por sarah gonzalez 3 anos atrás
253
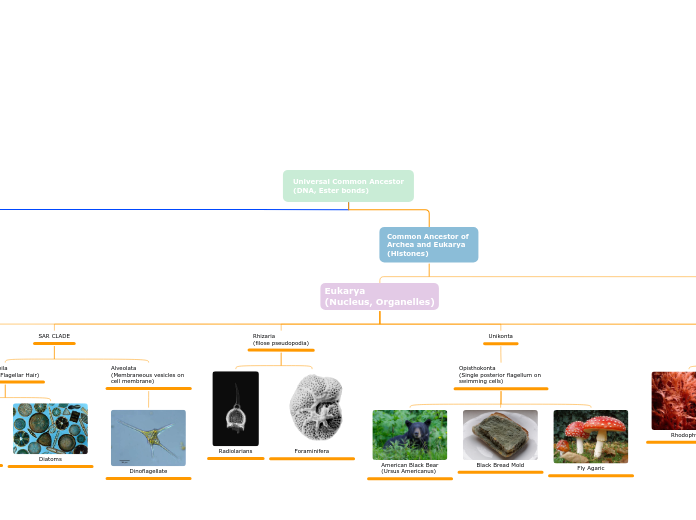
Universal Common Ancestor (DNA, Ester bonds)
Life on Earth shares a common ancestry that can be traced back to a universal common ancestor. This ancestor evolved into various lineages, including bacteria with distinct cell wall structures, and the more complex eukaryotes that house their genetic material within a nucleus and possess specialized organelles.