Structural Strength and Stability By: Brianne
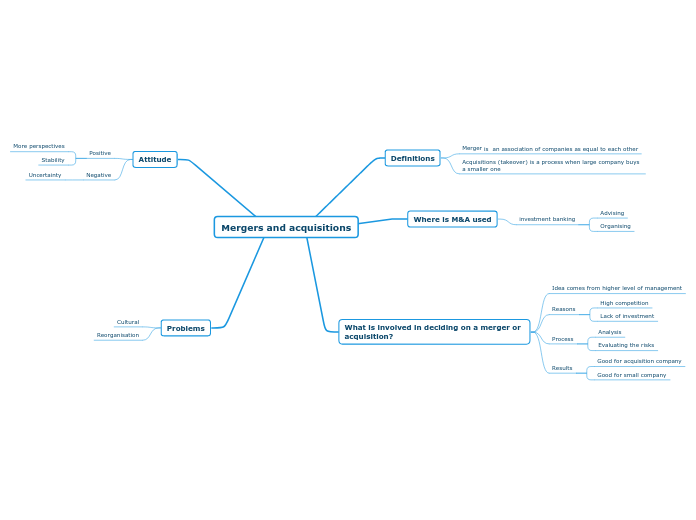
External Forces
Magnitude
Magnitude is the amount of force used or is being used to move or break an object or structure. An example would be giving a high five which uses very low magnitude and low force,but if your shoving something using to hands you are using allot more force and power.
Direction
Direction is on which angle something moves if something moves left the effect i has will also go left. An example would be car crashes if two car where driving the same way the force that effected then would continue going in that same direction. If two car hit head on no force would continue moving because they both counter acted each others force.
Point of Application
Point of application is where you are applying the force. Like if you were to sit properly on a chair in the center of it the chair would stay stable and standing up-wright, but if you are not sitting on your chair properly or if you are sitting at the front of it, it will most likely tip over.
Plane of Application
The plane of application is the angle at which point of application is going or being pushed at. An example would be if you are moving your fridge and push the bottom but the angle at which your at is upward so that the fridge does nit tip over and fall,but if you were pushing at the top your angle would be downward so that the fridge dose not fall backward.
Internal Forces
Torsion
Torsion is the force of twisting in opposite directions in order to do something. An example of torsion would be twisting a lid onto a jar. When you twist the lid it is making the lid go on tighter and also making it harder to remove. The lid is using torsion with in itself to tighten the jar.
Tension
Tension is the force that if you were walking on a slack line,tension is keeping the slack line tight so that you are not on the ground ratter than just a few feet in the air. If we did not have tension our seat belts also wouldn't work well because if you come in to a car crash the impact is enough to keep your seat belt tight so that you stay safe.
Compression
Compression is making something smaller and stronger by using opposite forces working against each other. An example of that could be a hydraulic press when you put an object on the press and it starts to lower and touch that object the object and press are both using there forces to try and counter act each other. As the press continuously pushes the object it gets smaller and tighter making harder for the press to crush it.
Shear
Shear is using to parallel forces to split or break something in half. An example of that could be a paper cutter. A paper cutter has two blades in a parallel position that when you pull down to top blade it can easily slice through parer etc. these two forces work in opposite directions to work and do there job properly.
Stability
Base of Support
The base of support refers to the spot underneath an object or person, that includes every point of contact that the object or person makes with the certain structure. These points of contact may be body parts for example feet or hands, or they may include things like crutches or the chair a person is sitting in or a bike etc. The base of support can be disturbed or moved causing something to fall or break.
Center of Gravity
The center of gravity is the spot where gravity would hold down onto an object. This usually is in the center of the object.lets say you a object in half and the center of gravity is evenly distributed through out both. An example of center of gravity would be us humans we have a center of gravity so we can stand up and move without falling every time.
Unstable
To be unstable is to not be steady like if you were to stand on one foot and you did not have your balance you would be unstable and could fall and or get hurt. A example of something unstable could be a table with only 3 legs but four corners, it only having 3 legs would through of the center of gravity.
Stable
To be stable is to be able to keep your balance and when you have your balance then you are stable,A chair is stable when set on all 4 legs the correct way.
Loads
Static Load
Live Load
A live load is the active load that is not permanently attached to the structure. It's like your car when you drive, your car is a live load to the earth because your car is heavy enough to keep itself on earth using gravity and its own weight that it carries within itself.
Dead Load
A dead load is when a force is applied on a structure, it causes forces within the structure. A dead load also does not move it is stationary. Gravity is whats holding it down on to the surface,just like how gravity is holding us down to earth.A example is when you go over the monkey bars, the monkey bars are the dead load being held down by gravity.
Dynamic Load
The dynamic load is the load that due to forces changes while they are in contact with the structure. Like a truck driving across a bridge. It constantly changes its points of contact on the bridge. Due to wind speed, direction and point of contact, it changes it's contact to the bridge due to the wind.