realizată de Aiden Broughton 2 ani în urmă
129
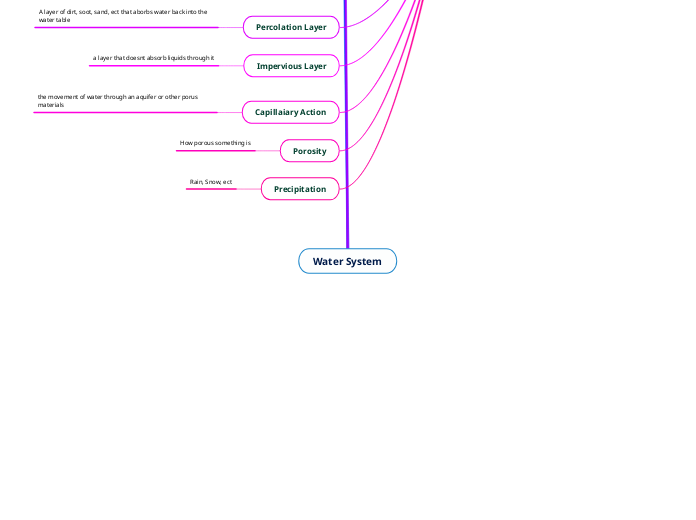
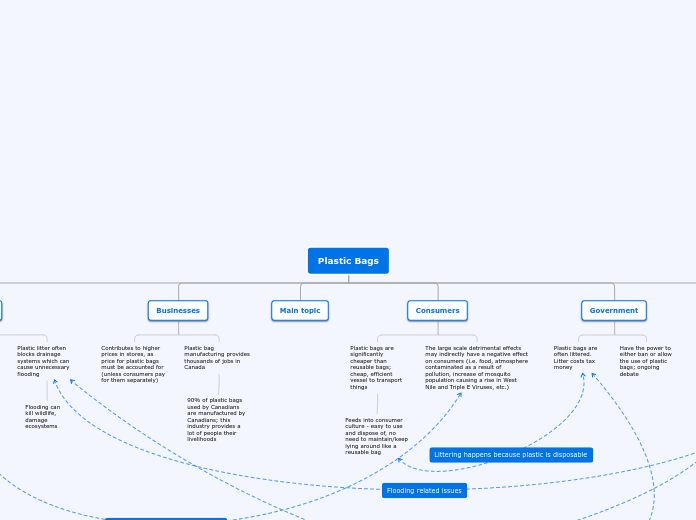
Water System
Watersheds are crucial systems that drain into major bodies of water such as the Atlantic Ocean, Arctic Ocean, Hudson Bay, Gulf of Mexico, and Pacific Ocean. Understanding the dynamics between groundwater and surface water reveals key differences in quality, temperature, availability, ease of access, mineral content, and pollution levels.