faulkner) and SDLP (Gerry Fitt) formed a government.
Agreement had a cross- border council of ireland.
Proposed governmet sharing for northern ireland.
Course of troubles
Bloody Friday
11 People were killed.
IRA set off 20 bombs
Forensic evidence also showed that none of them fired a gun that day.
13 People were killed, none of whom were susequently found been armed.
Basil Brooke (prime minister)
He said to employers that they would be a disgrace to northern ireland if they employed catholics.
Born into a weaalthy protestant family
IRA and border campaign
Ira from south began to attack british army barracks this is known as Border campaign.
Fergal o'hanlon and sean south killed.
1929 Wall street crash
Poverty increased due to due to the aforemention
Discrimination against catholics continued
The world economy declined and unemployment increased.
The IRA
The SDLP
Its first leader was Gerry Fitt.
It brought together different nationalist groups and became the largest nationalist party.
Social Democratic and Labour Party.
British troops
The british government sent in troopes to protect the people of bogside.
The troubles escalate
Major voilence was sparked off by the protestant apprentice boys marching in derry.
This was known as the battle of the bogside.
This march led to a clash with the catholics/nationalists of the bogside in derry.
Voilence increased from 1969 onwaards.
North-South relations
Irish government believed the particions was the cause of these troubles.
The RUC and loyalist paramiliteries began to attack catholic ghettos.
However in the late 60s tension grow
Relations between north and south improved during 1960s
The day the troubles began
A civil rights march in Derry was stopped by the RUC
Course of Troubles.
1971- Interment introsuced.
1970- july- falls road curfew.
August 1969
16th- British Embassy attacked in Dublin
15th- Burning of bombay street.
14th- deployment of british troops
12th- Battle of Bogside
Belfast- Peoples democracy March or the derry march, 1st January, 1969- Burntollet bridge.
5th October 1968- Duke street protest- start of troubles.
June 1968- Caledon Protest
1867- NICRA Founded.
Conn and Patricia McCluskey founded the Homeless citizens league.
Causes of the troubles
Internment
They could be put in jail without trial.
Putting people in jail on suspicion of being part of the IRA.
Civil rights and beginning of the troubles.
Catholics and nationalists in the north set up (NICRA) Northern Ireland Civil Rights Association.
Its leaders were- Gerry Fitt, John Hume, Austin Currie and Bernadette Devlin.
NICRA's demands
"End to discrimination in housing and jobs"
"End to gerrymandering"
"One man one vote"
Gerrymandering was when the unionists rigged the votes so the Catholics elected unionists in local elections.
Consituencies were divided so protestants got more votes every time.
The Welfare State
A new better generation of catholics which would not put up with discrimination.
Free secondary education which benefited catholics.
A free health service increased.
Old age pensions and social welfare benefits increased.
Protestant-catholic tension
Voting rights
housing
employment
education system
Divided loyalties
Protestant vs catholics
Segregation is when the nationalist and unionist communities did not mix.
Sectarianism is to dislike someone because of their religion.
Internment is people could be arrested if they were suspected of republican activities and their house could be searched without a warrant.
The special powers act was passed in 1921.
this gave power to secuirty forces.
Covernment of ireland act 1920
the northern ireland governenment formed an armed police force called the royal ulster constabulary. (RUC)
Unionists set up their own parliment at stormont
Opened by king Henry
Ireland is partitioned
What were the troubles?
The nationalists wanted more civil rights and the unionists said "no" because they didnt want the nationalists to gain power.
The troubles refers to a conflict which occurred in northern Ireland from the late 1960s to 1998, it involved unionists and nationalists.
