Social-Emotional Learning Best Practices
Trauma
Guiding Principles
Sensitive to cultural, historical, etc. issues
Empower others
Collaboration
Peer support
create chances for deep mutual connection
Trust
Between all stakeholders
not keeping secrets, not withholding info
Safety
from students' perspective
Teacher mindset
From "What is wrong with this child?"to "What has happened to this child?"
From "bad student"to "behaviours trying to soothe emotional dysregulation"
Continuous learning about trauma
Affects
Relationships: unhealthy attachments, hard to form bonds
Regulate emotions: difficulty expressing/managing emotions, over-respond
Academic performance:difficulties with language, communication, info processing
hypersensitive to stimuli(light, sound, event)
Examples
Complex trauma(multiple, ongoing events)
financial, food, housing insecurities
living with alcoholism, substance abuse
abuse, neglect
Chronic trauma
domestic violence
Acute trauma(maybe easier to identify)
victim of crime
medical procedure
accident
Everyday practices
Teacher self-care
Rejuvenate and Refresh
SE Check-Ins
SE Learning Circles
Normalize/routinize journaling
Teach mindfulness exercises
Attune to 5 senses
breathing
Teach growth mindset: Respond positively to mistakes/failures
Assign students role, task, responsibility to build self-worth/efficacy
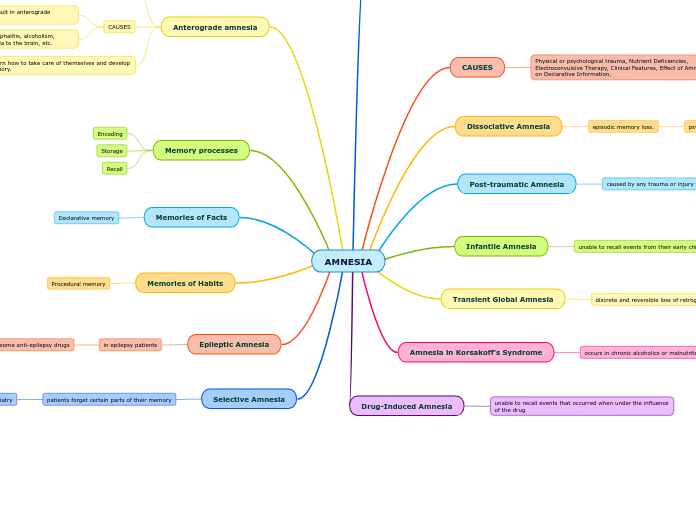
When reading, discuss how characters might feel
PBIS
Tier 1-AllPrevention
Firm and fair corrective discipline
Instead: Restorative(relationships, environment)
aims: respect, accountability, healing
actions: listen, understand, respond
peer juries
talking circles
Not punishment oriented
only removes student from environmentno consideration of student
detention/suspension/expulsion
Clear, immediate and consistent consequences for problems
Effective instruction and classroom management
Establish classroom expectations for routines and behaviours
School-wide good behaviour recognition programs
Positive school climate initiatives (antibullying, mental health clubs)
Intervene before unwanted behaviors escalate
Tier 2-Some
Tier 3: Select
From zero-tolerance policyto restorative practice
Not punishment-oriented