Floating topic
Biotechnology Term 1
Applications of Biotechnology
GMOs
improve quality of food
plants to produce new proteins
BT corn
extend growing season
fishberries
to protect crops from insects
Genetically Modified Organisms
White
use of enzymes and microorganisms to produce products
industrial processes and gene based technologies
Red
CRISPR technology
pair of molecular scissors and can cut DNA and edit genomes
can aid in curing/treating a range of medical conditions
producing new drugs, use of stem cells etc
biological advances within the health department
Black
vaccines are an innovation that is effective against bio-terrorism
the use of biological agents to cause illness or death to plants, animals and humans
bioterrorism and biological warfare
Green
improving crops in a accurate, targeted way
agriculture-related
Yellow
golden rice
adult cow stem cells to make bovine muscle tissue (hamburger meat)
water use down by 96%
greenhouse gas emissions down by 96%
land is decreased by 99%
goals include producing more nutritious and fortified foods while reducing environmental impacts
food production
Grey
environment and biodiversity
environmental protection
Purple
laws, ethics and philosophy around biotech
Golden
computational science
bioinformatics
Blue
ocean resources to create products
aquatic
Microorganisms
Diseases
Pneumonia
hospital to recieve antibiotics and fluids through an intravenous line
incubation period - depends on type of pathogen causing it
transmitted when people infected cough, sneeze or talk
sends respiratory droplets into air
streptococcus pneumoniae
HPV
incubation period - 2-3 months
surgery, cryotherapy, podofliox etc
spread through intimate contact
genital-skin during sexual acitivty through tiny breaks in the skin
not spread through blood or body fluid
human papillomavirus
Viruses
Differences
viruses always cause harmful effects, bacteria can be useful and dont always cause harm
viruses don't fit in any kingdom of life
viruses are non-living, bacteria are living
Similarities
no nucleus, yet still contains genetic material
both prokaryotic
both can cause disease
both can be considered pathogens
Bacteriophage
Bacteriophage Life Cycle
release (lysis)
host cell lyses and releases new viruses
assembly
viruses assemble
biosynthesis/synthesis
phage DNA replicates and makes new virus parts
entry/penetration
the viral DNA enters the host cell
attachment
the phage attaches to the surface of the host cell
infects bacteria
the host is bacteria specifically
contains
nucleic acid
can be RNA or DNA
protein coat/capsid head
they require a living host to reproduce
are unable to function outside of a living host cell
they do not fit into the 5 kingdoms of life
animals, plants, fungi, protists & bacteria
they are all hosts of viruses
viruses infect all types of organisms
considered non-living
due to being non cellular
Bacteria
isn't always harmful
treated using antibiotics
specifically targets bacteria (no other body cells)
considered living
due to having cells
reproduce via binary fission
exponential growth if bacteria has correct nutrients and conditions to grow
there are differences in bacteria due to
they impact they have on human life
the antibiotics used to treat them
their Gram Stain
either gram-positive or gram-negative
their shape
spiral
rod-shaped
e. coli
referred to as bacilli
spherical
streptococcus
referred to as cocci
the temperature they can survive in
the food they eat
autotroph
make their food using either photosynthesis or chemosynthesis
heterotroph
energy comes from eating other organisms/organic carbon
the environment they live in
alkaliphiles
live in alkaline environments up to pH 10-11
acidphiles
live in environment as acidic as pH 1-0
anaerobic bacteria
grows in the absence of oxygen
aerobic bacteria
