Macromolecules and
other things inside cells
DNA
Transcription
DNA to mRNA
Translation
Produces Proteins
Codon table. More than one codon sequences can make the same protein
A set of 3 codons codes for one protein
mRNA to protein
Replication
Needs certain polymerases, an origin of replicaton, replication fork, etc.
DNA to DNA
Can be seen in the form of Chromosomes
Nucleosomes and histones are responsible for giving chromosomes their curly shape; they increase the surface area
Made of nucleotides joined together by hydrogen bonds
Nucleotides include Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine
Stands for: Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
Lipids
Carbohydrates
Cell
Phosphlipid Bilayer
Hydrophobic (water repelling) tails
Hydrophillic (water loving) head
Organelles
Subtopic
Extracellular matrix
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Protein Synthesis
Mitochondria
contains own DNA
provides energy for the cell for processes
Powerhouse of the cells
Vacuoles
Golgi Apparatus
Nucelus
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Cell Division
Meiosis
Makes gametes
Forms four haploid cells
Mitosis
Makes somatic cells
Forms two diploid cells
Proteins
Other Cell
Contains the same DNA of all of the other cells
Transport proteins
Separated by different junctions
Cell Signaling through membranes
Sends out signals to other cells to make proteins amongst other thngs
Plant
Cell Wall
Organelles different from Animal cell include:
Choloroplasts
Double Membrane
Stroma
Thylakoid
Granum
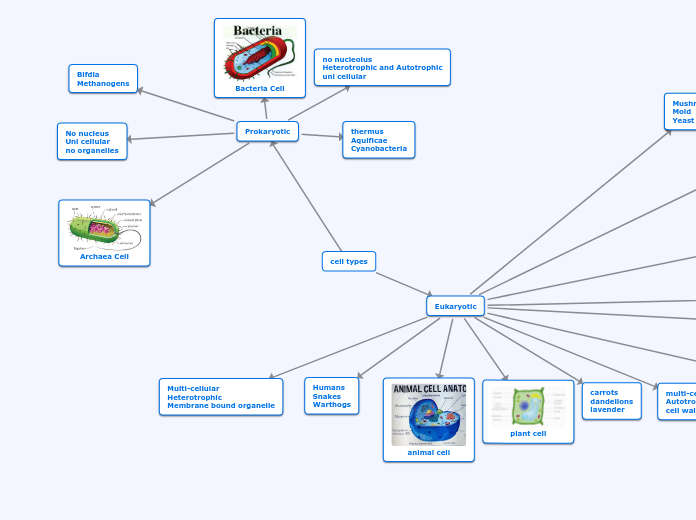
Prokaryotic Cells
Single Cellular Organism
May contain extra DNA in plasmids
Do not have a membrane bound nucleus
Ex. Bacteria
Can have flagellum or cilia
Water
Chemical Formula: H2O
Oxygen Ions
Hydrogen ions
Connected by hydrogen bonds
Can exist in different states of matter