Universo Educativo
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
Bibliografia: SILVA, Bento (2000). Âmago da Comunicação Educativa. Cadernos do Noroeste, Comunicação e Sociedade 2. Série Comunicação, vol.14 (1-2), pp. 689-710
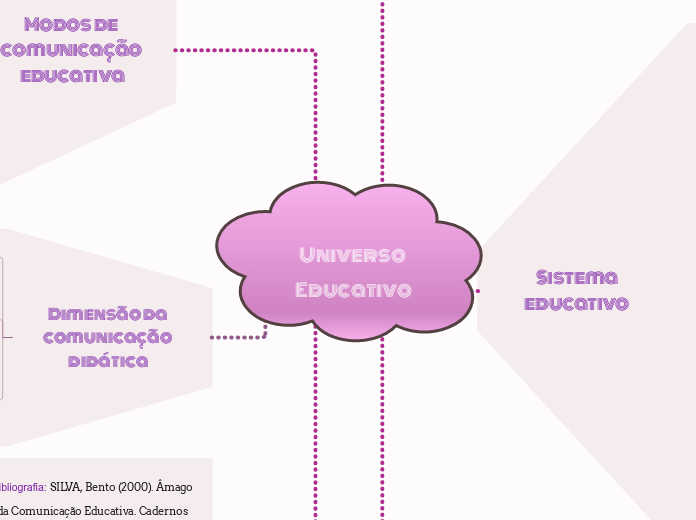
Dimensão da comunicação didática
Influência
A influência exercida através do processo comunicacional pode ser analisada a dois níveis: imposto pela própria natureza do processo comunicacional e o outro pela intensão de influenciar.
interação
A comunicação tem um aspeto de conteúdo, e um aspeto de relação, pode inclusive discutir-se se é mais importante, em termos de uma comunicação eficaz.
Didática
Permitem analisar o cenário das operações didáticas no enquadramento de sala de aula.
Modos de comunicação educativa
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
Comunicação informal
Future Continuous is used:
- for an action that is likely to happen in the future and continue for an expected length of time
- for an action that will be in progress at some point in the future
- for action verbs (e.g. running)
- for predictions about future events
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow at 5 o'clock)
Hipocodificação
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Be + Verb-ING
e.g. He won’t be having fun at the party.
O agente comunicador, embora possa produzir efeitos educativos, não elabora a mensagem a partir das regras reconhecidas como pedagógicas.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I will not be beingYou will not be beingHe/She/It will not be beingWe will not be beingYou will not be beingThey will not be being
Form of word "to have":
I will not be havingYou will not be havingHe/She/It will not be havingWe will not be havingYou will not be havingThey will not be having
Caracteriza-se pela inexistência , de um ponto definido no espaço ou do tempo.
Structure:
Subject + Will Be + Verb-ING
e.g. You will be having fun at the party.
Internet, comunicação social, TV, rádio (comunicação cultural)
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I will be beingYou will be beingHe/She/It will be beingWe will be beingYou will be beingThey will be being
Form of verb 'to have':
I will be havingYou will be havingHe/She/It will be havingWe will be havingYou will be havingThey will be having
Comunicação formal
Future Simple is used:
- to predict an event in the future
- to invite
- to give orders
- to express willingness
- for actions that have not yet occurred but that will occur at a future date
Hipercodificação
A mensagem adquire uma função pedagógica.
Continuum espacio-temporal (no mesmo tempo e no mesmo lugar)
Future Simple with 'will'' is used:
- to predict the future
- for something with absolute certainty
- when we're talking about a decision at the moment of speaking
- promises, requests, refusals, offers
- future facts
Some adverbs used with Future Simple:
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
Mesmo tempo/Diferente lugar
Structure:
Subject + Won’t (will not) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. You won’t see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
Os interlocutores comunicam no mesmo momento ou em tempo diferente (em deferido)
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I will not beYou will not beHe/She/It will not beWe will not beYou will not beThey will not be
Form of word "to have":
I will not haveYou will not haveHe/She/It will not haveWe will not haveYou will not haveThey will not have
Mesmo tempo/Mesmo lugar
Structure:
Subject + Will + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I will see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
Emissor e recetor estão em presença, no mesmo lugar (em direto)
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I will beYou will beHe/She/It will beWe will beYou will beThey will be
Form of verb 'to have':
I will haveYou will haveHe/She/it will haveWe will haveYou will haveThey will have
Comunicação eficaz
É a perspetiva conjugada, os critérios devem realizar-se conjuntamente, pois só faz sentido falar-se em comunicação eficaz se são obtidos bons resultados, possíveis de serem alcançados com a utilização de técnicas comunicativas apropriadas que proporcionem uma atuação diversificada, de adequação mútua e de adaptação aos diferentes contextos comunicativos.
