por DAVID ALEXANDER MOSQUERA VALENZUELA 1 ano atrás
122
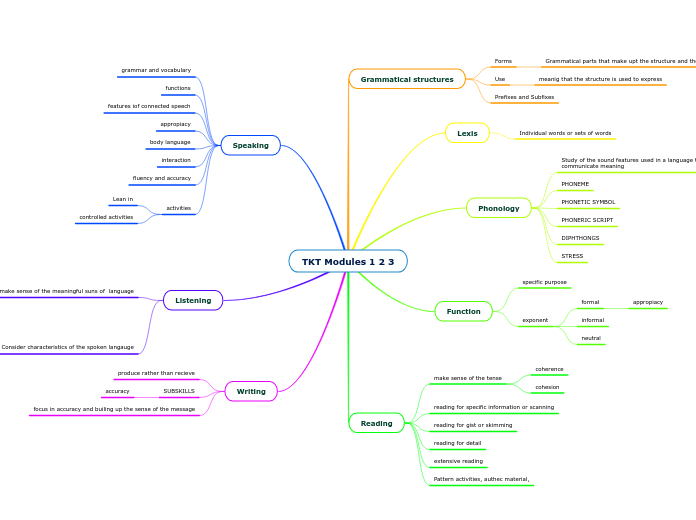
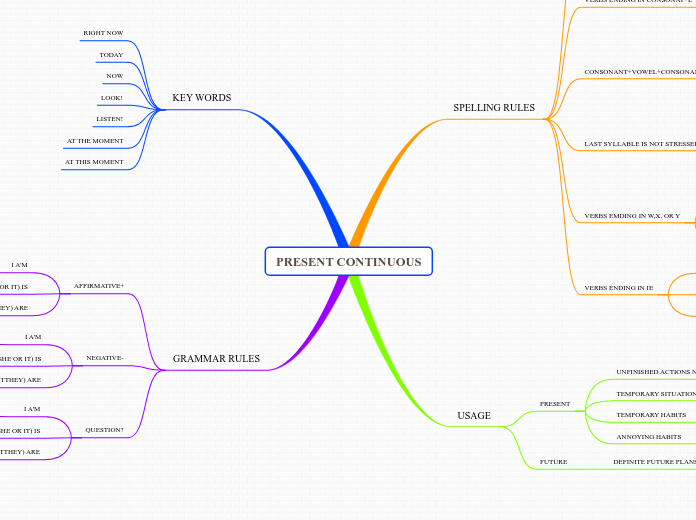
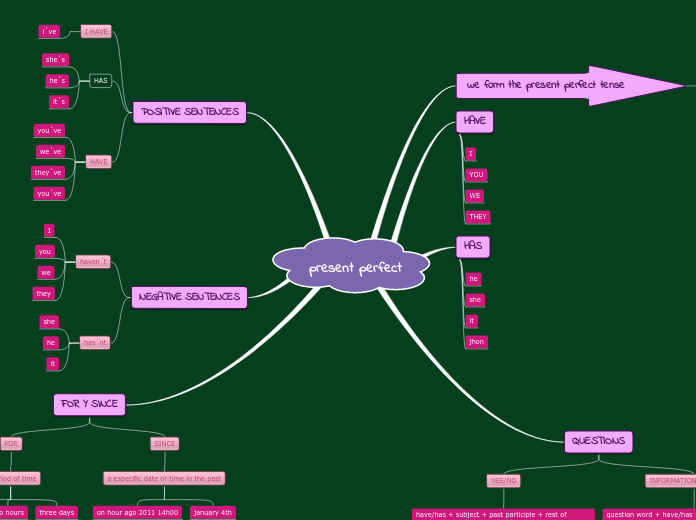
Semantics by Paducheva
Semantics involves the study of meaning in language, focusing on how words and phrases express concepts. Semantic features are critical for understanding and processing natural language, providing a foundation for semantic agreement and explaining unusual readings.