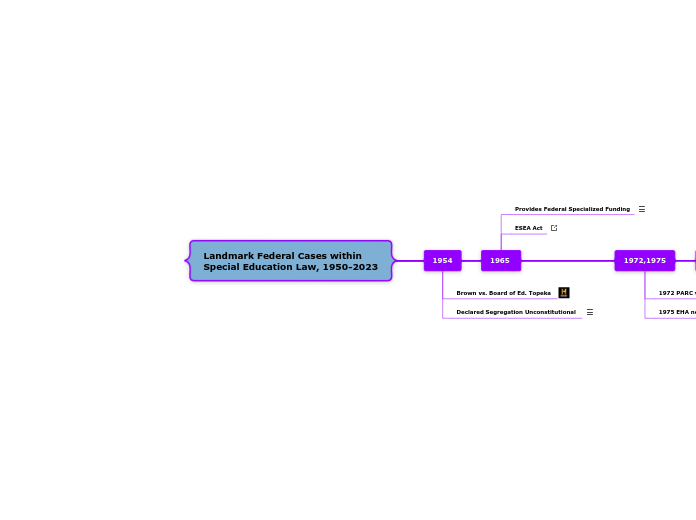
Landmark Federal Cases within Special Education Law, 1950-2023
2023
Perez v. Sturgis Public Schools, et al.
CASE - Miguel L.V. Perez Vs. Sturgis Public Schools, et al. 2023 :
Miguel Perez, a deaf student, sued his school for inadequate education, claiming ADA Act violations and other law violations. The case was dismissed for not exhausting administrative remedies after an IDEA Act violation claim settlement that provided for compensatory education.
2015,2017
2015 ,ESSA Act
LAW - Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) of 2015:
This federal landmark law replaced the No Child Left Behind Act ( NCLB ) This impacted special education as the law delegated greater control over public education standards to the states. Within the law, there is a continued emphasis on the education of special education students with disabilities.
2017, Endrew F. Vs. Douglas County
CASE - Endrew F. v. Douglas County School District (2017):
A landmark case that clarified the scope of the IDEA requirements. The ruling found that schools must offer an IEP reasonably calculated to enable a child with disabilities to make progress appropriate in light of the child's classified disability.
2001, 2004
2001 NCLB Act
LAW - No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB) of 2001:
This landmark federal law emphasized the reauthorization of ESEA that aimed to close the achievement gap with accountability, flexibility, and choice , so that no child is left behind. The NCLB Act included provisions for special education students with disabilities.
2004 IDEA Act
LAW- Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) 2004 :
The reauthorization of the IDEA Act enhanced accountability and outcomes for special education students with disabilities. The reauthorization of this federal legislation emphasized early intervention, high standards, and increased parent involvement in special education planning and the multidisciplinary decision-making processes.
1990
1990 ADA Act
LAW-Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990:
This landmark federal case mandated civil rights protections for individuals with disabilities in all areas of public life, including jobs, schools, and transportation. This included all public and private places open to the general public and impacted special education.
1990 IDEA Act
LAW-The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) of 1990:
This landmark federal case emphasized the reauthorization of the Education for All Handicapped Children Act (EHA). Which significantly enhanced special education services and the rights of students with disabilities. The IDEA Act emphasized the importance of individualized education programs (IEPs), free appropriate public education (FAPE), and the least restrictive environment (LRE) principle.
1982
Board of Education v. Rowley
CASE-Board of Education v. Rowley (1982):
The first Supreme Court interpretation of IDEA establishes that schools are not required to provide the best possible education for students with disabilities but must provide an education that is "appropriately ambitious" according to their capabilities.
Required Public Schools to provide an " appropriately ambitious" free education
1972,1975
1975 EHA now IDEA Act
LAW-Education for All Handicapped Children Act (EHA) of 1975 (now IDEA):
This major foundational and landmark federal special education case required public schools to provide free and appropriate education to all children with disabilities, ages 3-21, and introduced Individualized Education Programs (IEPs).
1972 PARC vs. Commonwealth of PA
CASE-Pennsylvania Association for Retarded Children (PARC) v. Commonwealth of Pennsylvania (1972):
This landmark special education case established the right for children with intellectual disabilities to receive public education.
1965
ESEA Act
Provides Federal Specialized Funding
LAW- Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) of 1965:
A landmark special education federal case. The law is aimed at educational equity for students from lower-income families, focused on improving primary and secondary education. It laid the groundwork for more specialized educational services.
1954
Declared Segregation Unconstitutional
CASE - Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka (1954):
An impactful Landmark Supreme Court case that declared state laws unconstitutional. The previous laws that established separate public schools for Black and White students were declared unconstitutional. The case declared segregation amongst races of people violated the United States Constitution. Though the case does not directly address special education, it sets a crucial precedent for equality. The law calls for equal opportunity in education, paving the way for inclusive education for students with disabilities.
Brown vs. Board of Ed. Topeka