Pharmacologicals
Corticosteroids
NSAIDS
DMARDS
Other joints including proximal interphalangeal joints, shoulder, elbows, hips, knees and ankles
Nursing Intervention: Educate patient to report signs and symptoms of infection
Nursing Intervention: Encourage patient to engage in physical activity to slow down joint damage
Nursing Intervention: Educate patient on using heat and cold therapy to relieve inflammation and pain
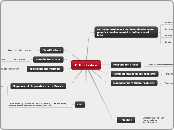
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS CONCEPT MAP
9. Destruction and calcification of articular
cartilage and underlying bone
Chronic Systemic Symptoms from calcification of articular cartilage
Rheumatoid nodules
Localized joint inflammation
Morning Stiffness for more than 30 min
Joint redness
Joint swelling
joint pain
Permanent hand deformity
Boutonniere
Swan's neck
Neutrophils and macrophages phagocytize immune complexes releasing lysosomal enzymes that destroys articular cartilage
Presence of Anti-cyclic citrulline peptide antibodies
70-80% of people who have RA have a RF factor which is an antibody that reacts with a fragment of IgG to form immune complexes
Cigarette smoking is the strongest risk factor for the development of RA
Disease onset: occurs at any age,
peak incidence between 50-75 years
old. Women are affected more frequently than males
1. Genetic environmental and
immunologic factors
2. Activation of T cell mediated immune response (CD4+ cells, interleukin, and tissue necrosis factor)
Mediator:
Release of
TNF, IL-1
3. RF antigen/ IgG interaction
4. Immune Complexes deposited into joint space and osteoclasts are activated
5. B and T lymphocytes to stimulate the inflammatory response
Chronic Inflammatory Symptoms
Rheumatoid Vascularitis
Acute inflammatory symptoms
Fatigue
Weakness
6. Angiogenesis in synovium
7. Synovial proliferation causing thickening and fluid accumulation
8. Pannus formation of granulation tissue that is composed of inflammatory cells that erodes the articular tissue.