Functional groups
Methyl Group (-CH3)
Phosphate Group (-OPO3^2-)
Sulfhydryl Group (-SH)
Amino Group (-NH2)
Carboxyl Group (-COOH)
Hydroxyl Group (-OH)
Carbonyl group (>C=O)
Biological Molecules
Protiens
Protein folding
Quarternary
Tertiary
Secodary
Beta pleated sheets
Alpha Helices
Primary
R groups
Basic
Acidic
Non-polar
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates serve as fuel and building materials
Alpha Glucose
Beta Glucose
Types of polysaccharides
storage
starch
glycogen
structure
cellulose
Isomers
Structural Isomers
Enantiomers
Geometric Isomers
Lipids
NOTE: LIPIDS ARE NOT POLYMERS!
- A process of dehydration occurs to make a fat molecule.
- Heating can change the chemical composition of an oil/fat. Repeated heating and cooling cycles can denature and change the composition of double bonds. However, only a fraction of fats are effected though.
Trans fats
removing double C bond and adding Hydrogen to convert cis to trans fat, however this incomplete formation of unsaturated to saturated fat is what leads to trans fat.
Unsaturated
Double bonded carbon
Liquid at room temperature
Hydrophobic
Saturated
"saturated with Hydrogen"
solid at room temperature
Nucleic acids
Nucleotides
Nucleic acids are polymers made of monomers-- called nucleotides
5 carbon sugar
phosphate group
Phosphodiester link connects phosphites and sugars
Nitrogenous base
DNA
- DNA provides directions for its own replication
- DNA directs the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA), and through mRNA, DNA can control protein synthesis, this process is known as gene expression
- DNA is double helix polymer
- Deoxyribose (DNA)--> no oxygen
G/C and A/T
H-bonding through complitary base pairing forms DNA double helix
RNA
Unlike DNA, RNA has oxygen
G/C and A/U
Partially Charged Atoms
Dipole-dipole Interaction
Hydrogen Bond
Water Properties
Universal Solvent
Denser as liquid than solid
High Heat of Vaporization
High Specific Heat
Cohesive behavior
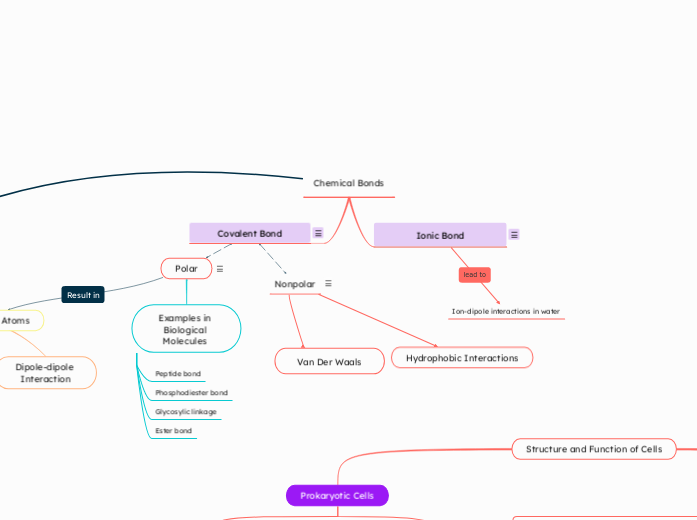
Polar
Sharing of electrons between two atoms with an EN difference of 0.5 or greater
Examples in Biological Molecules
Ester bond
Glycosylic linkage
Phosphodiester bond
Peptide bond
Nonpolar
Sharing of electrons between two atoms with an EN difference of less than 0.5
Hydrophobic Interactions
Van Der Waals
Structure and Function of Cells
Eukaryotic Cells
Both
Vesicles
Vehicle of the cell, the golgi apparatus packages things into vesicles where vesicles can then transport cellular materials.
Smooth ER
attached to nucleus synthesizes lipids (can also help detoxify)
Rough ER
composed of ribosomes that perform protein synthesis
Cytoskeleton
reinforces cell shape; functions in cell movement; components are made of protein, includes…
Microtubules
made of tubulin, this hollow shape maintains the shape of the cell. very structural and moves organelles
Intermediate filament
in the middle, anchor organelles to the cell and help maintain a cell’s shape, composed of keratin proteins.
Microfilaments
made of actin, helps maintain cell shape but also aid with movement
Microvilli
projections that increase the cells surface area
Peroxisome
organelle with various specialized metabolic functions; produces hydrogen peroxide as a by product and then converts it to water
Mitochondria
organelle where cellular respiration occurs and most ATP is generated
Lysosomes
digestive organelle where biomolecules are broken down, hydrolysis reaction
Golgi apparatus
organelle active in synthesis, modification, sorting, and secretion/transportation of cell products
complexes that make proteins; free in cytosol or bound to rough ER or nuclear envelope
Plasma membrane
membrane enclosing the cell
Chromatin
material consisting of DNA and protein; visible in a dividing cell as individual condensed chromosomes
Nucleolus
non membranous structure involved in production of ribosomes; a nucleus has one or more nucleoli
Nuclear Envelope
double membrane enclosing the nucleus; performed by pores; continuous with ER, also known as the nuclear lamina
Plants
Plastids
store food and make pigment
Plasmodesmata
channels found in plant cells that allow for the movement of water and other materials to move between cells
Central Vacuole
stores water, nutrients, and waste
Chloroplast
double membrane organelle that has its own DNA and performs photosynthesis
located outside the cell membrane, made of cellulose, and helps maintain cell shape
Animal
Gap junctions
structures that connect cells, things can pass through very easily
Tight junctions
secure cells very tightly, keeps stuff from freely moving around
Desmosomes
structure connects cells together that are semi-sealed. Desmosomes use proteins and are programed to selectively allow materials
Extracellular matrix
located outside the membrane, this structure has many parts: fibronectin, proteoglycan (animal cell ECM), and collagen. Changes in this structure can trigger processes inside the cell
proteoglycan
found in the ECM, proteoglycan are proteins with sugars attached, involved in organizing extracellular matrix
Prokaryotic Cells
Bacteria
Endospore
survival under harsh environmental conditions
Flagella
movement
Pili
bacterial mating
Fimbriae
attachment to surfaces
- slime layers
adherence to surfaces
Capsules
resistance to phagocytosis
Cell wall
Gives bacteria shape and protection from lysis in dilute solutions
Periplasmic Space
contains hydrolytic enzymes and binding proteins to nutrient processing and uptake
Nucleoid
localization of genetic material (DNA)
Inclusion bodies
storage of carbon, phosphate, and other substances
Ribosomes
protein synthesis
Gas Vacuole
buoyancy for floating in aquatic environments
Plama Membrane
selectively permeable barrier, mechanical boundary of cell, nutrient and waste transport, location of many metabolic processes (respiration and photosynthesis), detection of environmental cues for chemotaxis
Archaea
Cytoplasm
gel like substance that fills the cell and and keeps the organelles in place
Circular chromosome
stores genetic information
Chemical Bonds
Covalent Bond
Two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve stability.
Ionic Bond
Transfer of electrons between oppositely charged irons
Can lead to ion-dipole interactions in water
Ion-dipole interactions in water