realizată de Kahlon Harleen 8 luni în urmă
64
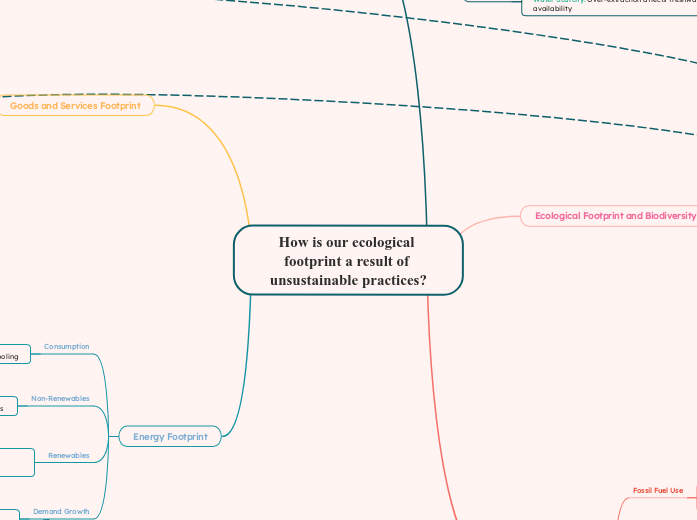
How is our ecological footprint a result of unsustainable practices?
The ecological footprint is significantly influenced by unsustainable practices, particularly prevalent in developed countries where consumption and resource use are high. The inequitable distribution of resource consumption and waste generation further exacerbates global disparities.