Freud
Individual Personality
Our favourite things, our least favourite things, how we see others, how we see ourselves, and what we believe our purpose is.
False Memories
We sometimes remember things that never happened. This may be due to outside influence or factors which can't be identified.
What lessons do psychologists teach us about interdependence?
Humanistic Psychology
Abraham Maslow, Viktor Frankl, Carl Rogers.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Pyramid, Self-Actualization, Client Centered Therapy.
Focuses on the Individual
The Brain, Sensation, and Perception
The Mind
Perception
Things can have different meanings depending on who you are.
How our mind views certain things and situations that don't have to be physical things.
Conscious part of our self.
The Brain
Sensors
The Brain and the Sensors
Parts in our brain that help us identify physical things.
The functioning and processing part of our body.
Cognitive Psychology
Focuses on the processes of the brain
The IQ Test, Bobo Doll Experiment, Linguistic Theory.
Jean Piaget, Noam Chomsky, Albert Bandura, Elizabeth Loftus.
Behavior
Perspectives on behavior
Subtopic
Erik Erikson
Key stages of life model. Positives and negatives are identified. Each stage is resolved as it comes.
Jean Piaget
Four operational learning stages as children. Development in thought process.
Sigmund Freud
Behavior is influenced by the Id and Super-Ego.
Influences on Behavior
Mental/Physical Health
Behavior may be influenced consciously, unconsciously or involuntarily according to our state of health.
Attitudes
Explicit
What we consciously thin about.
Implicit
What we do not consciously think about.
Formed by environment (People, places, things).
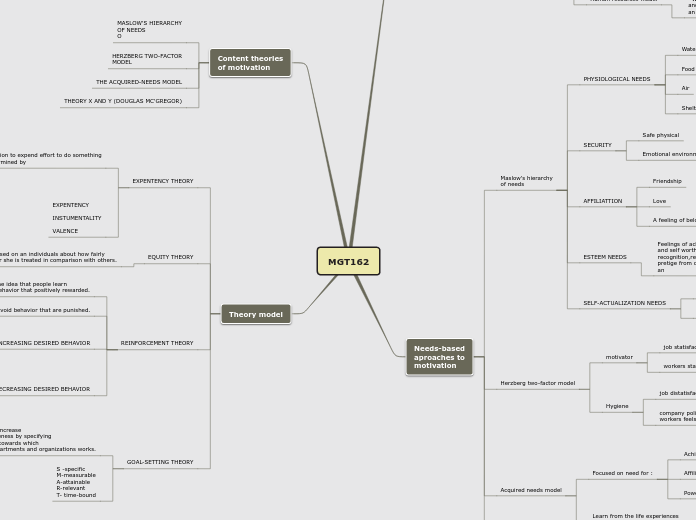
Motivation
The desire to do something. Can be Intrinsic (Naturally belonging) or (From outside).
Social Thinking
Interactions with people cause us to think certain things about them. What we think about them will determine our behavior towards them.
Behavioral Psychology
Focuses on learning and human behaviour.
Pavlov's Dog - Classical Conditioning, Little Albert, The Skinner Box.
Ivan Pavlov, John B. Watson, B. F. Skinner.
Identity
Biological
Parents DNA.
Psychical Characteristics
Hair Colour
Skin Colour
Eye Colour
Environmental
Society
Expectations, limits, behaviours.
Family
Discipline, habits, behaviours.
Friends
Hobbies, Interests, behaviours
Psychodynamics
Sigmund Freid, Carl Jung, Karen Horney, Erik Erikson.
Free Association (Talk Therapy), Social Roles, Archtypes - Representations of Self.
Focuses on life experiences and the connections between the conscious and the unconscious mind.
Mental Health
Mental Illness
Mood disorders, anxiety disorders, eating disorders.
Eating Disorders: Anorexia Nervosa. When one does not eat due to factors such as their own thoughts of them becoming fat.
Anxiety Disorders: Depression. Negative thoughts on many different aspects of life.
Mood Disorders: OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Disorder). An obsessive urge to do something exactly the way you want.
Can be cured through therapy and medication.
Typically Environmental
Mental Disease
Can be moderated through therapy, diet, and medication.
Typically Biological
Psychotic disorders, Dementia's, Developmental/processing disorders.
Developmental/processing disorders: Autism. An impairment in social interaction and communication skills.
Dementia's: Alzheimer's: Late stage of Dementia where the patient will forget basic things like their name.
Psychotic disorders: Schizophrenia. An altered state of reality.
Memory
Long Term Memory
The holding of any information indefinitely. Can be recent or in the far past.
Short Term Memory
Small pieces of information readily active in mind for a short period of time.
Sensory Memory
Impressions of sensory information after the original stimuli have ended.