realizată de Yare SP 4 ani în urmă
393
MAPA CONCEPTUAL EN INGLES, EVIDENCIA 1
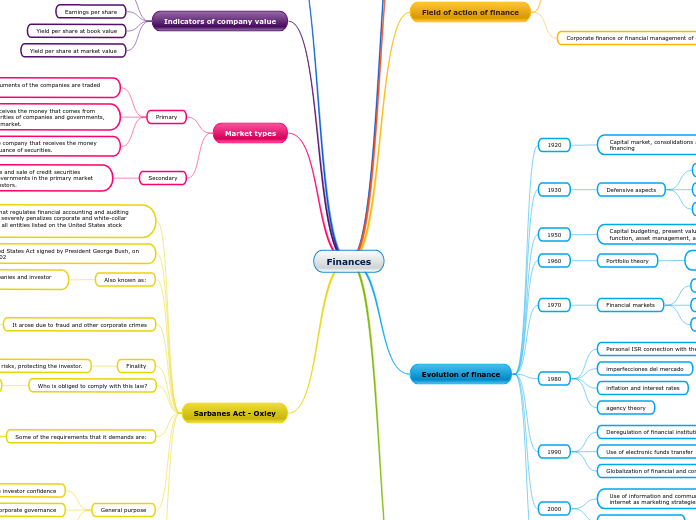
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act, also known as the Act of Reform of public accounting of companies and investor protection, was signed into law by President George Bush on July 30, 2002. It regulates financial accounting and auditing functions, aiming to prevent corporate fraud and protect investors.