MALIGN AND BENIGN PATHOLOGIES IN BREAST
SELF-EXAMINATION
Palpation, inspection
Questioning and physical examination
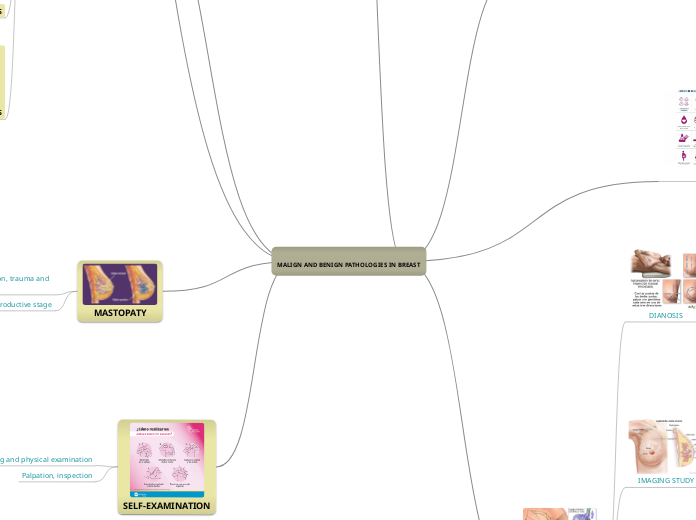
MASTOPATY
-In reproductive stage
-Is associated with pregnancy, lctation, trauma and thrombophlebitis
BENIGN ALTERATIONS
FIBROCYSTIC ALTERATIONS
-Premenopause
-More common
- Pain
-Edema
PLOTIFERATIVE ALTERATIONS
*Athypical dictated epithelium
*Seropurulent exudate
*Adenosis
*Hyperplasia
Phylloid tumor
Slow-growing epithelial neoplasia
- Any age
- Total surgical diagnosys
DUCTAL ECTASY
*Hard and tender erythematous mass
*Perimenopause and postmenopause
* Small abscess at the base of the nipple
MASTITIS
- Related to lactation factors
-Sthapylococcus aureus
- May appear in puerperal phenomena
LIPOMA
*White tummor
*Mobile
*Fatty
*Most common non-epithelial neoplasm
ADENOMA
https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/9e93328e26e5643c8903793c13926345556b5e90/2-Figure3-1.png
-Circumscribed tumors
-Peak incidence at 20-30 years
-Scattered stroma
GALACTOCELE
*Painful breast cyst
*Condensed
*Thick milky liquid
BREAST CANCER
BIOLOGICAL MARKERS
*Axillary lymph node status
The lymph nodes are responsible for filtering lymphatic fluid and detecting chemical changes that indicate infection. When these filter points are in the armpit, doctors may call them axillary lymph nodes.
*HER2/neu
Medir la cantidad del HER2/neu en algunos tipos de células cancerosas sirve para planificar el tratamiento. También se llama c-erbB-2, HER2, receptor 2 del EGF humano y receptor 2 del factor de crecimiento epidérmico humano.
p53
TP53 is a gene that helps stop tumors from growing. It is known as a tumor suppressor. A tumor suppressor works like the brakes on a car. Stops cells from dividing too quickly
*Tumor size
Malignant (cancer): they grow rapidly and often metastasize, that is, they migrate to other parts of the body causing new tumors
*Progesterone
Again, this means that cancer cells can receive signals from progesterone that stimulate their growth.
*Estrogen receptors
A breast cancer tumor is described as “estrogen receptor positive” if it has receptors for that hormone.
IMAGING STUDY
*MRI
*Ultrasound
*Mammography
*Biopsy
DIANOSIS
*Thorough questioning
RISK FACTORS
the use of hormone replacement therapies.
-Age
-Ductal hyperplasia
Subtopicthe diet rich in fats and meats, as well as obesity, sedentary lifestyle and the consumption of tobacco and alcohol.
-Radiotherapy
-Menopause
family history
grandmother, mother, or sister
LUMP
A breast lump is a growth of tissue develops withing your breast. Different types of breast lumps can vary in the way they look and feel.
MAIN FINDINGS
Galactorrhea
*Involutive, bilateral, spontaneous, with pregnanciy and hipothyroidism
Purulent discharge from the nipple
*Atibiotic treatment
*Can produce an abcess
*Infection
Intraductal papilloma
*Surgical removal of the duct
*Bloody discharge
*Main cause of women who are not breastfeeding
Mammary duct ectasia