по Emily Kroening 6 лет назад
444
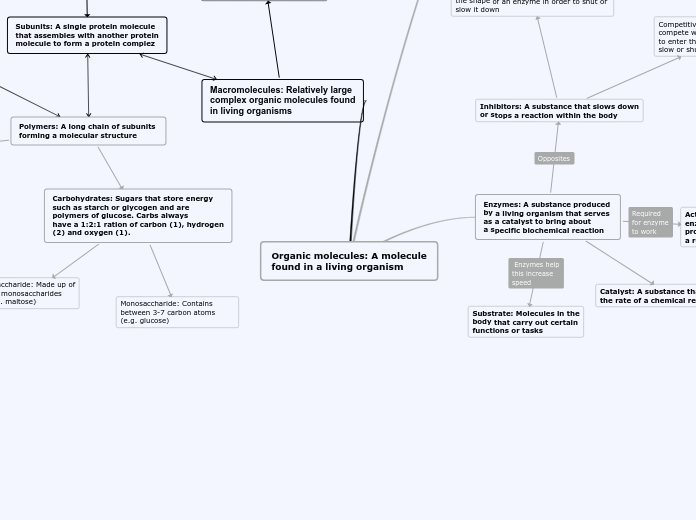
Organic molecules concept map
Living organisms contain a variety of organic molecules, including macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Enzymes, which are proteins, act as catalysts to speed up biochemical reactions, with their activity centered around the active site.