Policies and Retirement Plan
Retirement: "Retirement developed along with industrialization, surplus labor, and a rising standard of living. Social Security, passed in 1935, established the right to financial protection in old age on the basis of past economic contributions to society." (Carstensen, 2009)
Caregiving: There are many communities that offer relief financially, physically, medically, and mentally for older adults. If an older adult is injured, ill, or unable to perform daily life activities, they can receive help from a caregiver or be taken to a home which offers further assistance.
Supplemental Security Income (SSI): This provided relief for those living in poverty, impaired, or hurt/injured. This also allows qualification for medicaid and food stamps. This may be a way for helping older adults, but it requires a lot and has many limitations in terms of who qualifies for it.
Social Security: " a foundation of retirement protection for nearly every American, and its benefits are not means tested (e.g., eligibility is not determined by your income, but rather by what you have paid into the Social Security system through your payroll taxes as an employee)." (Hooyman, 2017)
Three Legged Stool: This is a trio consisted of personal savings, social security and pensions which make a solid retirement plan.
Social Security age: can be obtained around the age 62 years old, but if one waits (around 70), the money will increase.
Statistics/Facts: "Latina and Asian older women are least likely to receive Social Security, in part because many of them are immigrants who may not be eligible (Caldera, 2012"
Retirement differs for everyone depending on their finances, age, environment, demographic, family life, race and many more things. Depending on these factors, one can take a look at how they will be able to save for their retirement starting preferably as early as one can.
Statistics show those with lower income, loving in lower income environments, as well as minorities is where we see a less comfortable retirement shift. Especially African American Men among the males. Between sexes, we see a more comfortable transition into retirement with men rather than women.
Cognitive Aging
Executive Function: "the ability to organize our learning and then efficiently use the information stored in our secondary memory to plan and make decisions and shift attention from one task to another" ((Brooks, Weaver, & Scialfa, 2006).
Attentional Control: Being able to sustained attention on something for a known time and knowing when to shift this attention when needed somewhere else.
Sustained Attention: Seeking a specific thing or more things for a period of time.
While attempting simple tasks, young and older people do about the same to perform, since it doesn't use much memory, but for more complex tasks especially with stress involved, older people do worse.
Selective Attention: Being intentionally selective about what you are doing/focusing/working on and ignoring other information.
Memory: Ability to recall information that has been collected throughout one's lifespan.
Secondary memory and Aging: episodic memory, semantic memory, and procedural memory.
Procedural Memory: memory pertaining to how we do things, actions. Procedural memory is not likely to decline as one ages. Once you know how to ride a bike, you'll always know.
Semantic Memory: "The part of long-term memory dealing with words and their meanings shows the least decline with aging, because it is stimulated by concepts learned throughout one’s life." (Hooyman, 2017)
Episodic Memory: memory of events, places, etc that associated with one's emotions. Older adults have no problem at recalling memory from events. It's stated that educated older people are better at recalling than those who aren't.
Sensory Memory: "is the first step in receiving information from the long-term storage of memories via our touch, taste, or smell." ((Pearlman & Storandt, 2004).
Primary Mental Abilities (PMA): This is a series of tests that capture intelligence pertaining to mathematics, generalizing concepts and facts, absorbing content while reading as well as recalling, speed, and spatial relations. This consists of two types of intelligence which are fluid intelligence and crystallized intelligence.
Fluid Intelligence: This type of intelligence is not based on experience or educational history. This is more abstract, meaning it has to do with skill in mathematics, spatial relations and speed.
Fluid Intelligence declines as one ages and become harder for older adults to problem solve, learn new information and absorb information as quickly especially about technology.
Crystalized Intelligence: Intelligence based on previous knowledge and experiences.
As one ages, crystalized intelligence remains intact unless one develops a cognitive illness that may otherwise impact one's crystalized intelligence.
Physiological Changes
Secondary aging is also another way of aging and can be connected to primary aging, but is different in a sense where it occurs due to lifestyle, sudden injury or disease, and environment affects.
Heart Attack: restriction in blood flow through the vessels connected to the heart resulting in the heart not functioning properly. "Heart disease is the primary cause of death, although death due to heart disease is declining; it is also a leading cause of serious long-term disability and limitations in ADLs" (Hooyman, 2017)
Cardiovascular Disease: condition that affects the heart and blood vessels which can cause hypertension, heart attacks or strokes.
