Las texturas
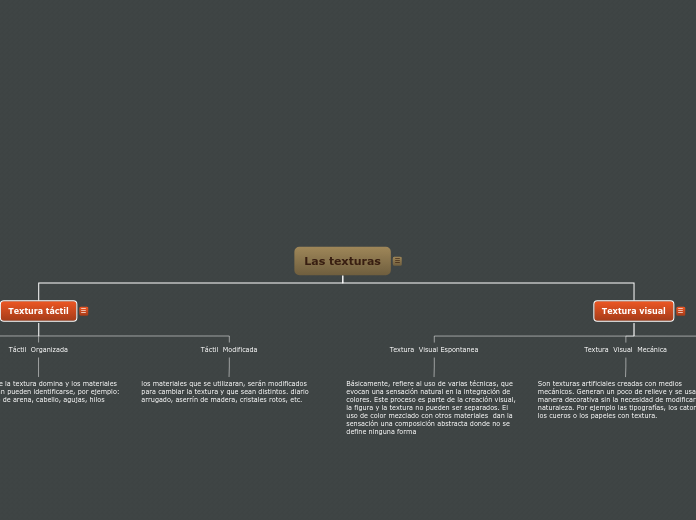
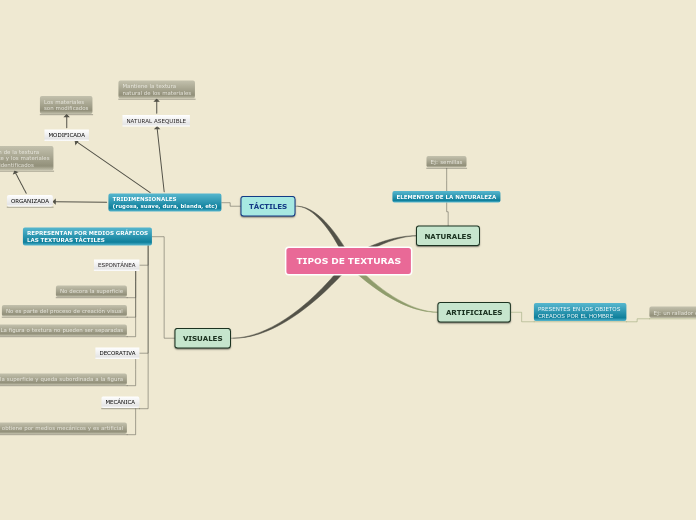
elemento que se refiere a la superficie de una figura. Se dividen en:
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
Textura visual
De diseño bidimensional.
Textura Visual Decorativa
Decora la superficie y es subordinada a la figura. Es decir que la textura puede ser suprimida y no cambiara mucho al resultado final. La textura puede ser creada a mano o por computadoras con programas de edición por ejemplo.
fuente de información: Diseñoartdesignina.wordpress.com
Textura Visual Mecánica
Son texturas artificiales creadas con medios mecánicos. Generan un poco de relieve y se usan de manera decorativa sin la necesidad de modificar su naturaleza. Por ejemplo las tipografías, los catones, los cueros o los papeles con textura.
Textura Visual Espontanea
Básicamente, refiere al uso de varias técnicas, que evocan una sensación natural en la integración de colores. Este proceso es parte de la creación visual, la figura y la textura no pueden ser separados. El uso de color mezclado con otros materiales dan la sensación una composición abstracta donde no se define ninguna forma
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
Textura visual.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
Textura táctil
No solo es visible si no que puede sentirse, la textura táctil se acerca a un diseño tridimensional.
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
Táctil Modificada
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
los materiales que se utilizaran, serán modificados para cambiar la textura y que sean distintos. diario arrugado, aserrín de madera, cristales rotos, etc.
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
Táctil Organizada
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
La sensación de la textura domina y los materiales que se utilizarán pueden identificarse, por ejemplo: semillas, grano de arena, cabello, agujas, hilos retorcidos
Type in a quote that points out the character's position about the issue.
Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'She said he was unusually talented, and she hoped he wouldn't let anything discourage him.' (Paterson, 2. 8)
Táctil Natural Asequible
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
Se conserva la textura natural de materiales como papel natural, madera, algodón, cebada, canela entera, pétalos y lentejas. Entre otros ejemplos.
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
Textura táctil.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)