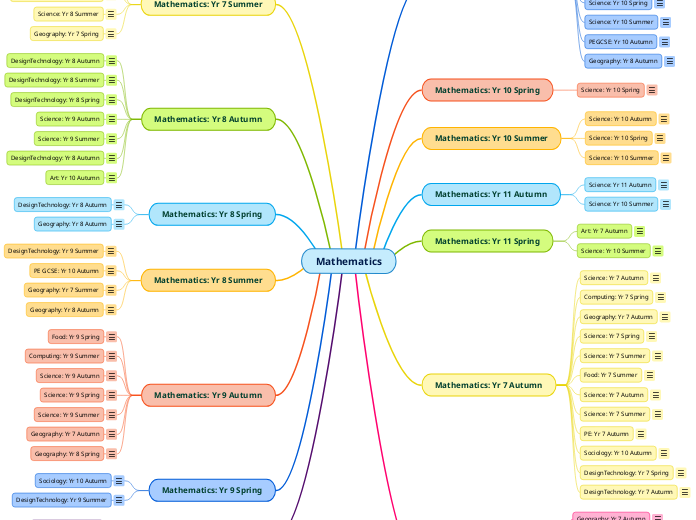
Where next?
You can continue to develop this map without the Smart Map wizard by saving it as a normal Mindomo map.
When have a comprehensive description of the problem, you can move towards finding solutions. Consider a brainstorm as a next step, using the Brainstorming Toolbox Smart Map.
You can delete this topic from the saved map.
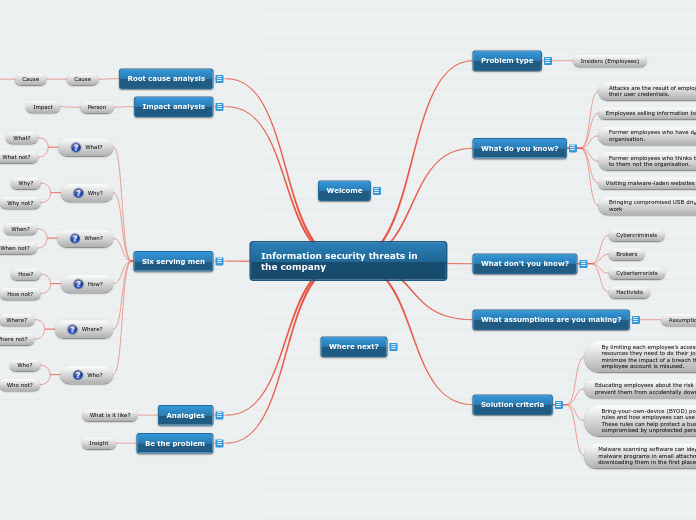
Where next?
You can continue to develop this map without the Smart Map wizard by saving it as a normal Mindomo map.
When have a comprehensive description of the problem, you can move towards finding solutions. Consider a brainstorm as a next step, using the Brainstorming Toolbox Smart Map.
Welcome
Researching and describing a problem clearly is the foundation for solving it. Solutions based on incomplete research or poor descriptions can often fail to reach the root causes.
This Smart Map helps you to research and describe a problem from a number of different angles. It contains a mix of factual information-gathering tools and lateral thinking techniques, to develop perspectives that can point towards solutions.
You can use this map individually and in collaboration with others. It is vital to get consensus on the actual problem you are facing, otherwise there may be no consensus on the solution. Putting the descriptions together in one place helps you to explain and agree upon the basis for finding and evaluating solutions.
You can delete this topic from the saved map.
Welcome, Guest
Researching and describing a problem clearly is the foundation for solving it. Solutions based on incomplete research or poor descriptions can often fail to reach the root causes.
This Smart Map helps you to research and describe a problem from a number of different angles. It contains a mix of factual information-gathering tools and lateral thinking techniques, to develop perspectives that can point towards solutions.
You can use this map individually and in collaboration with others. It is vital to get consensus on the actual problem you are facing, otherwise there may be no consensus on the solution. Putting the descriptions together in one place helps you to explain and agree upon the basis for finding and evaluating solutions.
Information security threats in the company
Name the problem
Identify the problem or issue in a few words and press Enter. This will become the title of your map.
Be the problem
Be the problem is a popular technique for understanding problems. It means developing a character for the problem and describing its nature as if it were a person.
