Cell Growth and Division
Section 4
Frontiers in Stem Cell Research
Ethical Issues
Most people are confused between stem cells and embryonic cells
The use of stem cell is fine, doesn't hurt anything or one
Some argue that the embryo is not yet alive
Subtopic
People think it's wrong to kill a human
Harvesting embryonic cells means to kill the embryo
Potential Benefits
Could end up saving peoples' lives
Make whole organs
Some want to use Embryonic cells to make more cells for other organs
Offer the chance to inject stem cells into damaged area
Scientists are using stem cells to make organs
Stem Cells and Development
Stem Cells
Different cells embryonic develop are neurons, fat cells, smooth muscle, and macrophage
Embryonic cells develops after fertilization
Stem cells are multipotent- can develop into many types of different cells
Embryonic cells are pluripotent, found in early embryo
Unspecialized cells
Human Development
Inner cells are pluripotent- can't develop into ANY cell
Outer cells form tissue, while cells become part of embryo mass
Totipotent- able to develop into any cell
At early stage blastocyst begin to specialize
Blastocyst, a hollow ball of cells
section 1
Limits to cells size
Division of Cell
Each daughter cell gets one complete copy of DNA
Results in an increase in the ratio of surface area to volume
Before division a cell copies all of it's DNA
Daughter cells are what the two cells that divided are called
The process of a cell dividing into two daughter cells is called cell division
Exchanging materials
Formula for volume- length x width x height
Formula for area- length x width
Rate of food and water being used up and waste produced depends on cell volume
Exchange of materials depends on surface area of cell
Waste products leave through cell membrane
Food, oxygen, and water enter through the cellular membrane
Information overload
As size of cell increases, DNA does not
Critical information stored in DNA moleclue
Causes cell to divide
DNA has too many things to do
Happens when cell is too big
Cell division and reproduction
Comparing Asexual and Sexual reproduction
Sexual, some offspring may have the right combination of genes to survive while others may not
Some organisms produce asexually and sexually
Sexual reproduction provides more diversity
Asexual only have to have one parent, makes reproducing faster and easier
For many single-celled organisms asexual is a form of survival
Sexual reproduction
Most animals an plants produce sexually
Offspring inherit genetic information from both parents
Is the fusion of two separate parent cells
Offspring shares features from both parents
Two parents
Asexual reproduction
Usually in single-celled organisms,but is found in many multi-celled too
Definition- production of genetically identical offspring from one parent
Enables populations to increase very rapidly
Offspring is identical to parent
One parent
Section 3
Cancer
Treatments
Chemo has dangerous side effects because also affects healthy cells
Chemotherapy slows cells growth process down
Use targeted radiation for cancers that grow rapidly
Some can be stopped if found early
When cancer tumor is localized, removed by surgery
Causes of Cancer
Others don't respond to internal regulators
Some cells don't respond to external growth regulators
Control over cell broken down
Sources- smoking, chewing, radiation exposure, genes defect, and viral infection
Caused by defects in genes that regulate growth and division
Section 2
Cytokinesis
Plant Cells
Spilt cell into two
Cell plate grows into cell membranes splitting the cell
Final stage in cell division
Cell plate forms forms halfway, dividing the nuclei
Can't draw inward because it has a rigid cell wall
Animal Cells
Each part contains a nucleus and organelles
Pinches in until cytoplasm is into nearly 2 parts
Cell membrane is pulled inward
Splits one cell into two
Cytokinesis is final stage in cell division
Mitosis
Telephase
NOT the final stage in cell division, only in mitosis!!!
Spindle fibers break apart and nucleuolus becomes visible
Nuclear envelope reappears
Chromosomes unravel into tangle of chromatin
Final stage of mitosis
Anaphase
Ends when chromosomes are separated into 2 groups
Move with spindle fibers to sides of cell
Chromosomes separate into 2
Begins with chromatids separate ad move away
3rd stage
Metaphase
Spindle fibers come from both sides of the cell
Spindle fibers attach
Chromosomes line up
Generally the shortest step
2nd Stage
Prophase
When done chromosomes coil and nucleus disappears
Spindle fibers extend from the centrioles
Chromosomes visible and spindle form
Usually longest step
1st phase
Cell Cycle
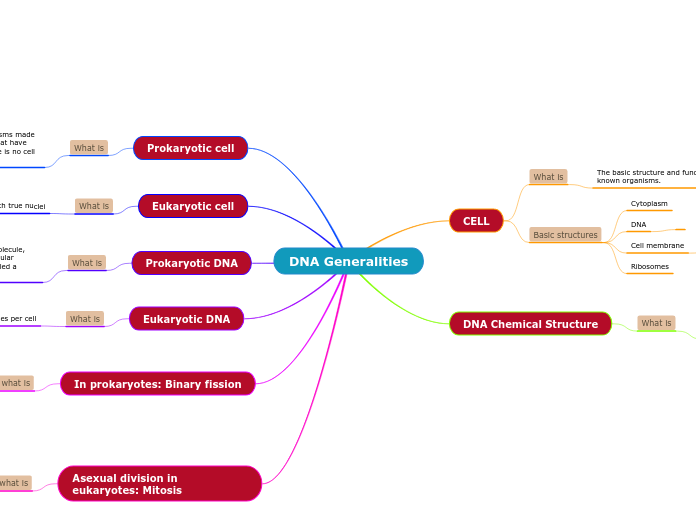
Prokaryote Cell Cycle
3. Cell divides with the product of 2 new cells
2. Cell membrane indents
1. DNA duplicates
Process of cell division in prokaryotes is known as Binary Fusion
Cell start to begin to start the process when they have grown to a certain size
3 main stages
Eukaryote Cell Cycle
Mitosis is the first step in the division of the cell's nucleus, second step is cytokinesis
Interphase is an in-between stage from one cell division to another G1, S, G2 are apart of interphase
Time taken in each depends on each type of cell
G1, S, G2, M phase
Four phases involved
Chromosomes
Prokaryote Chromosomes
Most of the contents of the cell are in the cytoplasm
DNA molecules found in cytoplasm
Circle chromosome contains all or almost all genetic infromation
Contain a single, circular DNA chromsomes
Lack nuclei
Eukaryote Chromosomes
Chromosomes make it possible to split the DNA correctly in cell division
DNA and histone molecules form structures called nucleosomes
Contain multiple chromosomes
Chromatin is chromosomes and histones
Generally have more DNA than prokaryotes