realizată de Karen Lizeth Esquivel Lopez 2 ani în urmă
201
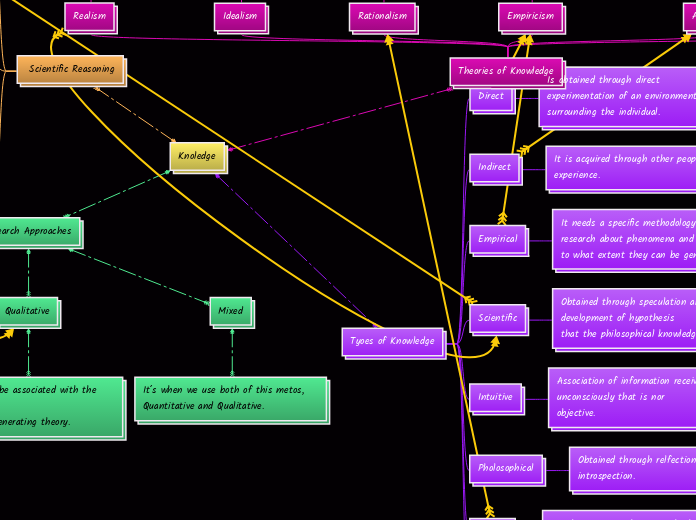
Knoledge
The study of knowledge encompasses various theories and methodologies. Rationalism emphasizes reasoning and logic as primary sources of meaning, while empiricism asserts that experience and experimentation are essential for understanding.