Be the problem
'Be the problem' is a popular technique for understanding problems. It means developing a character for the problem and describing its nature as if it were a person.
Insight
Add an insight
Add a statement describing the problem as if it were a person.
- What does the world look like from the problem's perspective?
- How does it respond in certain situations?
- What does it like or not like?
- What weaknesses does it look for in people or situations?
- What weaknesses does it have that make it vulnerable?
- What strengths does it have that make it 'successful'?
- Does it 'get lucky' sometimes?
- How does it help other people and support their goals?
Analogies
Can you find analogies for this problem?
The underlying characteristics of a problem can sometimes be clearer when it is taken out of context.
Analogies
Can you find analogies for this problem?
The underlying characteristics of a problem can sometimes be clearer when it is taken out of context.
What is it like?
What is 'Information security threats in the company' like?
Is 'Information security threats in the company' like anything else?
- Have similar problems or similar causes been seen in other places?
- What would it look like if you imagined the same problem in a completely different situation? For example, how would the problem behave at a wedding, at a concert, in a supermarket, or underwater?
Six serving men
"Six Serving Men" is based on Rudyard Kipling's poem, which begins:
''I keep six honest serving men
(They taught me all I knew);
Their names are What and Why and When
And How and Where and Who.''
We can profile a problem and perhaps discover more about it by asking structured questions.
Six Serving Men
'Six Serving Men' is based on Rudyard Kipling's poem, which begins:
I keep six honest serving men
(They taught me all I knew);
Their names are What and Why and When
And How and Where and Who.
We can profile a problem and perhaps discover more about it by asking structured questions.
Who?
Who not?
Who does not cause 'Information security threats in the company'?
- Are there people or users who manage to avoid this problem?
- Are they doing something different to everyone else?
Who causes 'Information security threats in the company'?
- Is there any connection with certain people or users?
- Are they doing something different to everyone else?
Where?
Where not?
Where does 'Information security threats in the company' not happen?
- Are there locations or places where the problem does not happen?
- Are there locations where it should happen but doesn't?
Where does 'Information security threats in the company' happen?
- Is there any connection with locations or places?
How?
How not?
How does 'Information security threats in the company' not happen?
- How do you know when the problem is not happening?
- Could the problem actually not be happening, when you think it is?
- Is it really there all the time?
How does 'Information security threats in the company' happen?
- How does the problem appear?
- How do you know the problems is happening?
- Could it be happening when you are not aware of it?
When?
When not?
When does 'Information security threats in the company' not happen?
- Are there times when this problem does not happen?
- Are there times when according to theory, it should happen, but doesn't?
- If it is intermittent, when does it start working again?
When does 'Information security threats in the company' happen?
- Is there any connection with dates, times or other events?
- Is it something that was working once, and has stopped working?
Why?
Why not?
Why is 'Information security threats in the company' not a problem?
- Are there times when this situation occurs, but it is not a problem?
Why is 'Information security threats in the company' a problem?
What?
What not?
What does not cause 'Information security threats in the company'?
- What does not trigger this problem?
- Are there situations or conditions that might be expected to cause it, but don't?
What causes 'Information security threats in the company'?
- What causes or triggers this problem?
- Are there situations or conditions that are not expected to cause it, but do somehow?
Impact analysis
Impact analysis looks at who is affected by the problem - what the consequences are, rather than the causes.
Impact analysis
Impact analysis looks at who is affected by the problem - what the consequences are, rather than the causes.
Person
Who is affected?
Type in a name or role of someone who is affected by 'Information security threats in the company'
Impact
What is the impact?
How is Person affected by 'Information security threats in the company'?
- What are the symptoms?
- What do they have to do when encountering the problem?
- Could they provide more information?
- Could they try doing things in a different way?
Rate the impact by clicking an icon:
High impact - significant consequences
Medium impact - annoying but tolerable
Low impact - negligible effect
Root cause analysis
For analytical problems, root cause analysis can help to unravel indirect causes of problems, leading to more effective solutions. One way to do this is to keep asking "Why?" down to five levels, to understand the reasons behind the reasons.
Root Cause analysis
For analytical problems, root cause analysis can help to unravel indirect causes of problems, leading to more effective solutions. One way to do this is to keep asking 'Why?' down to five levels, to understand the reasons behind the reasons.
Cause
Why does 'Information security threats in the company' happen?
Enter a reason that 'Information security threats in the company' happens.
