por JACOB DAVIS 1 ano atrás
264
SBI4U Summative Connections
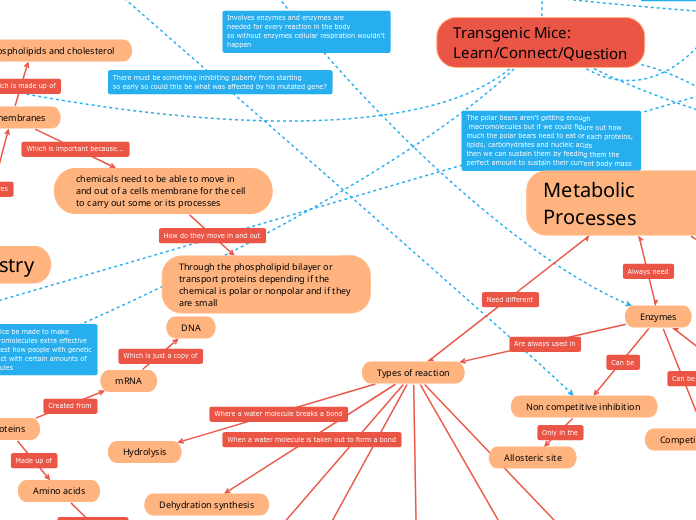
Biological systems rely on intricate mechanisms to maintain homeostasis and drive essential processes. Metabolic pathways, including the conversion of glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide, water, and energy, are fundamental to cellular function.