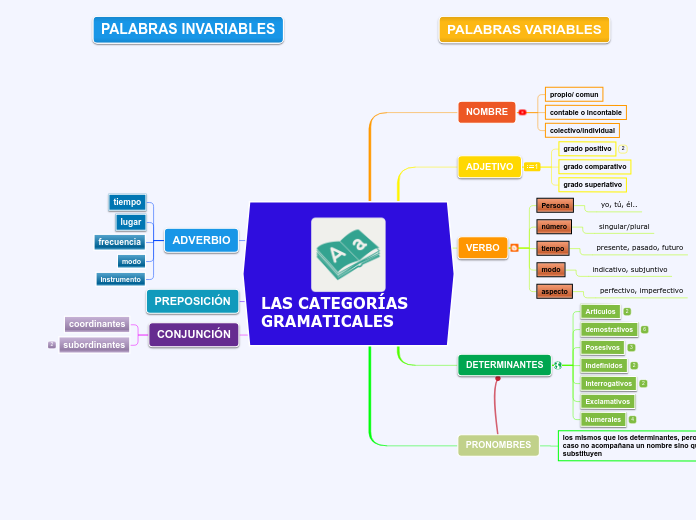
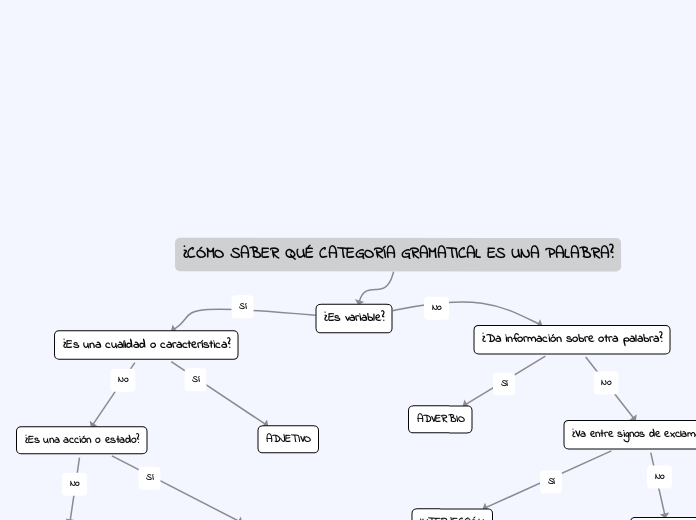
PALABRAS INVARIABLES
PALABRAS VARIABLES
LAS CATEGORÍAS GRAMATICALES
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
CONJUNCIÓN
A conjunction is a word like 'if' 'but' or 'and' which is used to connect sentences or clauses together.
subordinantes
Subordinating conjunctions are conjunctions that are used at the beginning of subordinate clauses. Some examples of these conjunctions are: although, after, before, because, how, if, once, since, so that, until, unless, when etc.
Although it was raining, I went out.
coordinantes
Coordinating conjunctions always connect phrases, words, and clauses. They are: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
PREPOSICIÓN
An interjection is used to express emotion in a sentence.
Think of other interjections!
ADVERBIO
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
instrumento
frecuencia
lugar
The intensifiers strengthen adverbs adjectives and adverbs and down- toners make them weaker.
PRONOMBRES
An article is a word used to modify a noun, which is a person, place, object, or idea. Technically, an article is an adjective, which is any word that modifies a noun.
los mismos que los determinantes, pero en este caso no acompañana un nombre sino que lo substituyen
Indefinite articles are the words 'a' and 'an.' Each of these articles is used to refer to a noun, but the noun being referred to is not a specific person, place, object, or idea. It can be any noun from a group of nouns.
A car in the parking lot.
DETERMINANTES
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
Numerales
Relative pronouns are used to add more information to a sentence. Which, that, who (including whom and whose), and where are all relative pronouns.
cardinales
un, dos, tres,...
ordinales
primero, segundo, vigésimo...
Exclamativos
Interrogativos
Interrogative pronouns are used in questions. Although they are classified as pronouns, it is not easy to see how they replace nouns. Who, which, what, where, and how are all interrogative pronouns.
Ejemplos: qué haces?
qué, quién ,cómo, dónde, cuándo...
Unlike demonstrative pronouns, which point out specific items, indefinite pronouns are used for non-specific things. This is the largest group of pronouns. All, some, any, several, anyone, nobody, each, both, few, either, none, one, and no one are the most common.
Hay varias personas
Alguno, bastantes...
Posesivos
Demonstrative pronouns are used to demonstrate (or indicate). This, that, these, and those are all demonstrative pronouns.
su, sus
tu, vuestro
mi, nuestro
demostrativos
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
Lejania
aquel, aquella, os, as
media distancia
ese, a, os. as
cercanía
este, a, os, as
Artículos
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
Indefinidos
Definidos
VERBO
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
aspecto
perfectivo, imperfectivo
modo
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).
indicativo, subjuntivo
tiempo
A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. The main modal verbs in the English language are: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.
presente, pasado, futuro
número
A linking verb connects the subject with a word that gives information about the subject, such as a condition or relationship.
singular/plural
Persona
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.
yo, tú, él..
ADJETIVO
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
Subtopic
Realiza los ejercicios relacionados con el adjetivo que encontrarás en el enlace adjunto.
http://www.apuntesdelengua.com/archivos/morfologia/adjetivo/ejercicios01.pdf
grado superlativo
grado comparativo
grado positivo
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
Create sentences
She is the prettiest princess.
NOMBRE
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
colectivo/individual
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
contable o incontable
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
propio/ comun
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.