Repressor binds to the operator (active)
Operon OFF
operon ON
EXAM 2
Integral: Proteins that are inside and outside the phospholipid bilayer; transmembrane protein
Carrier
Pinocytosis:cell continually gulps droplets of extracellularfluid
Phosphatase: removes a phosphate group
Phosphodiesterase: converts CAMP to AMP
Adnylyl cyclase: converts ATP to CAMP
BIG IDEA III
Cell Cycle
Recombinant DNA
Egg cell donor
Mammary cell donor
Egg cell from ovary
Grown in culture
Implanted in uterus of a third sheep
Embryonic Development
Gene Regulation
Transcription & Translation
DNA Structure & Replication
BIG IDEA II
Photosynthesis
PEP Carboxylase
CO2
Oxaloacelatate (4C)
Malate (4C)
Pyruvate (3C)
PEP (3C)
Calvin Cycle
Sugar
Vascular Tissue
Respiration
Metabolism
BIG IDEA I
Cell Communication
Biological Membrane
Cell Structure
Origin of Life
Biological Molecules
Chemistry for Biology
Biological Hierarchy
BIOLOGY 311C: introduction to structure & function, energy flow, and transmission & expression of genetic information in the living systems
EXAM 3
EXAM 1
Protein Kinase: adds a phosphate group
MACROMOLECULES
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Glycolysis
Glucose
Glyceraldehyde-3-P
Pyruvate
Acetyl CoA
Citric Acid Cycle
Oxidative phosphorylation
Fats
Fatty Acids
Glycerol
Carbohydrates
Sugars
Proteins
Amino Acids
Expresses protein that stimulates the cell cycle
Hyperactive Ras signals excessive protein
Produces an uncontrolled cell growth and leads to cancer
CELL CYCLE
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases: only active when bound to specific cyclins, always present in the cell
Cyclins: protein
Cancer
Oncogene: 'onco' means tumor
Ras: a G-protein
p53: tumor repressor gene
Proto-oncogene: normal cell growth and division
Interphase
Mitosis
Prophase: chromosomes condenses, nucleoli begins to break down and disappear
Prometaphase
Metaphase: chromosomes align in the center of cell
Anaphase: sister chromatids move to the opposite ends of the cell
Telophase: spindle fibers disperse, nuclear envelope forms around a group of chromosomes at each pole
Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides
Meiosis
Meiosis II
TelophaseII
Anaphase II
Metaphase II: Chromosomes align in the center of cell
Prometaphase II
Prophase II
Meiosis I
Prophase I: chromosomes condenses, nucleoli begins to break down and disappear
Prometaphase I
Metaphase I: homologous chromosomes align parallel in the center of cell
Anaphase I: homologous chromosomes move to the opposite ends of the cell
Telophase I: spindle fibers disperse, nuclear envelope forms around a group of chromosomes at each pole
Cytokinesis
Plants: cell plate forms
Animals: cleavage furrow
G2: more growth
S: DNA replication
G1: growth occurs
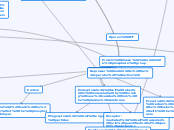
GENE REGULATION
EUKARYOTIC
Specific Transcription Factors
High Levels of Transcription
Activatiors
Attach to the enhancers
Activates to the DNA binding protein: bends and folds to gene to reach the promoter
General Transcription Factors
Low Levels (basal) Transcription
Distal control elemeents
Proximal control elements
DNA packaging
Nucleosome
Tight Helical Fiber
Looped Domains
Metaphase Chromosome
PROKARYOTES
Trp operon
Tryptophan Present
Repressor is inactive (not enough tryptophan avaliable)
Operon ON
Lac operon
Lactose Present
Yes
Repressor binds to allolactose (inactive)
Glucose Present
Adenylyl cyclase: inactive
cAMP levels low
cAMP inactive
operon OFF (basal)
No
Adenylyl Cyclase: active
cAMP levels high
CAP active
CELL SIGNALING
Enzymes
Signal transduction pathway: amplification of message
Cellular responses
Example: Produces transcription factors
p53: (tumor suppressor gene) produces protein that inhibits the cell cycle as a transcription factor
defective p53 as a missing transcription factor cannot activate transcription, causes cancer
Transduction
CAMP: second messenger
Protein Kinase A
Phosphorylation Cascade
Reception signal molecule binds to receptor
Tyrosine Kinase Receptor
Signaling molecule binds to kinases, makes a dimer
Produces ATP and adds 6 phosphate groups
Activates relay protein kinases
Signaling molecule
G protein coupled receptor
G protein
Ras: type of G-protein
Adenylyl Cyclase
MEMBRANE
Exocytosis: cell secretes certain molecules by the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane
Membrane fluidity: unsaturated tail and cholesterol
Diffusion: moving from high to low concentration
Subtopic
Molarity
Hypotonic: lower solute concentration
Animal
Shriveled
Normal
Lysed
Plant
Flaccid
Plasmolyze:
Turgid: normal; plant cell is hypertonic to the outside
Isotonic: same concentration
Hypertonic: higher solute concentration
Simple: no need for protein or ATP
Small non-polar molecules: CO2, O2
Active: needs protein and ATP
Endocytosis: cell takes in molecules by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane
Receptor-mediated: cell acquires bulk quantities of specific substances
Phagocytosis: cell engulfs particles
Protein
Peripheral: touch the outside of the phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid bilayer