por Rosa Cendros 5 anos atrás
334
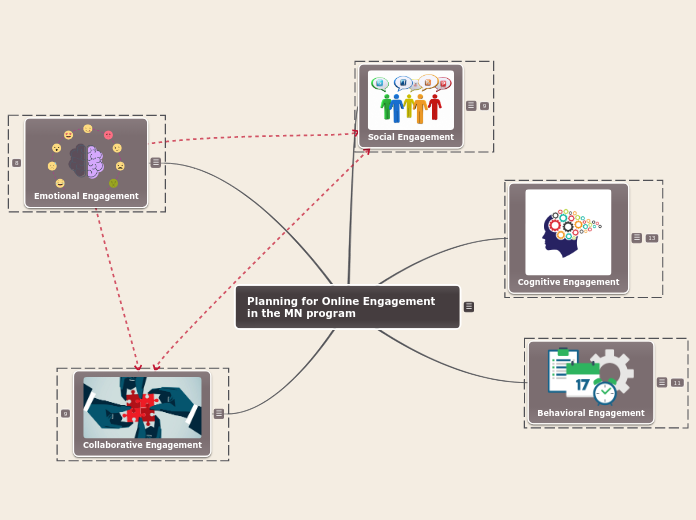
Planning for Online Engagement in the MN program
por Rosa Cendros 5 anos atrás
334

Mais informações
Being focused and engaged in course work as an online student is critical for success. But what does engagement involve?
Based on Redmond et al.'s (2018) Online Engagement Framework for Higher Education
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1179626.pdf
Collaborative engagement is related to the development of different relationships and networks that support learning, including collaboration with peers, instructors, industry, and the educational institution.
Emotional engagement refers to students’ emotional reaction to learning.
Sinatra, Heddy, and Lombardi (2015) reported that “both negative and positive emotions can facilitate activation of attention and engagement” (p. 2).
Behavioral engagement is doing the work and following the rules.
Cognitive engagement is the active process of learning.
Social engagement refers to students’ social investment in the collegiate experience.