Lecture 5
Communities of Practice
Organizational Learning & Social Capital
Social Capital
Values
Hard to quantify value
need strong relationships within groups as well as "bridging" ties between groups
maintenance of positive relations between different subgroups
different than other types of capital
institutions, relationships and norms that shape the quality and quantity of an organization's social interactions
Human Capital
education, skills and background necessary to be productive in an organization or profession
Knowledge Sharing
Implications
Avoiding mistakes
Standardizing professional practices.
Connecting professionals across platforms, across distances.
Obstacles
lack of trust between provider of knowledge and receiver of knowledge
rewarded for what they know
disincentive to share
Facilitating
credibility of content and the source
organizational culture and climate
knowledge is property
knowledge is power
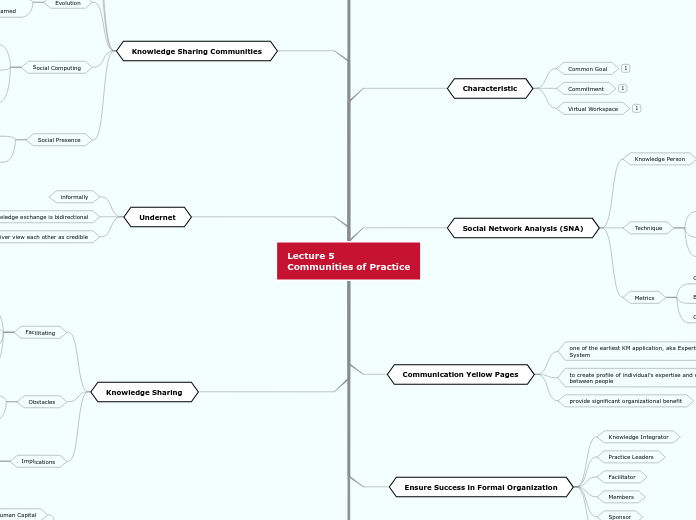
Undernet
Sender and receiver view each other as credible
Knowledge exchange is bidirectional
informally
Knowledge Sharing Communities
Social Presence
Example
- Facebook news feed on recent posts on friend's walls
How much of a sense members have that other people are present
Social Computing
Example
- recommender systems such as those the advise you on which books you would enjoy
to enhance the activity and performance of people, organizations and systems.
Digital systems that draw upon social information and context
Evolution
Lessons Learned
Best Practice
Interconnecting the social networks of people who produced the knowledge
Provide access to data and documents
Roles and Responsiblities
Elders
Leaders
Regulars
Novices
Visitors
Ensure Success in Formal Organization
Champion
Sponsor
Members
Facilitator
Practice Leaders
Knowledge Integrator
Communication Yellow Pages
provide significant organizational benefit
to create profile of individual’s expertise and connections between people
one of the earliest KM application, aka Expertise Location System
Social Network Analysis (SNA)
Metrics
Closeness
who are the shortest paths to all others but have an excellent view of happens
Betweenness
who holds a powerful positions as the sole "boundary spanner" between different groups
Centrality
who having the most connections of the link
Technique
can be automated (e.g. email mapping)
Cluster Analysis - process of identifying highly integrated subgroups
visualization tools that can be used together with surveys
Knowledge Person
Knowledge Broker
who develop relationships and networks with, among and between producers/sharers and users of knowledge
Knowledge Sharer
who actively, purposely and happily gives knowledge to others
Knowledge Hoarder
who gathers and guards knowledge for personnel preservation and future use.
Characteristic
Virtual Workspace
A place to store stories, artifatcs, tools, discussions, glossaries, historical events
Commitment
participation fueled by trust, interest, credibility, professionalism, ethical behaviors
Common Goal
improvement of members' profession
Forms of Joint Work in Organizations