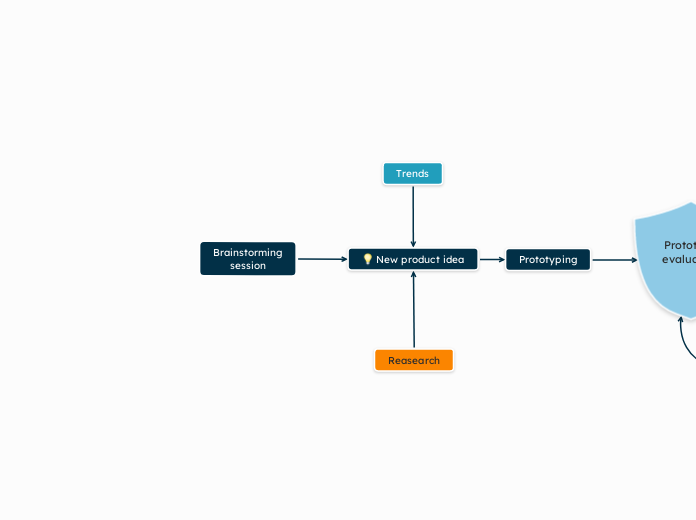
Teaching, Learning & Developing
Curricular
Assessment
Standardized tests
Cons
Does not always match what is taught in class
Puts pressure on students and teachers
Pros
Ensure a standard for instruction
To assess effectiveness of instruction
Norm-referenced test
Criterion-referenced test
Constructed-response questions
Essay
Short-answer
Selected-response questions
Multiple-choice
Matching
True/false
Table of Specifications
Help teachers build a well-balanced tests
Summative evaluation
After instruction to indicate how well students learned the material
Formative assessment
Feedback most effective when it is specific and gives guidance for improvement
Use seatwork, homework, class participation, or quizzes to assess understanding
Ask students questions throughout lesson and close monitoring to assess understanding
Diagnostic assessment
Completed before instruction to determine starting point
Philosophy
Constructivist
Students construct their own meaning and knowledge under teacher guidance
Student-centered and teacher-centered
Behavioral
Operant conditioning (Skinner)
Learn behavior through consequences and reinforcement
Classical conditioning (Pavlov)
Learn behavior through association
Cognitive
Focus on mental processes of learning
Instructional method
Dynamic classroom management
Explicit expectations & routines
Caring, supportive relationship with students
Differentiated instruction
Problem-, project-, and inquiry-based learning (PPIL)
Direct instruction
How People Learn (HPL) framework
Assessment-centered
Community-centered
Learning-centered
Knowledge-centered
Universal Design for Learning
Example of a classroom with UDL
Physical spaces and learning adjusted to suit students
Variety of instructional and assessment methods
Stiggins's achievement targets
5. Attitudes & dispositions
4. Products
3. Skills
2. Reasoning
Bloom's taxonomy
6. Evaluation
5. Synthesis
4. Analysis
3. Application
2. Comprehension
1. Knowledge
Backwards design
Learning objective
Assessment question
Instructional content
Assessment consideration before instructional consideration
Students
Socio-cultulral
Aboriginal education
Invite elders from First Nations communities
Decolonizing mindset
Incorporate local First Nations practices
Multicultural education
Culturally Responsive Teaching and Learning
The Danger of a Single Story
Parenting style
Authoritative
Permissive
Authoritarian
Socio-economic status
Greatest impact on scholastic achievement
Stereotype threat
Intelligence
Special education
Low-incidence exceptionalities
High-incidence exceptionalities
Person-first language
Inclusion
Individualized education plan
Intelligence tests
WISC-IV
Sternberg's triarchic theory of intelligence
Practical/contextual intelligence
Creative/experiential intelligence
Analytical/componential intelligence
Multiple intelligence theory (Gardner)
Linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, musical, interpersonal, intrapersonal, naturalistic
Carroll's hierarchical model of intelligence
General intelligence
Visual-spatial reasoning
Crystallized intelligence
Fluid intelligence
Development
Growth mindset
Embrace challenges, puts in effort and learns from mistakes
Language acquisition
Language-acquisition device
Ecological theory
Chronosystem
Macrosystem
Exosystem
Mesosystem
Microsystem
Moral
Kohlberg's six-stage theory
Heteronomous vs. autonomous morality
Personal & social
Development of self-concept and self-esteem
Erikson's psycho-social theory
Psychological
Domain-specific learning (Case)
Horizontal decalage
Central conceptual structures
Vygotsky's theory
Scaffolding
Zone of proximal development
Piaget's theory
Assimilate or accommodate new information
Schema development
Cognitive/learning
Physical/biological