por Sara Gómez Omaña 4 anos atrás
1164
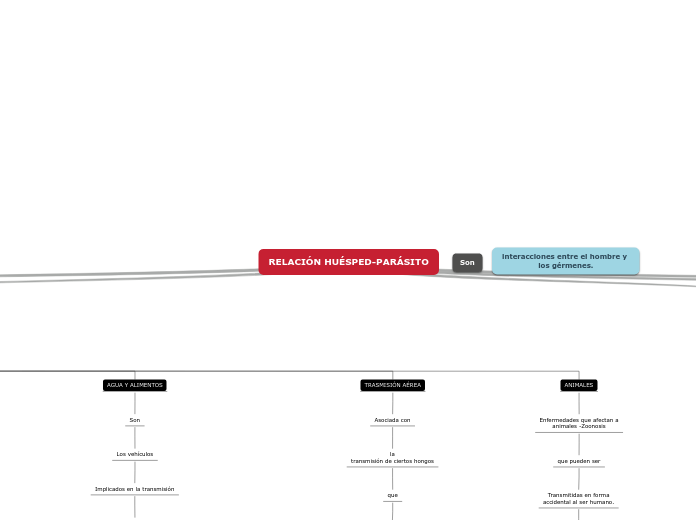
RELACIÓN HUÉSPED-PARÁSITO
por Sara Gómez Omaña 4 anos atrás
1164

Mais informações
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
Cuando el microorganismo
Se multiplica en los tejidos del huésped
Causando una respuesta inmunológica detectable
Pero sin síntomas ni signos
La expresión clínica de la infección
Pone en evidencia el daño de
Células y tejidos
Propiciando síntomas y signos
Extenso, leve, inaperente
A) Tracto respiratorio, gastrointestinal o urogenital
B) Piel cortada, quemada o perforada
1. Una vez dentro debe vencer algunas defensas del hospedador
2. Ocurre la fagocitosis
3. Ácidos de estómago o tracto urogenital
4. Enzimas de saliva, estómago e ID
El número de microorganismos requerido
Producir la infección
El shigella necesita solamente 10-100 microorganismos
En el caso de la salmonela requiere de 10 - 5 bacterias para producir diarrea
El organismo que tiene la capacidad de causar alguna enfermedad
esto depende de
C. LA SUSCEPTIBILIDAD DEL HUÉSPED.
B. LA PUERTA DE ENTRADA AL ORGANISMO Y ESPECIALMENTE
A. LA DOSIS INFECTANTE DEL GERMEN
Enfermedades que afectan a animales -Zoonosis
que pueden ser
Transmitidas en forma accidental al ser humano.
Garrapatas
Malaria
Brucelosis
Rabia
Se transmite con la mordedura
Asociada con
la transmisión de ciertos hongos
que
Causan enfermedades más o menos severas
Los vehículos
Implicados en la transmisión
Enfermedades infecciosas en la comunidad
EJEMPLOS
Los alimentos
Leches - cremas (Staphylococcus aureus y Listeria spp)
Huevo(salmonella)
del
AGUA
Epidemias de fiebre tifoidea, hepatitis A, shigelosis, salmonellosis, cólera,
vectores inanimados.
Ejemplos
Equipo de hospitales (ENFERMEDADES INTRAHOSPITALARIAS)
instrumental
Utensilios de higiene personal
Utensilios de comida
es
El contacto
entre
Un huésped susceptible
Y
Un individuo infectado.
Se da por
a través de
Gotitas de secreciones respiratorias
Tuberculosis
Contacto mano-mano
Fiebre tifoidea
Contacto sexual (ENFERMEDADES VENÉREAS)
Ejemplo
Hepatitis
Herpes
Infección por HIV
Gonorrea
El reservatorio
Personas infectadas en general asintomáticas
Ocurre de madre a hijo
Durante la gestación
o
En el momento del parto.
por
Medio de enfermedades como
N. gonorrhoeae
Streptococcus ß hemolítico grupo B,
Infección por VIH
Citomegalovirus
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
RELACIÓN HUÉSPED-PARÁSITO.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
What type of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
PARASITISMO
Relaciones donde uno
Los miembros obtiene un beneficio a expensas del otro.
COMENSALISMO
Relaciones que
son
De beneficio para uno de los miembros
y
causan poco efecto en el otro
SIMBIÓTICA
de
Beneficio mutuo