Why does 'Cause' happen?
Enter a reason that 'Cause' happens.
(Level 2 of 5)
Why does 'Cause' happen?
Enter a reason that 'Cause' happens.
(Level 3 of 5)
Why does 'Cause' happen?
Enter a reason that 'Cause' happens.
(Level 4 of 5)
Why does 'Cause' happen?
Enter a reason that 'Cause' happens.
(Level 5 of 5)
Solution criteria
How will you know when you have solved the problem?
* What will a successful resolution look like?
* How will you filter and assess potential solutions?
* How will you verify that the issue has been solved?
You might want to return to the solution criteria several times as you develop the definition of the problem.
Solution criteria
How will you know when you have solved 'Information security threats in the company'?
- What will a successful resolution look like?
- How will you filter and assess potential solutions?
- How will you verify that the issue has been solved?
You might want to return to the solution criteria several times as you develop the definition of the problem.
Malware scanning software can identify potentially dangerous malware programs in email attachments and block users from downloading them in the first place.
Bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies help set the ground rules and how employees can use personal devices at work. These rules can help protect a business from being compromised by unprotected personal devices.
Educating employees about the risk of malware can do a lot to prevent them from accidentally downloading ransomware.
By limiting each employee’s access to only the specific resources they need to do their job, organizations can minimize the impact of a breach that occurs when an employee account is misused.
Add solution criterion
Add a solution criterion. Make sure you consider:
- Minimum acceptable success criteria
- Meeting constraints on solutions, e.g. cost, time, resources
- Ensuring that the symptoms will disappear
- Resolving the impact on various users
- Addressing the root causes
- Validating the solution against known data
What assumptions are you making?
In identifying the problem and the probability of a solution, what assumptions are you making?
Assumptions can sometimes be hard to see or accept. For example, if the "problem" is that sales of a certain product are too low, you may naturally aim to increase sales. You are ''assuming'' that the market demand for this product will continue. But if the demand disappeared overnight in a storm of negative publicity, then the original problem and solution also change. So the problem and logical solution are partly based on an assumption.
What assumptions are you making?
In identifying the problem and the probability of a solution, what assumptions are you making?
Assumptions can sometimes be hard to see or accept. For example, if the 'problem' is that sales of a certain product are too low, you may naturally aim to increase sales. You are assuming that the market demand for this product will continue. But if the demand disappeared overnight in a storm of negative publicity, then the original problem and solution also change. So the problem and logical solution are partly based on an assumption.
Assumption
Add an assumption
Identify an assumption you are making in both the description of the problem and the logical solution.
- What would happen if the assumption changed?
- What if the assumption is not valid?
- Might different assumptions also apply?
What don't you know?
What other information might help, but is not available today?
* How would it help?
* How could you obtain it?
* Can you work without it?
* What are the risks or consequences of not knowing?
* Who else might have further information and insight?
What don't you know?
What other information might help, but is not available today?
- How would it help?
- How could you obtain it?
- Can you work without it?
- What are the risks or consequences of not knowing?
- Who else might have further information and insight?
Hactivists
Cyberterrorists
Brokers
Cybercriminals
Add an unknown factor
Identify information or data that is not known or not reliable, and what you can do to find it. Think about:
- Missing information
- Information that could be unreliable
- Information from reliable sources that is factually wrong
- Other people who might have useful information or experience
What do you know?
Factual data about the problem
What do you know?
What factual data do you already have about 'Information security threats in the company'?
Bringing compromised USB drives or other personal devices to work
Visiting malware-laden websites
Former employees who thinks that accumulated data belongs to them not the organisation.
Former employees who have demoted to fired within the organisation.
Employees selling information to Media or outsiders.
Attacks are the result of employees intentionally misusing their user credentials.
Add a piece of data
Add an item of data or a reference to it. Think about:
- Measurements and samples
- Statistics and trends
- Surveys
- Symptoms, documented evidence and verbal stories
- Possibly related incidents or symptoms
Problem type
Whether this is mainly a creative or analytical problem
What type of problem is this?
Is 'Information security threats in the company' a creative issue or an analytical one?
- Do you need an inventive or innovative solution, to create something that does not exist today?
- Do you need to change something and do it in a different way?
- Do you need to diagnose and fix something that is broken?
Insiders (Employees)
Describe the problem type
Select the problem type or enter your own description.
Create something newChange somethingFix something broken