grows in the presence of oxygen
Pathogens
pathogens are organisms that cause harm to another organism
viruses or harmful bacteria
DNA, RNA and Proteins
Codon Charts
Example
amino acids - meth, alu
mRNA - AUG GAA
coding DNA - ATG GAA
template DNA - TAC CTT
aids in identifying the amino acids made, based on the mRNA
Proteins
different arrangements of amino acids can make proteins that are extremely strong, or elastic and flexible
depends on overall function
about 42% of body's dry weight
made up of amino acids
RNA
Types
Ribosomal RNA
along with protein, makes up the ribosome
rRNA
Transfer RNA
transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are made
tRNA
Messenger RNA
produced in the nucleus but travels through the pores in the nucleus, into the cytoplasm
copies DNA's code and carries the genetic information to the ribosomes
used to carry a message based on the DNA
mRNA
mRNA will be complementary to DNA
Transcription
RNA polymerase binds the DNA just before the genes
separates the two strands - closes just behind it
like a zip
eg. ATG becomes AUG
when the DNA code becomes RNA code
the RNA bases (A,C,G,U) are grouped in threes
known as codons
the DNA bases (A,C,T,G) are grouped in threes
known as triplets
takes place in the nucleus
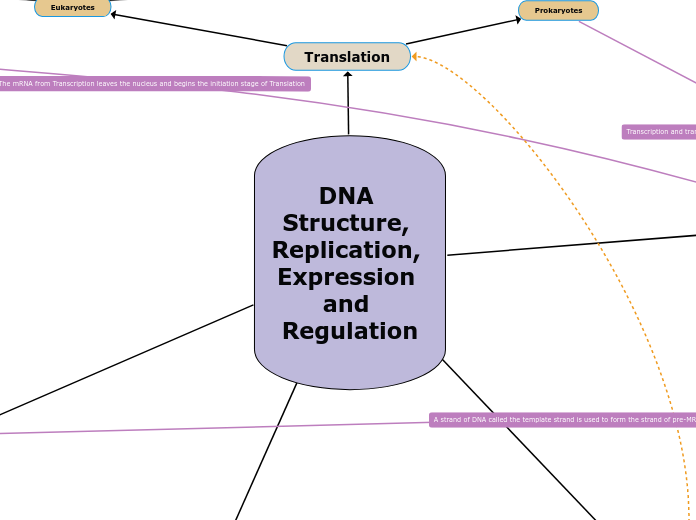
Translation
translating the mRNA sequence into an amino acid chain
amino acid chain = polypeptide
takes place in the cytoplasm (at ribosomes)
used to transfer genetic code from nucleus to the ribosomes
to make proteins
uracil (u)
ribose sugar
shorter chain of nucleotides (compared to DNA)
single stranded
Ribonucleic Acid
polymer - nucleic acid
monomer - nucleotide
Function
transmission of genetic information
to make other cells and new organisms
long term storage of genetic information
Composition
thymine (t)
cytosine (c)
guanine (g)
adenine (a)
phosphate backbone
deoxyribose sugar
long chain of nucleotides
forms a double strand
double helix
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Nucleic acid
phosphate, sugar (deoxyribose or ribose) and nitrogenous base
nitrogenous bases - A, G, T, C and U
A and U in DNA and RNA
G and C in DNA and RNA
A and T in DNA
the nucleotide is the monomer (subunit) of nucleic acid
DNA and RNA molecules
Cells and Organelles
Cell Theory
all cells come from pre-existing cells
through cell division
cells are the smallest working units of all living things
all living things are made up of cells
Prokaryotes
more simple - compared to eukaryotes
more energy efficient
most commonly unicellular
bacteria
DNA
no nucleus
have circular DNA
plasmid/s
Cytoplasm
holds organelles
gell-like substance
provides the cell with support and shape
controls what goes in and out of cell
Eukaryotes
animals, plants, fungi, protists cells
most commonly multicellular
have membrane-bound organelles
Plant Cells
Rigid, structural shape
Endoplasmic Reticulum
protein synthesis
Mitchondria
controls entry and exit of substances
Large vacuole
Chloroplast
turns sunlight into energy
responsible for photosynthesis
Cell wall
protects cell
provides cell with support and shape
Animal Cells
Organelles
Nucleus
Contains linear DNA
Golgi Body
involved in transporting materials
packages and transports materials around the cell
Ribosomes
protein synthesis
Mitochondria
"powerhouse of the cell"
provides energy for a cell to move and divide
Endoplasmic reticulum
Rough
protein production, protein folding, quality control
passageways that carry proteins around the cell
Smooth
steroid/hormone production
site of lipid (fat) manufacture & metabolism
Plasma membrane
controls entry and exit of substances from the cell
Small Vacuole
commonly filled with fluid and waste
a vesticle enclosed by a membrane
Lysosomes
transports undigested materials to plasma membrane
breaks down and digests waste
