benefit economies
and the environment
innovation
global effort
place less importance
on economic growth
importance on finite
resources
Cities consume 75%
of global resources
Cost to municipality
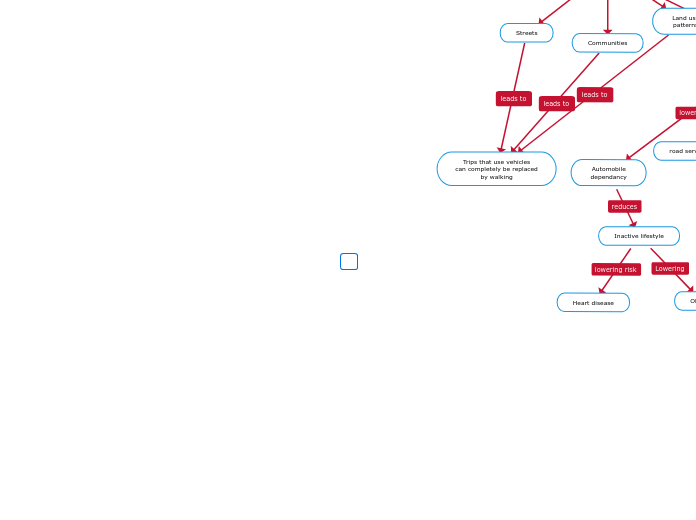
Automobile
dependancy
Inactive lifestyle
Obesity
Heart disease
Transit
servicing
road servicing
Trips that use vehicles
can completely be replaced
by walking
How can Mississauga transition
to a more sustainable city using
environmental-economy approaches?
Dependance on
non-renewable resources
Small scale
hydro
to install in
many places
can provide energy
in remote areas
Power distribution
GHG emissions
or waste while
generating electricity
cost-effective
Bioenergy
Chemical energy produced
from biomass
Forest, wood, and
mill residue
Agriculture crops and
waste, plants, fast growing
trees, and aquatic plants
Livestock residue and animal
waste
utilizes waste
Solar
So public is encouraged
to implement
No production of
pollution of GHG
emissions
free
Unlimited
Wind
be installed in
a variety of ways
and at a variety of
scales
Cost-effective
and reliable
for individual,
community, and
national use
Carbon Emissions
Hybrid
vehicles
Electric
vehicles
Public
transportation
Transit-oriented
development policies
24 hour
operations
transit
capacity
City to be
more walking
friendly
Land use
patterns
Communities
Streets
Only supports 11%
of population
Waste generation
Circular
economy
value driven
consumption
purpose driven
consumption
Resource
efficiency
raw material
inputs
Finite resources
waste
products/components/
materials in the economy
for as long as possible
Environmentally
friendly incinerators
Smoke converted
to steam
Carbon capture
system
Steam power
generation
Education on
proper disposal methods
Rates of compostables
going into landfills
Rates of recyclables
going into landfills
garbage sorting
centre for the city
Mississauga produces
500 000 tonnes of waste
annually
Rising costs
to the city
transportation
of waste to other
landfills
More pollution
degradation
of land
less crops for
trade and food
existing ecosystem
not enough space
to store waste
Eco fees on
products rise
More steps
in disposal
Resource Consumption
Automobile
consumption
Electricity
Usage
City-wide
implementation
Metering and
sub-metering
equipment
Pool heat recovery
Energy Management
information systems
Set goal of 1%
decrease per year
Water
Usage
Rain water
harvesting systems
Densly populated
residential areas
Industrial areas
Shorter
showers
Large impact
if everyone implements
Toilets and showers
use 40% of indoor water
Water-smart
landscaping
Residential areas
Greywater
system
Innovation
3D Printing
Asset
Tracking
better understanding
of consumption patterns
Economic Models
Degrowth
Reduce global
consumption and
production
Ecological
economics
growth
economics
Post-growth
Minimal inputs
and outputs
closed loop
system
Society can operate
more efficinetly without
the demands of constant
economic growth
Decoupling
Using less resources
for the same economic
output
happier
human race
sustainability
GHG
emissions
environmental
pressure