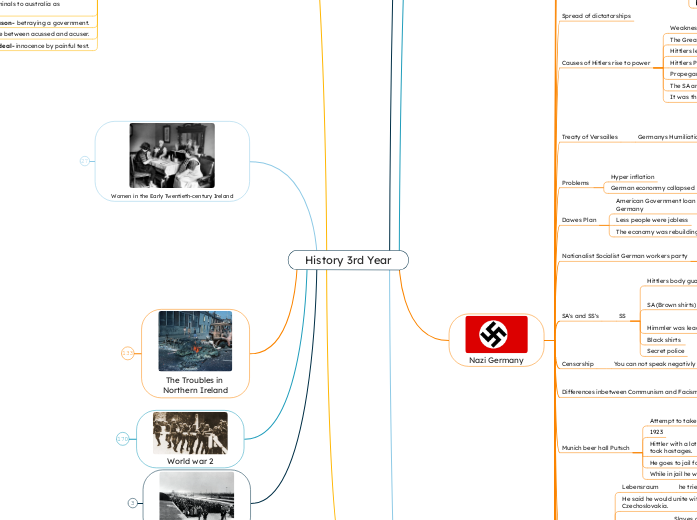
Women in the Early Twentieth-century Ireland
Women in the independance movement
After independance women over 21 could vote.
Countess Markievicz became first women to be elected to parliament. she did not take her seat.
Women play important role in independance mvement
Women and politics
women over 30 got the vote in 1918.
influence of ww1 on votes for women
opposed by Redmond and Carson
Hanna Sheehy-Skeffington founded Irish womens franchise league
Suffragette campaign
could not be elected to parliament
Women could not vote
Women in education
Opened up new careers.
Major change from 1960s onwards
Limited education in early 1900s
changes from 1960s onwards.
smaller proportion of women managers and senior executives.
many women worked part-time
limit size of family.
married women held onto jobs
More women work outside the home
Second class citizens
Limited education.
Expected to marry and have children.
Could not vote in general elctions.
Dependant on husbands, the breadwinners.
Crime and Punishment in the 19th Century
Key Words
Trial by ordeal- innocence by painful test.
Trial by combat- Battle between acussed and acuser.
Treason- betraying a government.
transportation- Sending criminals to australia as punishment.
Terrorism- use of voilence to achieve political aims
Stocks- legs locked in place.
Silent system- can't talk to people
Seperate system- everyone in differen tcells
Sarictury- protection in a safe place, usually a church.(Midieval times)
Pilory- Your head locked in place.
Maginstrate- A judge
Hue and cry- chasing a suspected criminal with loud shouts for help
Deterrent- Punishment to discourage people from commiting crime
Capital offence- the legal killing of someone as a punishment of crime
Changes within prisons
Hulks were former naval ships put next to ports for extra prisoners tha were working in the docks.
Hard labour within a prison
The crank
A large handle which people had to turn.
The treadwheel
Some prisons it made flour.
Like walking on a treadmill.
Why was it introduced?
to stop people from getting up to mischieve.
teach them value of hard work
cheap labour
Different systems
Seperate system
By themselves in their own cell
Silent system
they were not alowed to talk to anyone. You did your hard labour in silence.
Hard labour
they had to carry out work such as on a quarry or on roads.
Peels Gaols act 1823
Seperated by gender
They weren't chained up
What were the punishments?
Transportation
They were transported to australia to do free labour for there punishment (For 7 years).
They began to use punisment to improve an offender.
Executions was too severe for many crimes. the bloody code was ended.
Public hangings seen as a deterrent to crime.
Who enforced the law?
Robert Peel introduced the 1st police force they were called "Peelers". (1829)
The bloody code
More executions and 200 offences resulted in death penalty.
Ex, sheep stealing you would be hanged.
Factors influencing crime and punishment
Public opinions
people wanted more punishments
People wanted more policing
Growth of cities and towns
more oppertunities to commit crimes
People unknown to each other
Rising expectations
Advertising created expectations
People wanted tvs household appliances and cars
Economic changes
Greater gap betwween rich and poor.
Social changes and divisions
Conflict between different groups in society.
Life in Nazi Germany
Life For Workers
Hittler planned to conquer eastern europe to obtain lebensraum for workers and more raw materials.
Hittler encouraged the manufacure and design of volkswagon so everyone in the futurr ewould be able to afford a car.
The Nazis also set up:
Beauty of Labour
To improve working conditions such as better lighting and canteen food.
Strength through Joy
An orginisation to orginise leisure activities for the workers.
Rearament also provided employment this was the building of arms and vechiles for german armed forces.
He provided work through public work schemes which they build motorways (Autobahns) and housing.
He began to try to eliminate unemployment.
Hittler promised employment for everyone when he got in power.
Life For Christians
The Nazis made it difficult for christians to practice their religion.