Biotechnology Term 2
Antimicrobials
Antivirals
aims to target virus
not host cell
extracellular form of the virus is called a virion
once it penetrates the host, it dissembles
freeing its genetic material to translate new viral proteins
Antibiotics
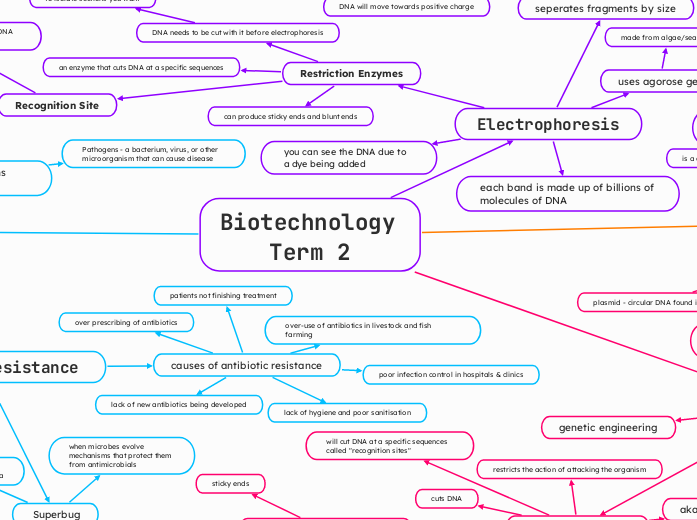
Antibiotic Resistance
Superbug
when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials
bacteria that are resistant to several types of bacteria
causes of antibiotic resistance
lack of new antibiotics being developed
lack of hygiene and poor sanitisation
poor infection control in hospitals & clinics
over-use of antibiotics in livestock and fish farming
patients not finishing treatment
over prescribing of antibiotics
causes naturally, through genetic changes
1. a few drugs are resistant
2. antibiotics kill bacteria causing illness susceptible/sensitive
3. drug resistant bacteria are not allowed to take over
4. some bacteria give their drug resistance to other bacteria
bactericidal - kills bacteria
bacteriostatic - slows the growth of bacteria
broad spectrum - if they affect a wide group of bacteria
more potential to make superbugs
narrow spectrum - if they affect only a few types of bacteria
target cell walls, ribosomes, enzymes for DNA & RNA synthesis
kills bacteria
not viruses or fungi
by blocking essential processes, killing them or stopping them from growing/multiplying
use to reduce the number of pathogens and prevent them from spreading
Pathogens - a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease
Antiseptics
non-specific
isocol, betadine
used to kill pathogens
Disinfectants
dettol, pine cleen, white king
used to kill pathogens on surfaces
eg. door handles and hospital equipment
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Step 3 - Elongation/Synthesis
use nucleotides to make new DNA strand
Step 2 -Annealing
primers connect to target
cool to 50 degrees
Step 1 - Denaturation
approx 90 degrees
separates DNA strands
Materials needed
Primer
define section of DNA to be cloned
can bracket target sequence
nucleotides
(A,T,C,G)
DNA polymerase enzyme
will add the nucleotides to make new copies of DNA
heat resistant polymerase enzyme
taq polymerase
template strand/target DNA
only need one piece of DNA
to make lots of copies of the target DNA
DNA Manipulation
allows the opportunity to put a gene of interest into a plasmid
plasmid - circular DNA found in bacteria
self replicating
small supplemental circles of DNA
Ligase joins sticky ends to form recombinant plasmids
ligase is an enzyme that glues DNA together
Restriction enzymes
act as scissors
ligase acts as tape/glue
produces equal lengths
not easy to join back together
blunt ends
produces overhanging ends
can bind to any complementary DNA
sticky ends
will cut DNA at a specific sequences called "recognition sites"
cuts DNA
aka restriction endonucleases
restricts the action of attacking the organism
genetic engineering
Electrophoresis
you can see the DNA due to a dye being added
each band is made up of billions of molecules of DNA
Restriction Enzymes
can produce sticky ends and blunt ends
Recognition Site
the site where the restriction enzyme will cut DNA at a specific sequence
DNA needs to be cut with it before electrophoresis
to isolate sections you want
an enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequences
seperates fragments by size
can determine the length of DNA
using a 'ladder'
can make it easier to determine the size/length of an unknown DNA through comparing it to known DNA lengths
using electrical field
DNA will move towards positive charge
long pieces travel slow and lag behind
small pieces of DNA travel further
DNA is negatively charged
uses agorose gel
is placed in a liquid called running buffer
will protect the user from electric shock
is a conducter
made from algae/seaweed