Estimula las funciones
envueltas en reposo
Grupo 1:
Zoriely Amador Ríos
Noritza Caraballo Rodríguez
Hans Ferrer Yulfo
Rafael Ramos Franco
Ivonne Rosario Calderón
Beverly Santos Sierra
Estimula las funciones
envueltas en las
respuestas del
"fight or fly"
COMPONENTES:
-Fibras preganglionares
largas se originan en el asta
lateral de la médula espinal
(nervios craneanos III, VII
IX, X y sacrales S2-S4 del
cordón espinal)
-Fibras postganglionares
cortas
-No presenta ramificación:
Específico
COMPONENTES:
-Fibras preganglionares
cortas se originan en
T1 al L2-L3 del cordón
espinal
-Fibras postganglionares
largas
-Presenta ramificación
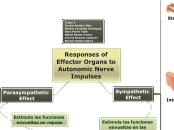
Responses of Effector Organs to Autonomic Nerve Impulses
Parasympathetic
Effect
Sympathetic Terminal Heteroreceptor
Parasympathetic Terminal
Autoreceptor
Receptors: M2 , M4
Nasopharyngeal glands
Increased secretion
Increased Potassium and water secretion
Receptors: M3, M2
Adrenal gland
Secretion of Epiniphrine & Norepinephrine
Receptor: N (α3)2 (β4)3 & M (secondarily)
Secretion
Sweat glands
Generalized secretion
Receptor: M2 & M3
Erection
Neurotransmitter:
Receptor: M3
Variable
Increase motility and tone of ureters (?)
Stimulation of trigone and sphincter
High contraction of detrusor muscle
Receptor: M3>M2
Renin Secretion
NO Innervation
Contraction of kidney ducts
Neurotransmitter:
Acetylcholine
Receptor: M
Increased secretions
Stimulation of secretions
Relaxation of the sphincter
Receptor: M3, M2
Increased motility and tone
Stimulation of
bronchial glands
Receptor: M2, M3
Contraction of tracheal and
bronchial smooth
muscle
Receptor: M2 = M3
Endothelium
Increases NO Synthetase
No innervation of Renal Blood Vessel
Dilation of Salivary Glands
Receptor M3
No innervation of Abdominal Viscera
No innveration of Cerebral Blood Vessel
Dilation of Skeletal Muscle
No innervation of Skin and Mucosa
No innervation in Coronary Artery
Slighltly decrease in ventricle contractility
Little effect in the
His-Purkinje system
Reduction in atrioventricular
conduction velocity: AV block
Reduction in atria
contractility and
shortened AP duration
SA node:
Raduction in
Heart rate
Receptor: M2>>M3
Contraction of
ciliary muscle for
near vision
Receptor: M3,M2
Contraction of the
sphincter muscle, iris
(miosis)
Neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine
Receptor: M3, M2
Sympathetic
Effect
Parasympathetic Terminal Hereroreceptor
Inhibition ofAcetylcholine release
Receptors: α2A>α2C
Sympathetic Terminal Autoreceptor
Inhibition of Norepinephrine release
Receptors: α2>α2C (α2B)
Neurohypophysis
ADH secretion
Receptors: β1
Pineal Gland
Melatonin Synthesis
Salivary Glands
Potassium and water secretion
Receptors: α1
Fat Cells
Lipolysis inhibition
Receptors: α2
Lipolysis; Thermogenesis
Receptors: α1; β1, β2, β3
Pancreas
Islet β cells
Increase secretion
slightly
Receptors: β
Decrease secretion substantially
Receptors: α2A
Acini
Decrease secretion
Liver
Glicogenolysis & gluconeogenesis
Receptor: α1, β2
Spleen Capsule
Constraction
Male Skin
Localized secretion
Pilomotor muscles
Neurotransmitter:Norepinephrine/Epinephrine
Sex Organs
Ejaculation
Uterus
Nonpregnant Relaxation
Relaxation of the uterus
Pregnant contractions
Urether
Increase motility and tone of ureters
Neurotransmitter:
Norepinephrine
Urinary Bladder
Contraction of trigone and sphincter
Relaxation of detrusor muscle
Neurotransmitter:
Norepinephrine/
Epinephrine
Kidney
High stimulation of renin secretion
Subtopic
Neurotransmitter: Norepinephrine/
Epinephrine
Receptor: β1
Decrease renin secretion
Relaxation of kidney ducts
Gallbladder
Relaxation
Intestine
Decreased secretions
Stomach
Contraction of the sphincter
Decreased motility and tone
Receptor: α1, α2, β1, β2
Inhibition of secretions
Receptor: α2
Lung
Lower secretion of
bronchial glands
Higher secretion of
bronchial glands
Relaxation of tracheal and
bronchial smooth
muscle
Neurotransmitter: Epinephrine/Norepinephrine
Receptor: β2
Blood Vessels
Veins Dilation
Veins Constriction
Increases Renal Dilation
Receptor:β1
Increases Renal Constriction:
Increase Salivary Glands
Constriction
Dilation of Abdominal Viscera
Increases Abdominal Viscera
Constriction
Increases pulmonary dilation
Increases pulmonary constriction
Slight cerebral constriction
Increases skeletal muscle dilation
Increases skeletal muscle contriction
Receptor:α1
Increases skin and mucosa constriction
Receptor:α1,α2
Increases coronary dilation
Increases constriction
of coronary artery
Receptor: α1,α2
Heart
Increases ventricle contractility,
conduction velocity, automaticity
and rate of idioventricular pacemakers
Increase in automaticity
and conduction velocity
in the His-Purkinje system
Increase in atrioventricular
conduction velocity
and automaticity
Receptor:β1>β2
Increase in atria
contractility and
conduction velocity
SA node:
Increase in
Heart rate
Receptor: β1>β2
Eye
Secretion in
lacrimal glands
Receptor: α
Relaxation of
ciliary muscle for
far vision
Neurotransmitter: Norepinephrine/Epinephrine
Receptor:β2
Contraction of the
radial muscle, iris
(mydriasis)
Neurotransmitter: Norepinephrine
Receptor: α1