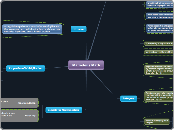
Marvelous Math
Models for Multiplication
Area/Array
Example: In the classroom there are desks lined up in 4 rows with 7 desks in each row. How many total desks are in the classroom?
Repeated Addition
Example: Ryan has 4 plates of cookies with 7 on each plate. How many cookies does Ryan have altogether?
Properties of Multiplication
Associative Property
a x ( b x c ) = ( a x b ) c
Identity Propertry
How does the number keep its identity?
a x 1 = a (Anything multiplied by 1)
Comutative Property
a x b = b x a
Distributiive Property
a x (b + c ) = ( a x b) + ( a x c )
Zero Property
a x 0 = 0
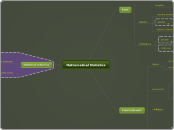
Division
solving division problems is very similar to multiplication. Most people use their multiplication facts or whatever prior knowledge they have to solve a division problem.
Partial Quoient
The only method of doing division that is drastically different from multiplication is the partial quoient. It looks very similar to long division, but ends up being more effcient. Instead of breaking the larger number down into smaller parts, you just simply estimate how many times you think a number can go into the larger number and then subtract that out.
Example of a partial quoient problem
Integers
Rules for Dividing Integers
Negative / Negative = Positive
Positive / Negative = Negative
Positive / Postiive = Positive
Rules to Muliplying with Inegers
Negative x Negative = Postive
Positive x Negative = Negative
Positive x Positive = Positive
Partitioning can help you solve an addtion problem if it is two numbers with the same sign. In this case you can break apart the number into equal groups to find your final answer. Example: 10/5 = 2
Picture of partinioning
Repeated substraction helps when dividing a negative number by another negative number. You can use repeated subtraction to take away an equal amount of groups multiple times. Example: -8/ (-2) = 4
Picture of how to use repeated subtraction
subtracting a positive= adding a negative
subtracting a negative= addiing a positive
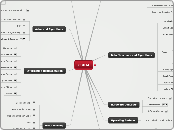
Multiplication
Partial Product: a little piece of the way we learned it as kids, but makes a lot more sense. Instead of having "flying numbers" just write the entire number down below and eventually add them all together.
Picture of Partial Product
Ratio Table: use derived facts like 2, 5, 10, and 20 to quickly move up a table to find your answer.
Picture of Ratio Table
Area Model: slice up the numbers into something much easier to work with to get your end result.
Picture of Area Model
Derived Facts for Multiplication
10
5
2
Expanded Notation: write out each number that is apart of a larger number, for example 348 would be written in expanded notation as 300 + 40 + 8.
Create a Story problem
45 / 9
There are 45 starbursts and 9 kids at a birthday party. How many pieces of candy does each kid get in their goody bag?
8 x 7
Katie has 7 groups of 8 cookies. How many cookies does she have altogether?