Unit 2 - Element Compound Mixture
Compound
A compound is formed when 2 or more different elements combined
together by a chemical change to create a new substance.
Compounds are pure substances that can be split into smaller substances.
Examples: Water, Sugar, Salt, Carbon dioxide, Ammonia, Acids
Compounds
Examples:
CO2
H2O
NaCl
NaOH
CaO
A compound is formed when 2 or more different elements combined
together by a chemical change to create a new substance.
Compounds are pure substances.
Compounds can be split into smaller substances.
Examples:
CO2
H2O
NaCl
NaOH
CaO
Element
Element is the simplest form of matter.
Element is a pure substance, it cannot be broken into something smaller.
Element is made of only one type of particles / atoms.
All (and ONLY) the elements can be found in the periodic table.
Metal,Non-metal,Metalloid
Ex.Sliver,Helium,Silicon
Mixture
Tyndall Effect
The Tyndall effect is the scattering of light as a light beam passes through a colloid.
The tiny particles scatter and reflect light, making the beam visible.
The amount of scattering depends on the frequency of the light and density of the
particles.
Blue light is scattered more strongly than red light by the Tyndall effect.
The Tyndall effect was first described by 19th-century physicist John Tyndall.
Example:
The visible beam of headlights in fog is caused by the Tyndall effect.
The water droplets scatter the light, making the headlight beams visible
Mixtures
A mixture is formed when 2 or more substances are mixed together by a
physical method such as stirring, shaking, dissolving.
No new substance is formed
Examples of mixtures:
Blood – mixture of
• red blood cells
• white blood cells
• platelets
• plasma
Can be separated in the lab by centrifuge.
Air - Air is made of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, inert
gases etc.
We can separate the oxygen from the air by our lungs, no
chemical reaction, electricity or heat is needed.
Sea water– mixture of water and salt
Can be separated by evaporation of the water.
Concentration
The volume of liquid is measure in cm3 or mL or dm3
Concentration of solution is measured in g/dm3 or g/L
Ex - 10 gram of solute in 1000 cm3 of solution
RAdioactive Element
Uses of Alpha Radiation
Used in smoke detectors.
Radioactive element americium releases alpha
radiation, which ionizes the air inside the
detector. Smoke from a fire absorbs alpha
radiation, changing the ionization and
triggering the alarm.
Uses of Beta Radiation
Doctors may use radioactive chemicals called
tracers for medical imaging, as these chemicals
concentrate in different damaged or diseased
parts of the body.
Radiation detectors placed outside the body
detect the radiation emitted and, with the aid of
computers, build up an image of the inside of the
body.
Uses of Gamma Radiation
Gamma radiation is used in the treatment of
cancer, testing equipment and sterilising medical
instruments.
Radioactivity was first discovered in 1896
by the French scientist Henri Becquerel ,
while working on phosphorescent (glow in the dark) materials.
He wrapped a photographic plate in black paper and
placed various phosphorescent minerals on it.
All results were negative until he used uranium salts.
Marie Curie isolated a new element polonium
and separated a new element radium from barium.
Uses of radioactive elements
1) Determine the age of Fossils
By analyzing the percentage of carbon-14
(radioactive element) in fossil we can know their
age.
2) Producing Energy
Nuclear fission releases huge amounts of heat that can be used to produce
electricity.
3) Medical Uses
Some radioactive elements are used
to diagnose and treat cancer.
4) Atomic Bomb
An atomic bomb gets its explosive force from
the release of atomic energy from fission of Uranium.
The first atomic bomb was successfully tested on
July 16, 1945
First atomic bomb was used during WWII
(World War 2) in Hiroshima, Japan (August 6, 1945)
Atom Structure
Protons and Neutrons are in the nucleus and cannot move.
Only the electrons can move around in the shells .
Protons are much bigger than the Electrons .
The number of protons is usually equal to the number of electrons.
Ex - Sulfer,Neon,Rubidium,Iron,Magnesium,Fluorine
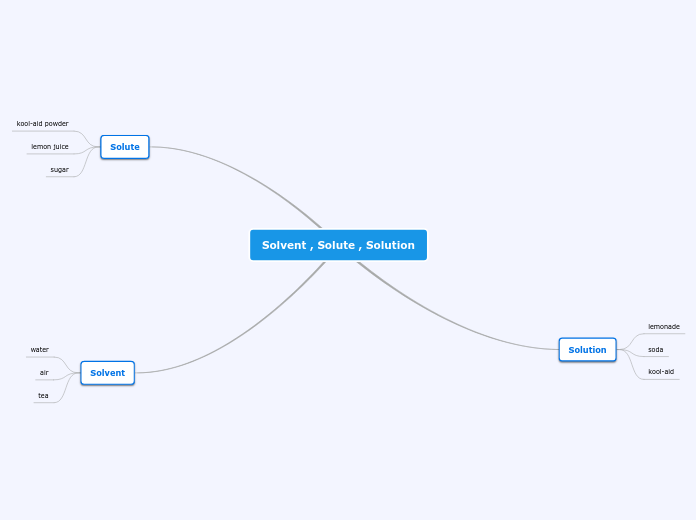
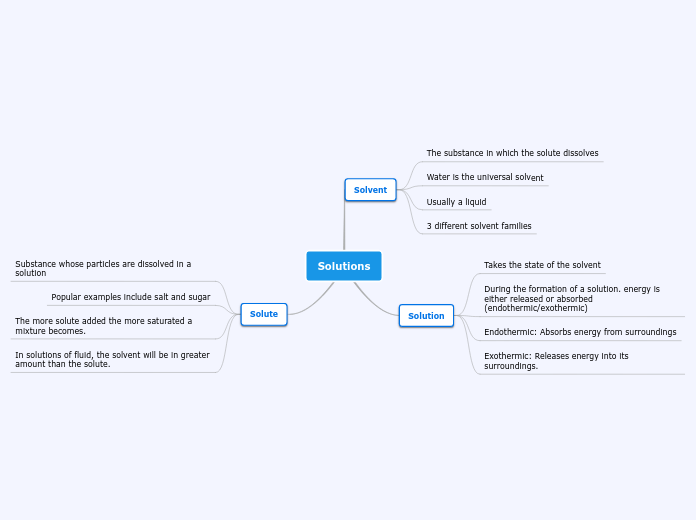
Solution
What is solution?
Solution is a homogenous (uniform) mixture that is formed when a substance
dissolves in another substance.
Example:
Mix sugar in water.
Solute = Sugar
Solvent = Water
Dissolve = Mix the sugar in the water
Solution = The final mixture
Solute - solid / liquid / gas
Solvent - liquid
Solution - liquid (not pure)
Dissolve
- the process of mixing the
solute in the solvent.