realizată de DALLAS HAVENS (Student) 4 ani în urmă
290
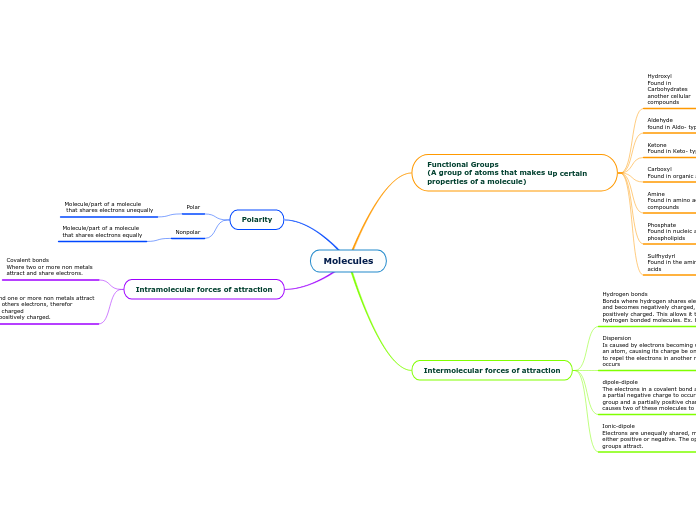
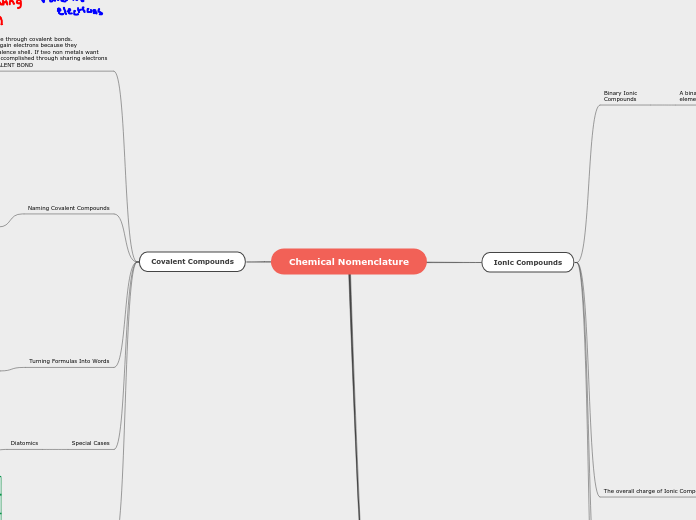
Molecules
Various molecular interactions are central to chemical structures and reactions. These interactions can be broadly classified into intramolecular and intermolecular forces. Intramolecular forces include ionic bonds, where electrons are transferred between metals and non-metals, resulting in oppositely charged ions.