realizată de Orayo Villarroel 2 ani în urmă
238
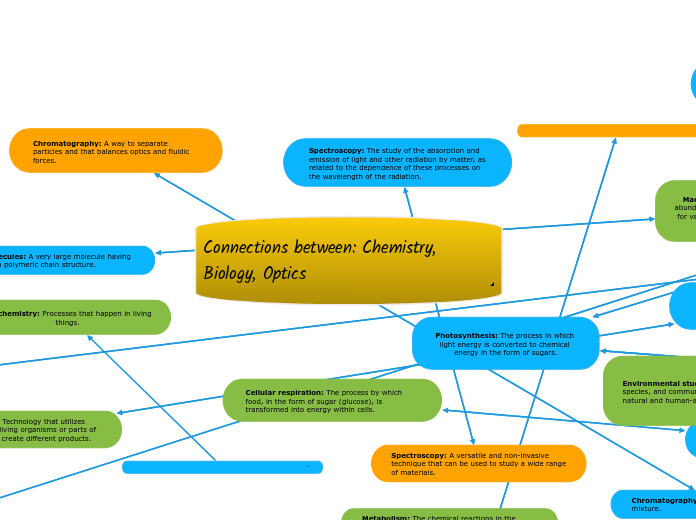
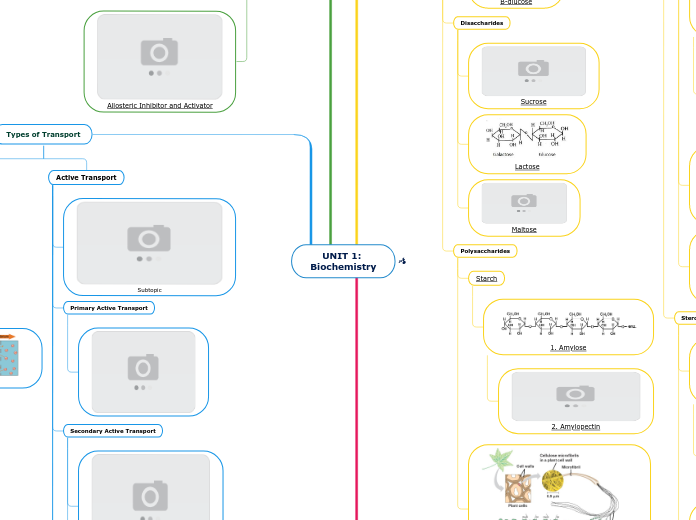
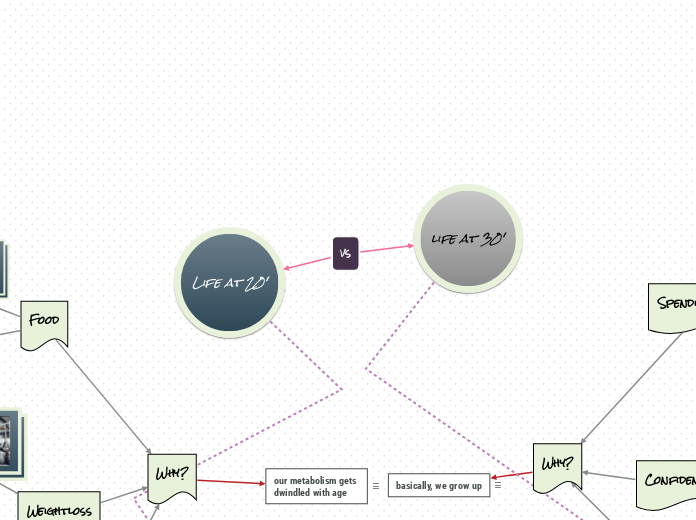
Science mind map 1
The transformation of light energy into chemical energy, known as photosynthesis, involves pigments in plant cells that capture light, initiating a series of reactions. Photovoltaics, on the other hand, convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconducting materials like silicon.