A prodestant leader, pastor Martin Niemoller was sent to a concentration camp in 1937.
Hittler set up a prodestant national church.
Most prodestants did not agree with it.
Prodestants were also attacked.
Pope Pius XI responded be criticising the nazis in a famous statement, 'With burning anxiety'
Catholic schools were closed
Priests were harrased
He viewed the catholic community as owing loyalty to another leader, the Pope.
Many christian churches were attacked.
Life for Jews in Nazi Germany
The Nuremberg Laws were passed in 1935
"For the promotion of german blood and honour".
Jews were banned from civil services.
Many German businesses were boycotted in 1933.
Gobbels used many forms of propaganda to icrease racist feelings against jews in Germany.
Hittler was very anti-semistic.
He used the governments power to prossucate them.
Nazi organisations used to harass Jews.
Jewish children were badly treated in schools, newspapers spread stories and propaganda about jews.
They said Jews (and others) were inferior.
Germans believed that they were pure blooded- aryan race or master race (Hettrnvolk).
Life for women in nazi germany
Nazis wanted to increase birth rate.
Nazis also provided maternity benefits to increase birth rates.
Family allowences and medals for mothers with big families.
they made mariage loans.
the future wife must also give up her job
Law for reduction of unemployment 1933
the wife must have spent at least 6 months in employment.
Germans who got married recieved a loan of up to 1,000 reichmarks.
Mother schools were made which trained women how to do housework.
The name for nazi ideal women was KINDER, KUCHE, KIRCHE (Children, kitchen, church)
Nazis promoted the ideal role for women as Mothers
Life as a Young person in Nazi Germany
In education loyalty to the Fuhrer (Hittler) was taught from kindergarden to university.
Life under Nazi Propaganda
Even the 1936 Olympic games in Berlin were used as propaganda
The Nuremberg rallies and torchlight parades were used as propaganda.
Hittler was glorified
He provided cheap radios and loudspeakers along streets to ensure people could hear all the speaches.
Gobbrels was minister for national enlightenment and propaganda.
Night of the broken Glass
Hittler made the jewish community pay for all the damages.
Roughly 90 Jews were killed and others were arrested and sent to concentration camps.
On the 10th of november 1938 (The night of the broken glass) Jewish shops and synagogues were attacked.
This was an excuse for a night of violence against many Jews.
When a Jew killed a German diplomat in Paris.
Nazi Germany
Einsthazgrupppan
killed a lot of jews
Nazi death squad
HJ
Hittler Youth
Gestapo
Secret Police
Led by Himmler
WehrMacht
German army
Hittler and SA
Night of the Long knifes is when the leaders of SA were eliminated.
Ernst Rohm was head of SA.
He wanteed SA to become official army
What Happend to Opposition?
Concentration camps were set up
The 1st camp was set up in Dachau.
The camps were established soon after hittler came to power.
A work camp
The Gestapo could arrest prisoners without trial.
1929 Wall Crash
America pulled loans out of Germany.
the great depression in USA
Hittlers becomes in power
Reichstag Fire
SS and Gestapo
Gestapo were secret police.
SS Private Army
Rule by decree
Banned all other political powers
Due to enabling act Hittler became dictator..
Enabling Act
Parliament bulidings set on fire
Dutch Communist arrested for burning riechstag
4,000 communists were arrested
Germany was in a bad economical state
In 1933 Hittler becomes chancellor
Hittlers Promises
End weak democracy.
Lebenstrawm
Living space for germans
Get rid of jews
Reverse treaty of Verrsailles
To be proud again
Jobs
Stability
Hittlers Propaganda
He was a powerful speaker
He kept his messaages simple
Rise of Nazi party
Hittler gets 107 seats in the 1930 election
People vote for communism or nazi party
President Paul Von Hindenburg
Hittler looses support.
Keeps Hittler in check
Was a War hero
Hittlers Ideas
He gained widespread popularity.
Germany should be ruled by a Fuhrer.
Germany should take what it laks from others
Herrenvolk
Master race was Germany
Slaves and jews were subhuman.
He said he would unite with austria and take over Czechoslovakia.
Lebensraum
he tries to make a living space for Germans.