Sistema educativo
There are four Past tenses:
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple
- Past Perfect Continuous
Educação informal
Past Perfect Continuous is used:
- for an action that started in the past and continued up to another point in the past
- to show cause and effect
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Continuous:
- since (e.g. since yesterday)
- for (e.g. for 10 years, for 6 months)
Projeção Pedagógica
Fatores educativos desconhecidos e descontrolados.
Dimensão descritiva da pedagogia
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
Had I been being?Had you been being?Had he/she/i been being?Had we been being?Had you been being?Had they been being?
Form of word "to have":
Had I been having?Had you been having?Had he/she/it been having?Had we been having?Had you been having?Had they been having?
A que não se realiza a partir da definição prévia de objetivos ou finalidades pedagógicas.
A que não é metódica, estruturada, consciente e intencional.
Structure:
Subject + had been + Verb-ING
e.g. They had been talking for over an hour before I arrived.
A que não se faz de forma institucionalizada.
Structure:
Had + Subject + been Verb-ING?
e.g. How long had they been living in London before moving here?
É espontânea a partir das relações do individuo com o seu ambiente humano, social, cultural, ecológico.
Structure:
Subject + hadn’t been/had not been + Verb-ING
e.g. I was tired because I hadn't been sleeping.
Educação não formal
Past Continuous is used for:
- an action that happened before another action in the past
- an action that started in the past and continued up to a given time in the past
- an action done several times up to a point in the past and continued to do after that point
- an action that happened in the past but is important at the time of reporting
Some adverbs used with Past Continuous:
- always, only, never, ever, still, just
Reconversão profissional
Reciclagem
Desenvolvimento comunitário
Tempos livres
Structure:
Was/ were + Verb-ING?
e.g. Were you studying when she called?
Animação sociocultural
Structure:
Subject + wasn’t (was not)/ weren’t (were not) + Verb-ING
e.g. You were not studying when she called.
Educação permanente e de adulto
Structure:
Subject + was/ were + Verb-ING
e.g. You were studying when she called.
Educação Formal
Past simple expresses:
- an action that happened in the past and has no connection with the present
- an action that happened once in the past
- an action that happened regularly in the past
- an action that was true for some time in the past
- an event or action that already occurred
- an action that is finite - has both a starting and a stopping point
Some adverbs used with Past Simple:
- yesterday
- last month, last year
- ago (e.g. two days ago)
- in (e.g. in 1997)
- never, always, seldom, often, frequently, occasionally, once, twice
Ensino-aprendizagem
Structure:
Did + subject + Base Form of the Verb?
e.g. Where did you meet her?
Meios de formação
Structure:
Subject + did not/didn’t + Base Form of the Verb
e.g. They didn’t like my food.
Instituições
Structure:
Subject + Verb in Past Simple (2nd form)
e.g. They lived in Spain three years ago.
Sistema comunicativo
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
Cultural
Present Perfect Continuous is used:
- to describe an action that started in the past and has continued up to the present
- to describe an action that has just finished
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect Continuous:
- always
- only
- never
- ever
- still
- just
Designado em massa
Structure:
Subject + have/ has been + Verb-ING
e.g. They have been learning French for two years.
Comunicação social para o público que utiliza o respetivo meio.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I have been beingYou have been beingHe/She/It has been beingWe have been beingYou have been beingThey have been being
Form of verb 'to have':
I have been havingYou have been havingHe/She/It has been havingWe have been havingYou have been havingThey have been having
Grupal
Present Perfect is used for:
- an action that occurred at a time which is indefinite and has its effect on the subject
- an action that occurred many times and has the possibility to occur in the present/future
- an action that began in the past and is still going on in the present
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect:
- just
- already
- yet
- for
- never/ever
- up to now
Colaboração entre vários indivíduos
Structure:
Subject + have/ has + Past Participle (3rd Form of the Verb)
e.g. She has finished the letter.
Os papeis de transmissão e de receção estão mais divididos do que no nível anterior .
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I have beenYou have beenHe/She/It has beenWe have beenYou have beenThey have been
Form of verb 'to have':
I have hadYou have hadHe/She/It has hadWe have hadYou have hadThey have had
Interpessoal
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
- now, right now
- at this moment
- at the moment
- continually
- perpetually
- this year
- this season
- forever
Entre dois indivíduos
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + Verb-ING
e.g. You are eating now.
Contexto físico muito próximo (Face to Face)
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I am beingYou are beingHe/She/It is beingWe are beingYou are beingThey are being
Form of verb 'to have':
I am havingYou are havingHe/She/It is havingWe are havingYou are havingThey are having
Intrapessoal
Present Simple is used for:
- habits
- general truths
- repeated actions of events
- fixed arrangements/timetables
- feelings/opinions/beliefs
- instructions.
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
- always
- usually
- seldom
- never
- sometimes
- often
- frequently, generally
- habitually, occasionally
- once, twice
Autocomunicação
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + do not / don’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
Subject (He, She, It) + does not / doesn’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
e.g. He doesn’t work in a bank.
Ocorre dentro da própria pessoa, que assue as funções de emissor e de recetor.
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.