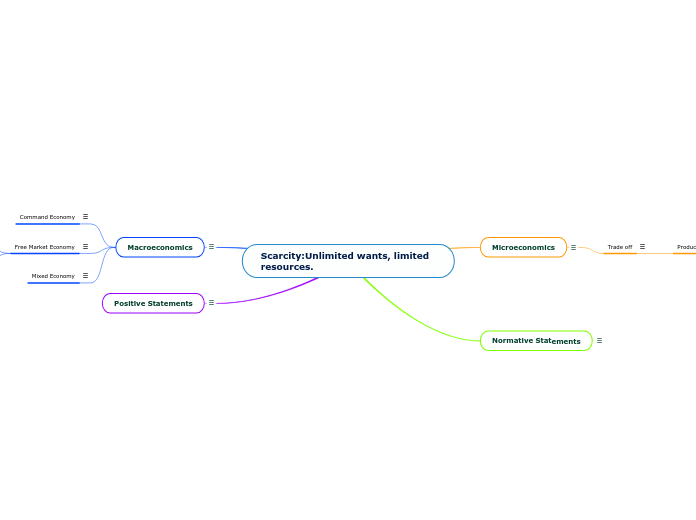
Scarcity:Unlimited wants, limited resources.
Positive Statements
Statements based on facts.
Macroeconomics
Study of economy as a whole like governments spending or inflation.
Mixed Economy
An economy that is a combination of a free market and a command economy, freedom from the government, but with regulation. Most countries use this economy.
Free Market Economy
Economy with no government control or influence
Perverse Incentive
A negative unintended consequence of giving someone an incentive to do something
Incentive
The reason one has to do something
Command Economy
Government controlled economy, like in communism
Normative Statements
Included value judgements
Microeconomics
Study of small economic units such as individuals, firms, and markets.
Trade off
Every choice has a cost. For example, if you had to choose between wearing a red shirt and a blue shirt and you chose the red shirt, the trade off would be not wearing the blue shirt.
Productivity
The amount of output per unit of input
Entrepreneurship
People that use their ambition and innovation skills to produce goods and services
The four factors of production
Human Capital
Any skills gained by a worker through education and experience. An example would be a baseball player's ability to pitch, hit, field, or run.
Capital
Human made resources that are used to produce other good and services
Labor
Any effort someone puts in to produce a product that they are then paid for.
Land
All natural resources that are used to produce goods and services
Cost
Amount seller pays to produce a good
Investment
The money spent by businesses to improve their production.
Price
Amount the consumer pays for a product
Utility
The satisfaction the customer feels with the product
Allocate
The distribution to the various consumers by the seller