Floating topic
Subtopic
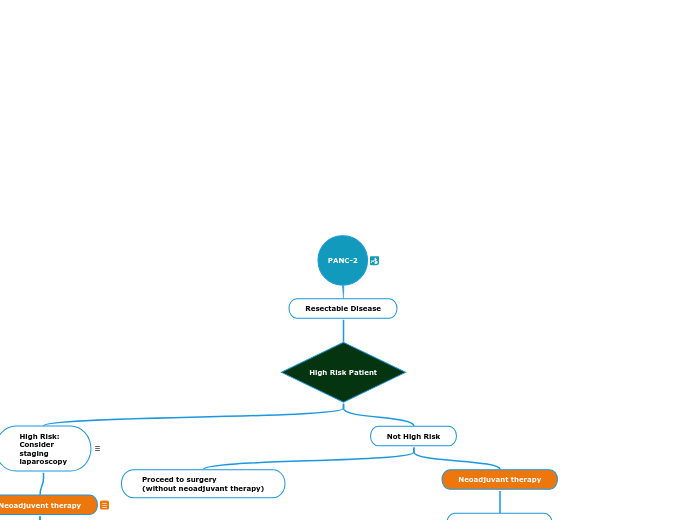
PANC-2
Resectable Disease
High Risk Patient
Not High Risk
Neoadjuvant therapy
EUS guided biopsy
Stent
See Principles of Stent Management (PANC-B).
PANC-B
CA 19-9
Elevated CA 19-9 does not necessarily indicate cancer or advanced disease. CA 19-9 may be elevated as a result of biliary infection (cholangitis), inflammation, or obstruction, benign or malignant. In addition, CA 19-9 will be undetectable in Lewis antigen-negative individuals.
Chest/Pelvic CT
Imaging with contrast unless contraindicated.
Surgery
Surgery (laparotomy or minimally invasive surgery)
See Principles of Surgical Technique (PANC-D) and Pathologic Analysis: Specimen Orientation, Histologic Sections, and Reporting (PANC-E).
Successful
Resection?
See Principles of Surgical Technique (PANC-D) and Pathologic Analysis: Specimen Orientation, Histologic Sections, and Reporting (PANC-E).
PANC-4
PANC-5
Pancreatic CT/MRI
Proceed to surgery
(without neoadjuvant therapy)
High Risk:
Consider
staging
laparoscopy
High-risk features include imaging findings, very highly elevated CA 19-9, large primary tumors, large regional lymph nodes, excessive weight loss, extreme pain.
Neoadjuvent therapy
There is limited evidence to recommend specific neoadjuvant regimens off-study, and practices vary with regard to the use of chemotherapy and chemoradiation. See Principles of Systemic Therapy (PANC-F) for acceptable neoadjuvant options.
Subsequent chemoradiation is sometimes included; see Principles of Radiation Therapy (PANC-G).
PANC-G
PANC-F