作者:Kahlon Harleen 8 月以前
64
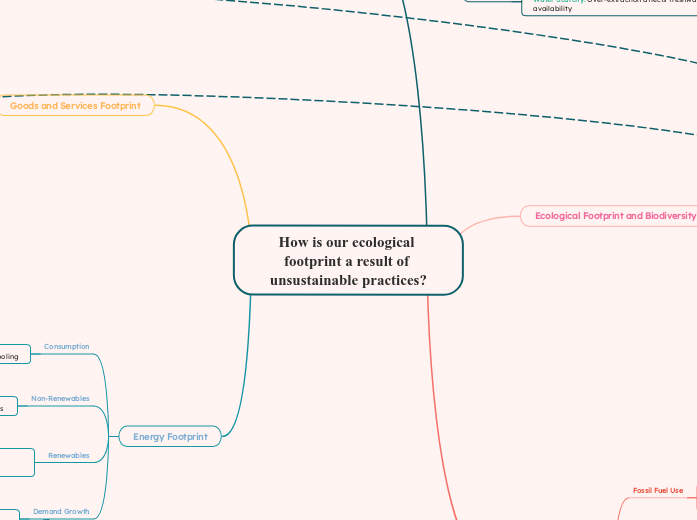
How is our ecological footprint a result of unsustainable practices?
The ecological footprint is significantly influenced by unsustainable practices, particularly prevalent in developed countries where consumption and resource use are high. The inequitable distribution of resource consumption and waste generation further exacerbates global disparities.
開啟
How is our ecological footprint a result of unsustainable practices? Energy Footprint Demand Growth Growing industries: require more energy Increasing energy demand: urbanization & industrialization Renewables Solar Energy: Requires large land areas & hazardous materials in production Wind Energy: Wildlife impacts, bird and bat collisions, noise pollution Non-Renewables Air pollution: emissions from burning fossil fuels Fossil fuel use: significant environmental harm & resource depletion Consumption Significant energy use: heating and cooling Heavy reliance on energy: households and industries Goods and Services Footprint Consumerism High consumption rates: increase pressure on natural resources Consumer demand causes overproduction Resource Depletion Finite resources deplete quickly Over-extraction of non-renewable resources Waste Generation Landfills & recycling systems overwhelmed by waste volumes High levels of waste from packaging & consumer goods Manufacturing Impact Industrial pollution: air, water Large resource consumption Carbon Footprint Industrial Emissions Power Plant Emissions: coal-fired power plants Factory Emissions: CO2 & pollutants from manufacturing processes Transportation Emissions Urban Air Quality: Pollution impacts affect health Vehicle Emissions: Cars, trucks, & airplanes Greenhouse Gas Emissions Methane Emissions: from agriculture (livestock, rice, paddies) & waste (landfills) CO2 Emissions: fossil fuels & industrial processes Fossil Fuel Use Electricity Generation: Extensive use of fossil fuels for power Coal, Oil, Gas: Major contributors to carbon emissions Ecological Footprint and Biodiversity Ecological Deficit Resource depletion: environmental degradation & unsustainable consumption patterns Footprint Exceeds Biocapacity: Creating an ecological deficit Global Trends Disparities in Resource Use: Inequitable distribution of resource consumption & waste generation Developed countries: larger ecological footprints due to higher consumption & resource use Biocapacity Imbalance Resource Overconsumption: Demand exceeds the Earth's capacity to regenerate Decreased biocapacity: loss of productive land & ecosystems due to human activity Human Impact on Ecosystems Urban Sprawl: Expansion of urban areas leads to habitat fragmentation Clearing forests reduces biodiversity & disrupts ecosystems Food Footprint Water Use Water Scarcity: Over-extraction affects freshwater availability Agricultural Water Usage: High demand for irrigation leading to water scarcity Land Use Forests cleared, causing habitat loss Deforestation for Agriculture: biodiversity loss & carbon release Food Waste Emissions from Waste: Greenhouse gases & methane Wasted Resources: during production and distribution Agricultural Practices Soil Degradation: Erosion, fertility loss &nutrient depletion Intensive Farming: chemical use and monoculture, leading to soil degradation