HIV & AIDS
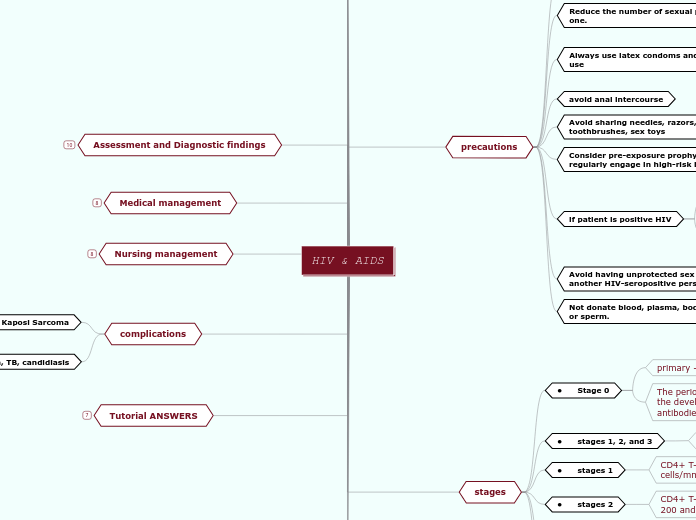
Tutorial ANSWERS
Q7: B
Q6 : KAPOSI S
Q5: D
Q4: B
Q3: C
Q2: D
Q1: A
complications
pneumonia, TB, candidiasis
Kaposi Sarcoma
Cutaneous signs may be the first manifestation of HIV; they can appear anywhere on the body and are usually brownish pink to deep purple.
Nursing management
monitor and manage complications
improve knowledge and coping strategies
improving nutritional status
reliving pain and discomfort
improving activity tolerance
preventing infections
promoting usual bowl pattern
promoting skin integrity
Medical management
treatment of immunodeficiency complications
antiretroviral therapy (ART)
Optimal viral suppression is defined generally as a viral load persistently below the level of detection
adherence is important
doesn't cure
but help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives
HIV treatment regimen
involves taking a combination of HIV medicines every day
Assessment and Diagnostic findings
nucleic acid (RNA) tests.
directly detect HIV
antigen/antibody test
directly detect HIV and antibodies
antibody test
tests for antibodies only
ELISA test
it allows early diagnosis of the infection before the onset of symptoms
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
used to test for The HIV antibody
Clinical manifestations
symptoms related to the immunosuppressed state
Sore throat and painful mouth sores. Swollen lymph glands
depression and psychological stress
weight loss
diarrhoea
headache
rash
fatigue
fever
stages
• stages unknown
Cases with no information on CD4+ T-lymphocyte count or percentage
• stages 3
the person is considered to have AIDS for surveillance purposes
stage 3 when the count drops below 200 cells/mm3 of blood
• stages 2
CD4+ T-lymphocyte cells are between 200 and 499
• stages 1
CD4+ T-cell counts drop to 500 to 1,500 cells/mm3 of blood
• stages 1, 2, and 3
based on the CD4+ T-lymphocyte count.
• Stage 0
The period from infection with HIV to the development of HIV-specific antibodies
primary - acute infection
precautions
Not donate blood, plasma, body organs, or sperm.
Avoid having unprotected sex with another HIV-seropositive person
risk for cross-infection
if patient is positive HIV
Inform previous, present, and prospective sexual and drug-using partners of their HIV-positive status
Take ART regularly to achieve viral suppression.
Consider pre-exposure prophylaxis if regularly engage in high-risk behaviors.
Avoid sharing needles, razors, toothbrushes, sex toys
avoid anal intercourse
Always use latex condoms and don't re-use
If the patient is allergic to latex, nonlatex condoms should be used; however, they will not protect against HIV infection.
Reduce the number of sexual partners to one.
Abstain from exchanging sexual fluids (semen and vaginal fluid).
mode of transmission
anal and vaginal sexual intercourse
sharing needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment.
blood transfusions
mother to child
occur in utero, at the time of delivery, or through breast-feeding
transmitted in body fluids
blood, seminal fluid, vaginal secretions, amniotic fluid, and breast milk that contain infected cells.
What is it?
AIDS
first case identified
in 1981
acquired immune deficiency syndrome
used to describe a number of potentially life-threatening infections and illnesses that happen when the immune system has been severely damaged by the HIV virus.
HIV
human immunodeficiency virus
a retrovirus that attacks the body's immune system.