por Lillian Hyde 4 anos atrás
301
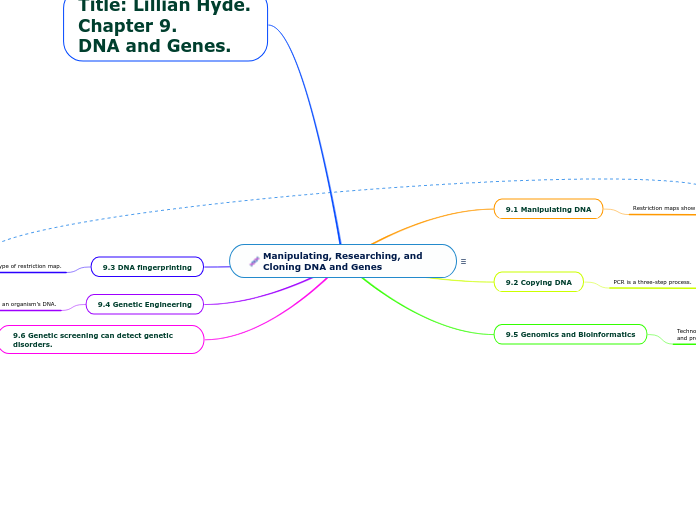
Manipulating, Researching, and Cloning DNA and Genes
Modern research into DNA and genes has made significant strides in various areas of genetic science. Techniques such as gel electrophoresis are used to separate and sort DNA fragments by size, enabling the creation of restriction maps that show the lengths of these fragments between restriction sites.