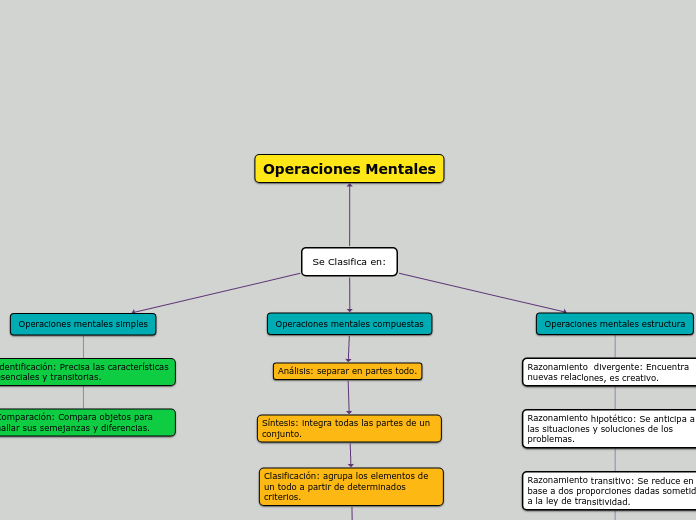
Se Clasifica en:
Name the character
Type in the name of the character whose change throughout the story you are going to analyze.
Example: Nick Carraway.
Operaciones mentales compuestas
Análisis: separar en partes todo.
Síntesis: integra todas las partes de un conjunto.
Clasificación: agrupa los elementos de un todo a partir de determinados criterios.
Codificación: sustituir los objetos por símbolos convencionales.
Decodificación: da significado o traducción.
Proyección de relaciones virtuales: capacidad para ver y establecer relaciones entre estímulos externos.
Diferenciación: Reconocer, distinguir características relevantes e irrelevantes entre estímulos extremos.
Representación mental: Interiorizar las imágenes convencionales de nuestros conocimientos.
Transformación mental: Operación mental que nos permite transformar y modificar las características de los objetos para producir representaciones de un mayor nivel de complejidad o abstracción.
Operaciones mentales estructura
Character's behavior
Think of the character's behavior at the beginning of the story and look for the way it changed throughout the story.
Razonamiento divergente: Encuentra nuevas relaciones, es creativo.
Razonamiento hipotético: Se anticipa a las situaciones y soluciones de los problemas.
Razonamiento transitivo: Se reduce en base a dos proporciones dadas sometido a la ley de transitividad.
Razonamiento analógico: Comparar los atributos de los elementos dados para ver su relación con un tercero e inducir una conclusión.
Razonamiento lógico: Proceso basado en normas, puede ser inductivo y deductivo.
Razonamiento silogístico: Elaboración lógica formal basada en las leyes silogísticas.
Razonamiento inferencial: Permite evaluar nueva información a partir de la información dada.
Operaciones mentales simples
Character's feelings
Focus on the way the character's feelings are presented at the beginning and at the end of the story, while explaining why they have changed.
Identificación: Precisa las características esenciales y transitorias.
Comparación: Compara objetos para hallar sus semejanzas y diferencias.
Operaciones Mentales
Title
Type in the title and author of the literary work that introduces the character.
Example: The Great Gatsby, by F. Scott Fitzgerald.