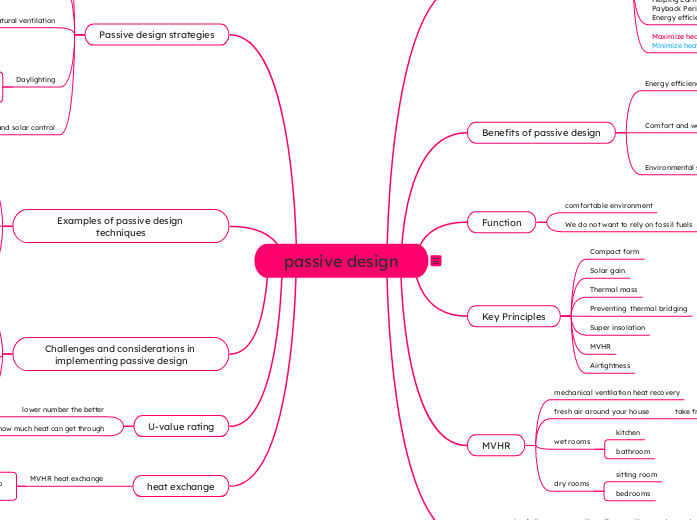
passive design
Note: The detailed breakdown of each section and subsection can include explanations of the concepts, case studies, real-world examples, and specific passive design techniques.
heat exchange
MVHR heat exchange
takes bad air from wet rooms and put it outside to prevent mold and odors through heat exchange
takes fresh air from outside through heat exchanger and puts in inside
U-value rating
how much heat can get through
lower number the better
0.15
Challenges and considerations in implementing passive design
Cost implications
Affordability and availability of materials
Initial investment vs
long-term savings
Building codes and regulations
Overcoming potential barriers to implementation
Compliance with energy efficiency standards
Climate-specific design requirements
Balancing heating and cooling needs
Adaptation to different climate zones
Examples of passive design techniques
Passive lighting solutions
Clerestory windows and reflective surfaces
Light tubes and light shelves
Passive cooling strategies
Natural ventilation techniques like stack effect
Green roofs and cool roofs
Passive solar design
Trombe walls and sunspaces
Solar panels and solar water heating systems
Passive design strategies
Shading and solar control
Incorporating reflective surfaces and low-E glass
Using shading devices and overhangs
Daylighting
Controlling glare and optimizing natural light
Utilizing windows
and light shelves
skylights
Natural ventilation
Incorporating operable windows and vents
Designing for cross ventilation
Insulation and thermal mass
Utilizing thermal mass to regulate indoor temperature
Importance of insulation in reducing heat transfer
Orientation and building layout
Minimizing solar heat gain in summer
Maximizing solar gain in winter
dry rooms
bedrooms
sitting room
wet rooms
bathroom
kitchen
fresh air around your house
take fresh air from outside
mechanical ventilation heat recovery
Key Principles
Airtightness
MVHR
Super insolation
Preventing thermal bridging
Thermal mass
Solar gain
Compact form
Function
We do not want to rely on fossil fuels
comfortable environment
Benefits of passive design
Environmental sustainability
Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
Lower carbon footprint
Comfort and well-being
Optimal natural lighting
Natural ventilation and airflow
Energy efficiency
Decreased reliance on mechanical systems
Reduction in heating and cooling costs
Definition of passive design
Maximize heat gain
Minimize heat loss
Helping Earth with fossil fuels +
Payback Period+
Energy efficient
Will keep warm for a long period of time without constantly putting on heating
Energy efficient house
Importance of passive design in sustainable architecture
Explanation of passive design principles