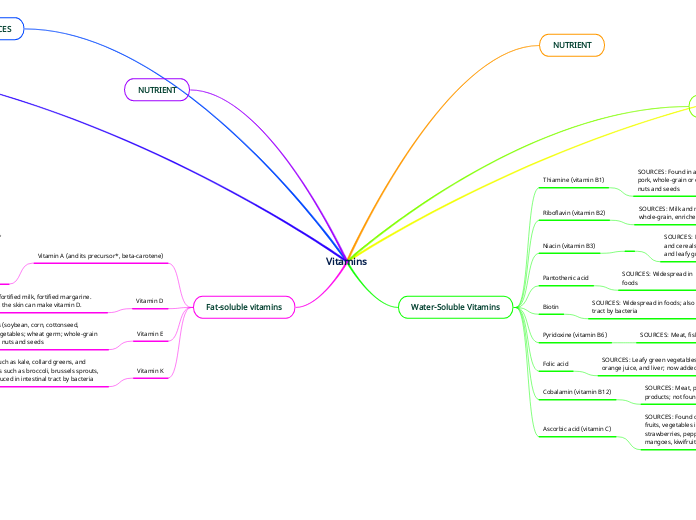
Vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins
Vitamin K
Leafy green vegetables such as kale, collard greens, and spinach; green vegetables such as broccoli, brussels sprouts, and asparagus; also produced in intestinal tract by bacteria
Needed for proper blood clotting
Vitamin E
Polyunsaturated plant oils (soybean, corn, cottonseed, safflower); leafy green vegetables; wheat germ; whole-grain products; liver; egg yolks; nuts and seeds
Antioxidant; protects cell walls
Vitamin D
Egg yolks, liver, fatty fish, fortified milk, fortified margarine. When exposed to sunlight, the skin can make vitamin D.
Needed for proper absorption of calcium; stored in bones
Vitamin A (and its precursor*, beta-carotene)
Vitamin A from animal sources (retinol): fortified milk, cheese, cream, butter, fortified margarine, eggs, liver
Beta-carotene (from plant sources): Leafy, dark green vegetables; dark orange fruits (apricots, cantaloupe) and vegetables (carrots, winter squash, sweet potatoes, pumpkin)
Needed for vision, healthy skin and mucous membranes, bone and tooth growth, immune system health
Water-Soluble Vitamins
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
SOURCES: Found only in fruits and vegetables, especially citrus fruits, vegetables in the cabbage family, cantaloupe, strawberries, peppers, tomatoes, potatoes, lettuce, papayas, mangoes, kiwifruit
FUNCTIONS: Antioxidant ; part of an enzyme needed for protein metabolism; important for immune system health; aids in iron absorption
Cobalamin (vitamin B12)
SOURCES: Meat, poultry, fish, seafood, eggs, milk and milk products; not found in plant foods
FUNCTIONS: Part of an enzyme needed for making new cells; important to nerve function
Folic acid
SOURCES: Leafy green vegetables and legumes, seeds, orange juice, and liver; now added to most refined grains
FUNCTIONS: Part of an enzyme needed for making DNA and new cells, especially red blood cells
Pyridoxine (vitamin B6)
SOURCES: Meat, fish, poultry, vegetables, fruits
FUNCTIONS: Part of an enzyme needed for protein metabolism; helps make red blood cells
Biotin
SOURCES: Widespread in foods; also produced in intestinal tract by bacteria
Pantothenic acid
SOURCES: Widespread in foods
FUNCTIONS: Part of an enzyme needed for energy metabolism
Niacin (vitamin B3)
Riboflavin (vitamin B2)
SOURCES: Milk and milk products; leafy green vegetables; whole-grain, enriched breads and cereals
FUNCTIONS: Part of an enzyme needed for energy metabolism; important for normal vision and skin health
Thiamine (vitamin B1)
SOURCES: Found in all nutritious foods in moderate amounts: pork, whole-grain or enriched breads and cereals, legumes, nuts and seeds
FUNCTIONS: Part of an enzyme needed for energy metabolism; important to nerve function
SOURCES
FUNCTIONS
NUTRIENT