por GABRIELA ALVAREZ BUCURU 12 meses atrás
114
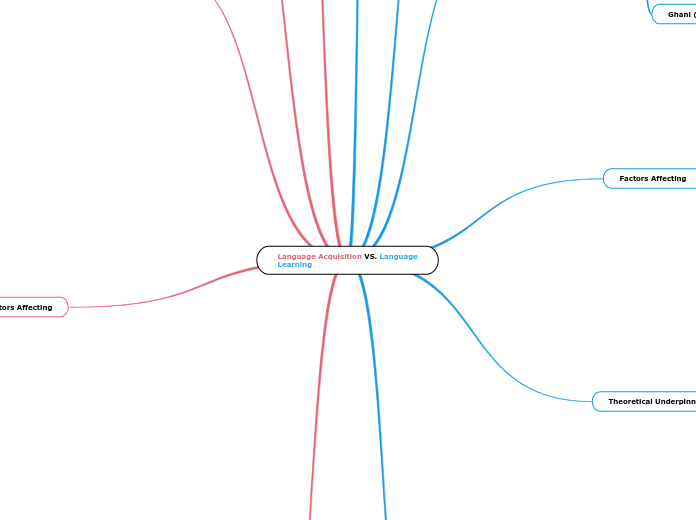
Language Acquisition VS. Language Learning
The process of acquiring or learning a language involves a range of factors and methodologies. Language acquisition tends to be more natural, often occurring through unconscious and implicit means, such as interaction with parents or siblings, and is heavily influenced by age, brain maturity, and cognitive abilities.