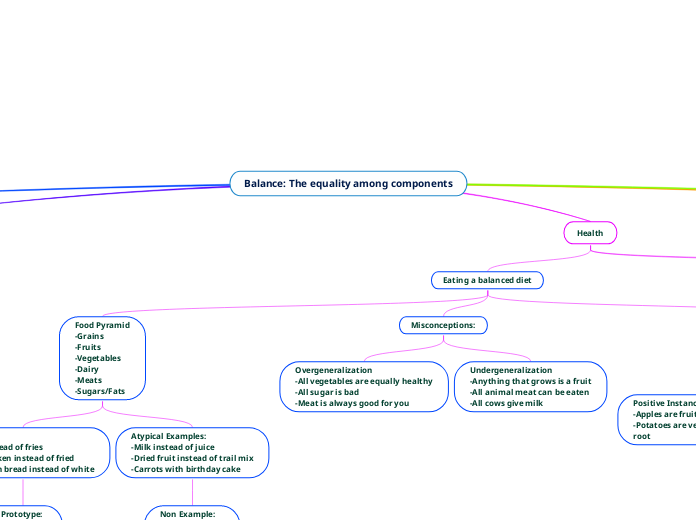
Balance: The equality among components
Physical
Balance while being active
Science
State of equilibrium
Health
Healthy Choices
-Food
-Exercise
-Sleep
Emotional Balance
Eating a balanced diet
Conceptual Understanding
-Fruits grow from flowering part of plants
-Vegetables are other parts of plants
-Farmers are crucial to food production
Negative Instances
-Tomatoes are vegetables
-Food production is not effected by farmers.
Positive Instances
-Apples are fruit because they have seeds
-Potatoes are vegetables because it is the root
Misconceptions:
Undergeneralization
-Anything that grows is a fruit
-All animal meat can be eaten
-All cows give milk
Overgeneralization
-All vegetables are equally healthy
-All sugar is bad
-Meat is always good for you
Food Pyramid
-Grains
-Fruits
-Vegetables
-Dairy
-Meats
-Sugars/Fats
Atypical Examples:
-Milk instead of juice
-Dried fruit instead of trail mix
-Carrots with birthday cake
Non Example:
-Frozen Burritos
-Cookies
-Ice Cream
Examples:
_Apples instead of fries
-Baked chicken instead of fried
-Whole grain bread instead of white
Prototype:
-Apple
-Chicken
Mathematical
Equality among equations
Third Grade Students: Ages 8-9
-Learning to manage feelings and emotions
-Becoming more independent and mature
-Passionate about meaningful subjects
-Speak with grammatic accuracy
-Express selves in writing
-Read multiple genres
-Better spatial understanding
-Starting on complex math problems
-30 minute attention span
Prior experience will be limited.
Vygotskian Considerations
-Stage one of ZPD: Need help with those more capable or experienced.
Piagetian Developmental Level: Concrete Operational Stage