Arthritis: Painful and inflamed joints from use and/or lifestyle.
Diabetes: Caused by the lifestyle of the individual if it's type II. What occurs when one has diabetes is impairment of the hormone insulin which doesn't allow glucose/carbs to metabolize as efficiently causing high sugar levels.
Secondary aging includes: diabetes, arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, atherosclerosis (fatty deposits in the arteries), and other diseases caused by an individuals lifestyle.
"Two-thirds of deaths among older adults are due to heart disease, cancer, strokes, and diabetes. Over 80 percent of people who die of heart attacks are age 65 and older. You may be surprised to learn that more women than men die of heart disease each year, due to higher rates of hypertension, with the highest incidence among African American women." (Hooyman, 2017)
Secondary aging may change one's social, financial, physical position depending on the disease which brings about other important topics like caregiving, social support, environment, retirement plans as well as other factors that might play a role when thinking ahead to when we age.
Primary aging is a normal factor of aging and happens to everyone, but to a degree. Meaning the changes that occur like wrinkles, organ deterioration, cognitive decline happens as we age, but everyone experiences it on different degrees.
Organ deterioration: Due to aging, some organs begin to slow down and are unable to function like they have before due to being used throughout one's life. Differs for everyone depending on genetics.
Wrinkles: deterioration of the skin due to decrease in collagen and elasticity due to age and sun exposure.
Primary aging includes: wrinkles, organ deterioration, height changes, weight changes, energy changes, cognitive changes, and other declines that happen gradually to everyone as they age. Other important things that change due to age include sensory, sexual changes, and sleep patterns.
This also applies for cognitive aging which does occur, but happens differently in terms of degree for everyone. This topic is often forgotten about because most people generally think of the physical aspect of aging.
Since everyone will experience primary aging to a degree, it's important to know when to start planning for retirement, possible support, savings, as well as being educated on the assistance and policies provided for older adults.
Biological theories play a key factor in aging and can impact the individual based on their genetics, environment, stressors, lifestyle, finances and other factors. Some theories
Biological theories: wear and tear theory (cells and organs deteriorating after years and lifestyle), cellular aging (cellular decline after decline in cellular regenerations due to injury, age, stress, telomere division) , immunological theory (immune system declines with age), and free radical theory (stressors, environment, and atmospheric impacts).
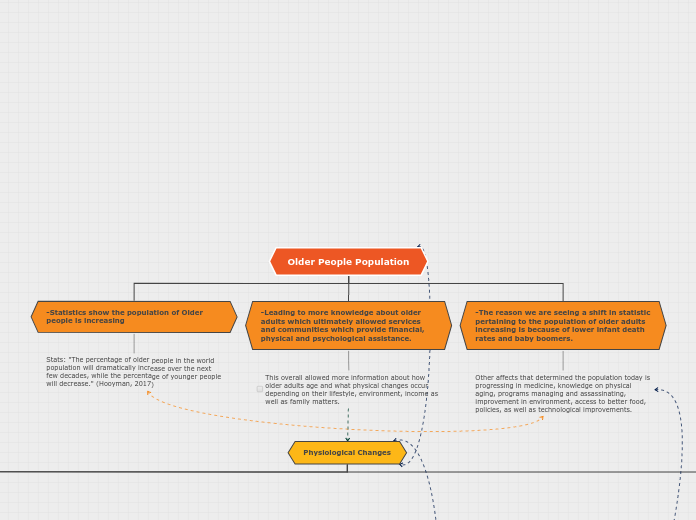
Older People Population
-The reason we are seeing a shift in statistic pertaining to the population of older adults increasing is because of lower infant death rates and baby boomers.
Other affects that determined the population today is progressing in medicine, knowledge on physical aging, programs managing and assassinating, improvement in environment, access to better food, policies, as well as technological improvements.
-Leading to more knowledge about older adults which ultimately allowed services and communities which provide financial, physical and psychological assistance.
This overall allowed more information about how older adults age and what physical changes occur depending on their lifestyle, environment, income as well as family matters.
-Statistics show the population of Older people is increasing
Stats: "The percentage of older people in the world population will dramatically increase over the next few decades, while the percentage of younger people will decrease." (Hooyman, 2017)