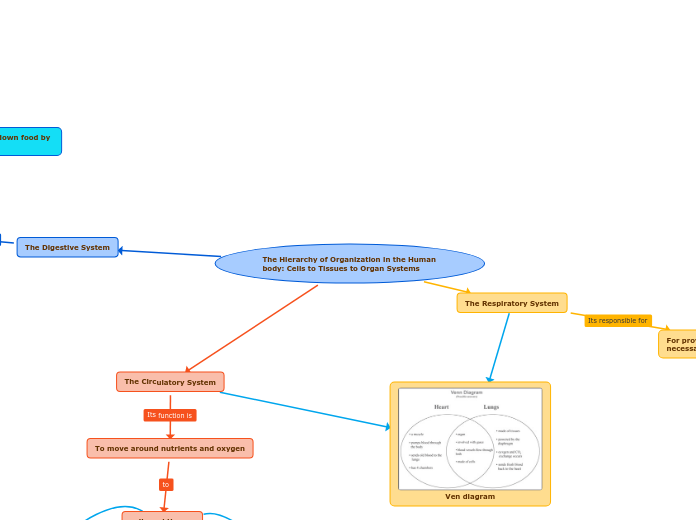
Ven diagram
Venn Diagram
The Hierarchy of Organization in the Human body: Cells to Tissues to Organ Systems
The Respiratory System
For providing the body with the oxygen necessary to operate
removing the carbon dioxide
The organs of the respiratory system
Order of respiratory system
The lungs
move fresh air into the body while also removing waste gases
spongy tissue
the diaphragm
allowing us to inhale and exhale
being the muscle responsible for contraction
just below the lungs
Muscle and fibrous tissue
The bronchi
Alveoli
are a cluster of air sacs
the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide gas by diffusion
thin tissue lining so it can diffuse quickly and more efficiently
Capillaries are surrounding those alveoli sacs to help get oxygen into bloodline
oxygen attaches to hemoglobin which is a protein in blood
surrounded by capillaries
Bronchioles
carry air to alveoli
small tubes originating from the windpipes, that carry air into each lung
Trachea
The windpipe
Carries air to the bronchi
epithelium tissue
cilia cells, goblet cells, and basal cells
Epiglottis
a flap of muscle tissue that covers the trachea
swallowing so that food does not enter the lungs
The Pharynx
The Throat
this is the path which takes air into lungs and food into the digestive system
The Nasal cavity
the space in the nose above where the nose and mouth connect
responsible for filtering air, and moistening it before it enters the lungs
where specialized cells reside which is why we are able to smell
olfactory sensory neurons
Cilia
hair follicles in your nose wich cathc onto debris coming into the nose
produced as your body uses energy for growth, repair, and movement
The Circulatory System
To move around nutrients and oxygen
cells and tissues
The organs of the circulatory system
Vessels
a large network of tubing which carries blood around the body
Divided into 3 groups
Veins
are responsible for carrying blood back
towards the heart
These vessels don't carry high pressure blood
they are not as thick as arteries
These vessels are made up of tissues similar to arteries
Valve
are tissues in vessels which control blood flow and keep your blood flowing in one direction
Arteries
are responsible for carrying blood away from the heart
the high pressure of blood being carried away from the heart
Are thicker than the walls of other blood vessels to withstand those pressures
These vessels are made up of 3 tissues
Artery
Endothelium
Smooth muscle
Connective tissue
Capillaries
Connect veins and arteries together through tissue
for waste product to be taken away from tissues
where oxygen and nutrients are exchanged for carbon dioxide and waste
Made of a single tissue called endothelium making it very thin
The Heart
is a organ made up from grouping of tissues: cardiac muscle tissue,
nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
The connective tissue gives the heart structure and unity
The Nerve tissue is responsible for the actual contraction of the heart
Cardiac muscle tissue is responsible for making each part of the heart contract at the same time
Pumping blood to ensure blood is circulating around the body
The Heart is divided into 4 Chambers
Heart
Right Atrium
Receiveas blood from the superior vena cava
The superior Vena Cava brings deoxygenated blood back from the upper boyd and head
Inferior Vena Cava brings deoxygenated blood back from the lower body
pumps blood into the right ventricle
Right Ventricle
Pumps blood deoxygenated
into the pulmonary artery
Pulmonary artery pumps
blood to lungs
Left Ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood
to aorta
Carries oxygenated blood
to all organs in the body
Left Atrium
Receives oxygenated blood
from the lungs
pumps blood into left ventricle
Blood
Composed
Platelets
Create blood clots
helps in stopping bleeding and heal injuries
Created in bone marrow where general cells become specialized into Platelets
Composition of blood
Plasma
Transports blood cells and Co2 out
55% of the content of blood
90% water and other 10% is salt and enzymes
White Blood Cells
Protect our bodies from bacteria which bring illnesses and disease
Bone Marrow
turn from general cells into specialized cells (WBC's)
Red Blood Cells
To carry oxygens to cells
The Digestive System
chemically and mechanically break down food
Digestive system
Mechanical: literally breaking down food by chewing, biting, etc.
Chemical: the breaking down of food by acids and enzymes
the hydrochloric acid in the stomach and intestines
to gain nutrient molecules
the body's cells can use from absorption
the organs of the digestive system
The anus/rectum
remaining food waste is compacted and released
poop/stool
The Intestines
The intestines
taking broken down food and absorbing it for nutrients and solidifying its waste
small intestine
Absorbs nutrients from food
has 2 section
Is the jejunum
also where villi pick up remaining nutrients
Ileum is a muscle tissue which pushes undigested foods remains into the large intestine
it reaches the duodenum
Fatty acids absorbed get picked up by the lymphatic vessels
Villi in the duodenum absorb water at nutrients
vile is small hair-like things that line the inside of the small intestine
enzymes are released from the pancreases
Bile is released from the gallbladder
Large intestine
reabsorbs water, salts,
and vitamins back into bloodstream
When the capillaries pick up the nutrients and deliver into the blood stream
The Stomach
food starts to get chemically broken down
Hydrochloric acid and pepsin acidly burn down food
Pepsin is released from chief cells
Hydrochloric acid is released from parietal cells
The esophagus
is where broken down food gets taken down towards the stomach
Peristalsis which is a series of muscle contractions that bring down the food
The mouth
is where mechanical digestion starts by the chewing and biting from the teeth
saliva is released from the salivary glands, moistening food and helping bite and break down food