Munich beer hall Putsch
While in jail he writes a book called Mein Kampf
He goes to jail for 5 years.
Hittler with a lot of men ran into a beer hall wih a gun and took hostages.
1923
Attempt to take power.
Differences inbetween Communism and Facism.
Dictatorship
You were allowed privaterly owned companies
Communsim
Private owned companies were not allowed, the wealth would be shared among the people (State controlled)
Censorship
You can not speak negativly about the government.
SA's and SS's
SS
Secret police
Black shirts
Himmler was leader
SA (Brown shirts)
Ernst Rohm was incharge of the SA's
Set up by nazis
Known as 'storm troopers'.
Hittlers body guards
Nationalist Socialist German workers party
Facist, racisist, nationalists.
The SWASTIKA was the symbol
Nazi Party
Dawes Plan
The economy was rebuilding
Less people were jobless
American Government loan Roughly $200 million to Germany
Problems
German econonmy collapsed
Hyper inflation
Treaty of Versailles
Germanys Humiliation
They were forbidden to join the league of nations or unite with Austria.
Germany lost a lot of territary to England and France
they were only allowed 100,000 in their army.
They had to pay £6,600 million in compensation
Germany accept blame for war
Causes of Hitlers rise to power
It was the largest party
The SA and SS (SS black ) SA (Brown)
Propeganda
Hittlers Policies
Hittlers leadership of the Nazis
The Great Depression
Economic crisis.
Weakness of Wellmar republic
Spread of dictatorships
Who were the Nazis?
Adolf Hitler
Leader of Nazi party
Hermann Goering
Chief of the Luttwaffe (German airforce)
Heinrich Himmler
Head of SS
Joseph Goebbels
Responsible for probeganda
Facism
Strong opposition to communisim and socialism.
Hostile to democracy
Racism
Cult of wise leader
Extreme Nationalism
The Treaty/Civil War
Main Events of the Civil War
7th March 1923, 5 Republician
6th March 1923, Daly, one of Collins squad, kills 9 Republician prisoners in Tralee, one managed to survive, The BallySeedy Massacre.
5th March 1923, 5 free-state men blown up by a trap while clearing a road.
Sean Hales TD, shot in December 1922 while coming out of mass.
WT Cosgrave became head of state.
Faced execution if you were found with weapons.
Passes a law Called the Public Safety Bill
Collins dies in Béal na mBlath on 22nd August 1922, it was an Ambush.
Arthur Griffith dies on 12th August 1922 from a brain haemorrhage.
Munnster Republic
Free state had 60,000 people now, they took over Cork City.
Republicians went south of a line from Limerick to Waterford.
Cathal Brugha is killed during fighting in O' Connells street, irregulars/Republicians were driven out of Dublin in a week.
28th June 1922, Collins ordered the attack in four courts.
Sir Henry Wilson, was shot on 22nd June 1922 in Londn, Important field marshall.
This caused civil War.
British gave Collins a choice, sort out the four courts, or Britain will put forces back into Ireland.
1922
Men who fighted in the war were violently against the treaty.
Dáil votes
De Valera walks out and resigns.
7 votes change the result
1921
Anti Treaty.
Oath of allegiance.
Pro Treaty
Stepping stone to full independance.
Irish wouldnt beat britain
Better than home rule
Reaction of treaty
De Valera refused to accept treaty
Terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty
De Valera Got the ports back just before WW2.
Governer Genral could overule any law from Dáil
British navy controlled 3 ports.
Lough Swillly County Donegal.
Berehaven in West Cork.
Cobh Spike Island
Boundry Commision
To set up boundry inbetween Irish Free state and britain.
The TDs would have to swear an OATH OF ALLEGIANCE.
Still part of British Empire.
We were allowed to have our own flag, army, stamps, passports and currency and all foreign change.
Dominion to British Commonwealth.
26 counties were called irish free state.
British Delegation
Lloyd george put Irish Delegation under huge Pressure and threatened immiatiade and terrible war.
Lloyd George, Austen Chamberlain, Lord Birkenhead and Wintson Churchill.
The Irish Delegation
The delagation were told then they could not actually sign anything.
Plenipotentiaries
They could sign on behalf of Dáil.
Collins and Griffith went.
