realizată de Lauren Kanooth 5 ani în urmă
141
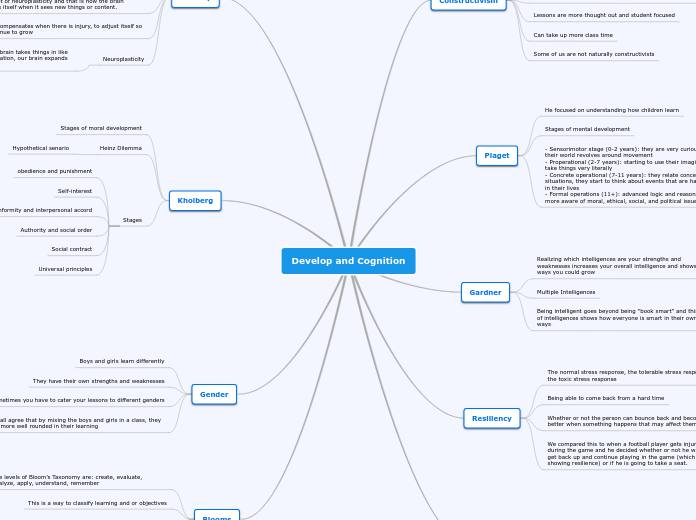
Develop and Cognition
The text discusses several educational and psychological concepts important for understanding human development and learning processes. It begins with resiliency, highlighting the ability to recover and thrive despite challenges, likening it to an injured football player deciding whether to continue playing or not.