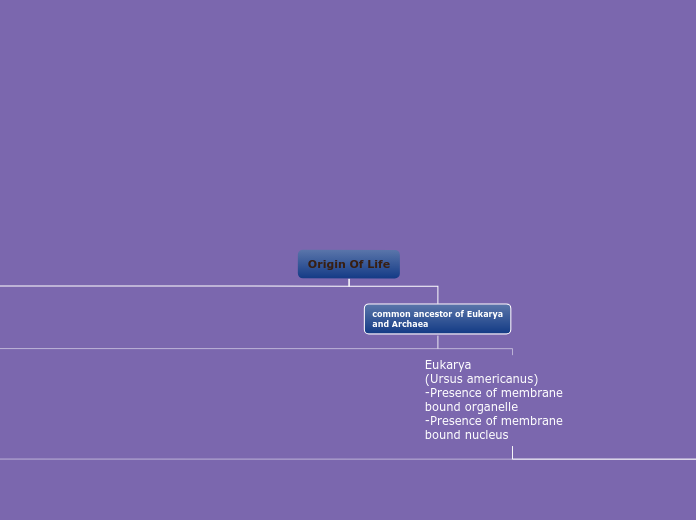
Origin Of Life
common ancestor of Eukarya
and Archaea
Eukarya
(Ursus americanus)
-Presence of membrane bound organelle
-Presence of membrane bound nucleus
Excavata
-feeding grove
-secondary plastids
(Ex Euglanosids)
SAR Clade
secondary plastids
Alveolata
membranous vesicle on cell membrane
(Ex Dino flagellates)
Strameopila (Diatoms)
tripartite flagellar hair
(Ex macrocystic purifiers)
Rhizaria
filose pseudopodia
(Ex Radiolarian)
(Ex Foraminiferas)
Archaeplastida
*primary plastids
(Ex Southern Magnolia)
common ancestor of
chlorophytes, charophytes, and land plants
chlorophytes
common ancestor of land plants
and charophytes
Green Algae
Charophyte
chlorophyte braun stonewart
Land plants
-sporic life cycle
-embroyos
-apical meristem
liverwort
common liverwort
Unikota
Opistokonta
single posterior flagellum on swimming cells
Opisthokonta
(Ex Black Bread mold and fungi)
Common ancestor of fungi and Nuclearlids
Fungi
Multicellular
Chitin cell wall
Zygote can life cycle
Black bread mold
(Rhizopus stolonifer)
(Fly Agaric) Amanita muscarla
Nuclearlids
Nuclearlid
(Nucleria thermophilia)
Common ancestor of choanoflagellate and Animalia
Choanoflagellates
Animalia
-multicellular
-mobility
-game tic life style
porifera
giant barrel sponge
eumetazoa
•tissue
cnidaria radiosymmetry and diploblasty
common ancestor of hydrozoa and scyphozoa
hydrozoa alternate between the polyp and medusa (pennaria disticha)
scyphozoa produce a medusa (jellies)
anthozoa occur only on polyps (elkhorn coral)
bilateria
bilateral symmetry
tripoblasty, cephalization
deutrostomia
-radial and indeterminate cleavage, blastopore becomes the anus
chordata
notochord,
hollow dorsal nerve cord, post anal fin,pharyngeal slits
cephalochordata lancelata (branchiostma lanceolatum)
vertebrate
vertebral column
cranium cartilaginous skeleton
agnathans (pacific hagfish)
gnathostomes
jaws
bony skeleton
ray-finned fishes (blue tang)
osteichthyes
lungs/lung derivatives
lobe-finned fishes (coelacanth)
common ancestor of echinodermata and hemichordata
echinodermata
water vascular system
ophiuroidea has flexible arms (serpent star)
echinoidea has no arms (purple sea urchin)
holothuroidea lack spines (california sea cucumber)
asteroidea arms radiating from the centeral disc and have tube feet on the underside (giant sea star)
protostomia
spiral and determinate cleavage
bloastopore becomes mouth
ecdyszoa
ecdysis
arthropods-
chesapeake blue crab and monarch butterfly
chelicerata clawlike feeding appendage that work as fangs or pincers (sothern black widow)
common ancestor of hexapoda and crustacea
crustacea highly specialisde apendiages two pair of antennae (cheaspeake blue crab
hexapoda have wings and dont need to sacrifice legs (monarch butterfly)
nematoda
roundworm
lophotrochozoa
trochopore larvae
lohopore
platyhelminthes
flatworms
rhabditophorans fresh water and marine species
free diving rhabditophorans (pseudobiceros sp.)
trematoda (sheep liver fluke) parasites
cestoda (pork tapeworm) parasites
Ancestor of annelids and mollusca
mollusca ( soft bodied organisms with protective shell
bivalva shell is divided in two and are hinged together (soft shell clam)
cephalopoda foot becomes modified into a muscular excurrent siphon and part of the tentacle has no hard shell (humboltd squid)
gastropoda move in a small pace by a rippling like motion of their foot (golden apple snail)
annelids body resembles a series of fused rings
(common earthworm)
Amebozoa
*movement w/ pseudopodia
(Ex slime mold)
Archaea (ex. Methanobrevibractor smitii)
-Ether bonds in cell membrane
-DNA as genetic storage
-Presence of histones
Bacteria
-Esther linkage
-DNA as genetic storage
-Presense of peptidoglycan