Militants like Brugha and Stack refused to go.
De Valera said he would not go.
Delegates had to return to him so they did not sign under pressure.
He could control militants at home.
July to October.
They knew they were not going to get a united Ireland.
De Valera and Lloyd george still wrote letters
July meetings.
There was no Agreement.
De Valera wanted Full Indepenndance
Dominion status -King would be in charge.
De Valera knew they were not getting a united Ireland
Lloyd George made it clear they were Offering Dominion Status.
There was meeting inbetween De Valera and Lloyd George
The group of negeotiators were De Valera, Arthur Griffith, Austin Stack and Erskine Childers.
Irish negoetiations started in london on 12th july 1921.
A truce was called.
Irish Side
IRA ran out of bullets.
Economic collapse
They had no money.
Martial law was making it hard for civilians.
British were gaining upper hand in some places.
British Side
King George V was being emmbaresed.
England were poor after WW1
It would be a huge political cost
Other countries were getting angry.
They would need a lot more troops.
It would be huge financial cost
1920
Conflict between unionists and Nationalists.
Many catholics lost jobs.
Many chatholics killed
Sectarian riots.
Special powers act
RUC- Royal Ulster Constabulary was set up.
Catholics were put in jail with out trial
This is called interment.
Unionists oppose United Ireland
War Of Independance
Devalera meets with Lloyd George.
Peace
British Government.
It caused embarresment.
Sinn Féin
The people wanted peace
IRA running short on ammunition
Major Incidents of the war of Independance.
Truce Called in 1921
IRA attack on the custom house in Dublin.
Over 80 IRA men were captured.
IRA started burning it.
De Valera Decides to attack customs house.
Collins was against it.
Ambush at Crossbarry.
1,300 troops encircled the IRA
But the British had the most Casualities.
One of the largest engagement of the war of independance.
1920 Government of Ireland Act.
Ireland was split.
The Counties Britain would have were (FATDAD).
Down
Armagh
Derry
Tyrone
Antrim
Fermanagh
Burning of Cork City
Pictures made news and Irish Diaspora were very angry.
The king was very angry.
They embarresed British Government
The Black and tans angry and retalliated by burning down Cork City Centre.
They were not caught
IRA outside Barracks and attempt Ambush
Kilmichael Ambush
Subtopic
1 Week after bloody Sunday.
This soon made international news.
They stopped the convey and killed 17 people.
Tom Barry planned ambush
The Auxilliers were brutall to west Cork Natives.
Bloody Sunday
This was very Bad publicity for the British Empire.
The King was getting very angry as it was making people turn on Britain.
Dick Mckee and Peader Clancy were arrested.
they left coffins open so people walking past saw what happened
Their bodies were mutilated
They were shot trying to escape.
Black and tans open fired on Croke park.
And shot 26 people.
Collins finds the British intelligences adresses
And the squad kill 12 of them.
Kevin Barry
Even The Pope got ivolved and asked British not to Hang Kevin Barry.
This angered many Irish Diaspora.
Put Pressure on British empire.
He was only 18 and hanged.
Collins was going to break him out but there was Women outside praying so he didnt because there would be too many deaths.
He was arrested and sentenced to death.
Terence MacSwiney.
His hunger strike took so long that it made the British empire look very bad.
It put a lot of pressure on British government.
Dies due to hunger strike in Brixton Prison, London, after 74 days.
The new Lord Mayor of Cork after MacCurtin.
RUC Kill Tomás MacCurtain
They shot him on front of his own family.
Lord mayor of Cork.
The Auxilleries
They were vicouis and were involved in burning of Cork City
Black and Tans
Over 13,000 black and tans come to Ireland.
Former solidiers brought in by government to help RUC.
Irish republican army.
Dan Breen and Sean Treacy killed two members of the RIC when police refused to surrender a consigment of gelignite they were guarding near Soloheadbeg, Co. Tipperary.
Collins and Brugha did not get along.
Cathal Brugha was the minister for Defence.
Collins was minister for finance.
They used Geurilla warfare.
De Valera was in america raising money during the fighting.
Eamonn de Valara was president of Dáil and the IRA.
British response
He recruited the Black and Tans.
David lloyd George prime minister